Engineering:Santana 20
 | |
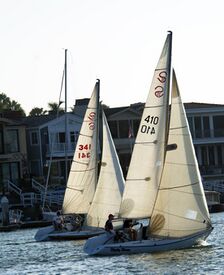 | |
| Development | |
|---|---|
| Designer | W. Shad Turner |
| Location | United States |
| Year | 1976 |
| No. built | 900 |
| Builder(s) | W. D. Schock Corp |
| Role | Day sailer-One-design Racer-Cruiser |
| Boat | |
| Crew | 3-4 |
| Boat weight | 1,350 lb (612 kg) |
| Draft | 4.00 ft (1.22 m) |
| Hull | |
| Type | monohull |
| Construction | fiberglass |
| LOA | 20.25 ft (6.17 m) |
| LWL | 16.00 ft (4.88 m) |
| Beam | 8.00 ft (2.44 m) |
| Hull appendages | |
| Keel/board type | fin keel |
| Ballast | 550 lb (249 kg) |
| Rudder(s) | internally-mounted spade-type rudder |
| Rig | |
| Rig type | Bermuda rig |
| I (foretriangle height) | 24.50 ft (7.47 m) |
| J (foretriangle base) | 8.20 ft (2.50 m) |
| P (mainsail luff) | 24.50 ft (7.47 m) |
| E (mainsail foot) | 7.00 ft (2.13 m) |
| Sails | |
| Sailplan | fractional rigged sloop |
| Mainsail area | 85.75 sq ft (7.966 m2) |
| Jib/genoa area | 100.45 sq ft (9.332 m2) |
| Spinnaker area | 385 sq ft (35.8 m2) |
| Total sail area | 186.20 sq ft (17.299 m2) |
| Racing | |
| D-PN | 91.3 |
| PHRF | 222 |
The Santana 20 is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by W. Shad Turner as a day sailer, one design racer and pocket cruiser. It was first built in 1976.[1][2][3][4]
Production
The design was built by W. D. Schock Corp in the United States starting in 1976. During its production run over 900 boats were completed, but it is now out of production.[1][3][5][6]
Design

The Santana 20 is a recreational keelboat, built predominantly of fiberglass, with wood trim. It has a fractional sloop rig, a raked stem, a raised counter reverse transom, an internally mounted spade-type rudder controlled by a tiller with an extension and a fixed fin keel or optional wing keel on later production boats. It displaces 1,350 lb (612 kg) and carries 550 lb (249 kg) of ballast.[1][3][4]
The boat has a draft of 4.00 ft (1.22 m) with the standard keel and 2.67 ft (0.81 m) with the optional wing keel.[1][4]
In 1996 the hull received some redesign work by Tom Schock , resulting in an open, walk-through transom a larger cockpit and an optional wing keel. The changes did not affect the performance and these later production boats are accepted for one design racing with the earlier boats. The wing keel-equipped boats are not competitive with the fin keel boats when racing.[6][4]
The design has sleeping accommodation for four people, with a double "V"-berth with stowage underneath, in the bow cabin. The cabin has a built-in liner and is trimmed with teak. Ventilation is provided by two opening cabin ports. Cabin headroom is 40 in (102 cm).[3][4]
For sailing the design is equipped with split controls, with the lines for the halyards and the boom vang forward on the cabin roof, while the mainsheet traveler is aft at the helm station.[3]
The boat is normally fitted with a small 3 to 6 hp (2 to 4 kW) outboard motor for docking and maneuvering.[1][4]
The design has a Portsmouth Yardstick DP-N racing average handicap of 91.3, a PHRF racing average handicap of 222 and is normally raced by a crew of 3-4 sailors.[3][4]
Operational history
The boat is supported by an active class club that organizes racing events, the Santana 20 Class Association. By 1994 there were active racing fleets on the United States west coast, as well as in Florida, Indiana, Oklahoma and Texas.[3][4][7]
In a 1994 review Richard Sherwood wrote, "this large day sailer has a cabin with two opening windows that will sleep four ... Sail the Santana 20 heeled about seven degrees, and roll tack."[3]
In a 2010 review Steve Henkel wrote, "This one-design racer was a very early entry—nine full years before the similar MX 20—in what eventually became known as the 'sport boat' category — speedy and light, easy to trailer, with minimum accommodations adequate for weekend regattas. It turned out to be extremely popular, with something like 900 boats being sold ... Best features: There is an extensive Class Association, mainly centered along the United States west coast, for those secking companionship on the race circuit, Worst features: With a four-foot draft, a hoist is the best bet when launching from trailer, Headroom is lowest compared with comp[etitor]s."[4]
See also
Similar sailboats
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Santana 20 sailboat". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/sailboat/santana-20.
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "W. Shad Turner". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/designer/turner-w-shad.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Sherwood, Richard M.: A Field Guide to Sailboats of North America, Second Edition, pages 112-113. Houghton Mifflin Company, 1994. ISBN 0-395-65239-1
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Henkel, Steve: The Sailor's Book of Small Cruising Sailboats, page 131. International Marine/McGraw-Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163652-0
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Schock W.D.". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/builder/schock-wd.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 W. D. Schock Corp (2020). "Santana 20". wdschockcorp.com. https://wdschockcorp.com/santana-20.
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Santana 20 Class Association". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/association/santana-20-class-association.
External links
 |
