IP (complexity)
In computational complexity theory, the class IP (interactive proof) is the class of problems solvable by an interactive proof system. It is equal to the class PSPACE. The result was established in a series of papers: the first by Lund, Karloff, Fortnow, and Nisan showed that co-NP had multiple prover interactive proofs;[1] and the second, by Shamir, employed their technique to establish that IP=PSPACE.[2] The result is a famous example where the proof does not relativize.[3] The concept of an interactive proof system was first introduced by Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff in 1985. An interactive proof system consists of two machines, a prover, P, which presents a proof that a given string n is a member of some language, and a verifier, V, that checks that the presented proof is correct. The prover is assumed to be infinite in computation and storage, while the verifier is a probabilistic polynomial-time machine with access to a random bit string whose length is polynomial on the size of n. These two machines exchange a polynomial number, p(n), of messages and once the interaction is completed, the verifier must decide whether or not n is in the language, with only a 1/3 chance of error. (So any language in BPP is in IP, since then the verifier could simply ignore the prover and make the decision on its own.)
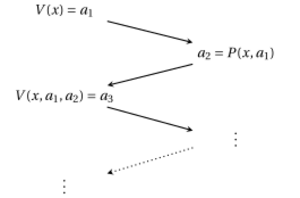
Definition
A language L belongs to IP if there exist V, P such that for all Q, w:
The Arthur–Merlin protocol, introduced by László Babai, is similar in nature, except that the number of rounds of interaction is bounded by a constant rather than a polynomial.
Goldwasser et al. have shown that public-coin protocols, where the random numbers used by the verifier are provided to the prover along with the challenges, are no less powerful than private-coin protocols. At most two additional rounds of interaction are required to replicate the effect of a private-coin protocol. The opposite inclusion is straightforward, because the verifier can always send to the prover the results of their private coin tosses, which proves that the two types of protocols are equivalent.
In the following section we prove that IP = PSPACE, an important theorem in computational complexity, which demonstrates that an interactive proof system can be used to decide whether a string is a member of a language in polynomial time, even though the traditional PSPACE proof may be exponentially long.
Proof of IP = PSPACE
The proof can be divided in two parts, we show that IP ⊆ PSPACE and PSPACE ⊆ IP.
IP ⊆ PSPACE
In order to demonstrate that IP ⊆ PSPACE, we present a simulation of an interactive proof system by a polynomial space machine. Now, we can define:
and for every 0 ≤ j ≤ p and every message history Mj, we inductively define the function NMj:
where:
where Prr is the probability taken over the random string r of length p. This expression is the average of NMj+1, weighted by the probability that the verifier sent message mj+1.
Take M0 to be the empty message sequence, here we will show that NM0 can be computed in polynomial space, and that NM0 = Pr[V accepts w]. First, to compute NM0, an algorithm can recursively calculate the values NMj for every j and Mj. Since the depth of the recursion is p, only polynomial space is necessary. The second requirement is that we need NM0 = Pr[V accepts w], the value needed to determine whether w is in A. We use induction to prove this as follows.
We must show that for every 0 ≤ j ≤ p and every Mj, NMj = Pr[V accepts w starting at Mj], and we will do this using induction on j. The base case is to prove for j = p. Then we will use induction to go from p down to 0.
The base case of j = p is fairly simple. Since mp is either accept or reject, if mp is accept, NMp is defined to be 1 and Pr[V accepts w starting at Mj] = 1 since the message stream indicates acceptance, thus the claim is true. If mp is reject, the argument is very similar.
For the inductive hypothesis, we assume that for some j+1 ≤ p and any message sequence Mj+1, NMj+1 = Pr[V accepts w starting at Mj+1] and then prove the hypothesis for j and any message sequence Mj.
If j is even, mj+1 is a message from V to P. By the definition of NMj,
Then, by the inductive hypothesis, we can say this is equal to
Finally, by definition, we can see that this is equal to Pr[V accepts w starting at Mj].
If j is odd, mj+1 is a message from P to V. By definition,
Then, by the inductive hypothesis, this equals
This is equal to Pr[V accepts w starting at Mj] since:
because the prover on the right-hand side could send the message mj+1 to maximize the expression on the left-hand side. And:
Since the same Prover cannot do any better than send that same message. Thus, this holds whether i is even or odd and the proof that IP ⊆ PSPACE is complete.
Here we have constructed a polynomial space machine that uses the best prover P for a particular string w in language A. We use this best prover in place of a prover with random input bits because we are able to try every set of random input bits in polynomial space. Since we have simulated an interactive proof system with a polynomial space machine, we have shown that IP ⊆ PSPACE, as desired.
PSPACE ⊆ IP
In order to illustrate the technique that will be used to prove PSPACE ⊆ IP, we will first prove a weaker theorem, which was proven by Lund, et al.: #SAT ∈ IP. Then using the concepts from this proof we will extend it to show that TQBF ∈ IP. Since TQBF ∈ PSPACE-complete, and TQBF ∈ IP then PSPACE ⊆ IP.
#SAT is a member of IP
We begin by showing that #SAT is in IP, where:
Note that this is different from the normal definition of #SAT, in that it is a decision problem, rather than a function.
First we use arithmetization to map the boolean formula with n variables, φ(b1, ..., bn) to a polynomial pφ(x1, ..., xn), where pφ mimics φ in that pφ is 1 if φ is true and 0 otherwise provided that the variables of pφ are assigned Boolean values. The Boolean operations ∨, ∧ and ¬ used in φ are simulated in pφ by replacing the operators in φ as shown in the table below.
| a ∧ b | ab |
| a ∨ b | a ∗ b := 1 − (1 − a)(1 − b) |
| ¬a | 1 − a |
As an example, φ = a ∧ (b ∨ ¬c) would be converted into a polynomial as follows:
The operations ab and a ∗ b each result in a polynomial with a degree bounded by the sum of the degrees of the polynomials for a and b and hence, the degree of any variable is at most the length of φ.
Now let F be a finite field with order q > 2n; also demand that q be at least 1000. For each 0 ≤ i ≤ n, define a function fi on F, having parameters , and a single variable ai in F: For 0 ≤ i ≤ n and for let
Note that the value of f0 is the number of satisfying assignments of φ. f0 is a void function, with no variables.
Now the protocol for #SAT works as follows:
- Phase 0: The prover P chooses a prime q > 2n and computes f0, it then sends q and f0 to the verifier V. V checks that q is a prime greater than max(1000, 2n) and that f0() = k.
- Phase 1: P sends the coefficients of f1(z) as a polynomial in z. V verifies that the degree of f1 is less than n and that f0 = f1(0) + f1(1). (If not V rejects). V now sends a random number r1 from F to P.
- Phase i: P sends the coefficients of as a polynomial in z. V verifies that the degree of fi is less than n and that . (If not V rejects). V now sends a random number ri from F to P.
- Phase n+1: V evaluates to compare to the value . If they are equal V accepts, otherwise V rejects.
Note that this is a public-coin algorithm.
If φ has k satisfying assignments, clearly V will accept. If φ does not have k satisfying assignments we assume there is a prover that tries to convince V that φ does have k satisfying assignments. We show that this can only be done with low probability.
To prevent V from rejecting in phase 0, has to send an incorrect value to P. Then, in phase 1, must send an incorrect polynomial with the property that . When V chooses a random r1 to send to P,
This is because a polynomial in a single variable of degree at most d can have no more than d roots (unless it always evaluates to 0). So, any two polynomials in a single variable of degree at most d can be equal only in d places. Since |F| > 2n the chances of r1 being one of these values is at most if n > 10, or at most (n/1000) ≤ (n/n3) if n ≤ 10.
Generalizing this idea for the other phases we have for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n if
then for ri chosen randomly from F,
There are n phases, so the probability that is lucky because V selects at some stage a convenient ri is at most 1/n. So, no prover can make the verifier accept with probability greater than 1/n. We can also see from the definition that the verifier V operates in probabilistic polynomial time. Thus, #SAT ∈ IP.
TQBF is a member of IP
In order to show that PSPACE is a subset of IP, we need to choose a PSPACE-complete problem and show that it is in IP. Once we show this, then it clear that PSPACE ⊆ IP. The proof technique demonstrated here is credited to Adi Shamir.
We know that TQBF is in PSPACE-Complete. So let ψ be a quantified boolean expression:
where φ is a CNF formula. Then Qi is a quantifier, either ∃ or ∀. Now fi is the same as in the previous proof, but now it also includes quantifiers.
Here, φ(a1, ..., ai) is φ with a1 to ai substituted for x1 to xi. Thus f0 is the truth value of ψ. In order to arithmetize ψ we must use the following rules:
where as before we define x ∗ y = 1 − (1 − x)(1 − y).
By using the method described in #SAT, we must face a problem that for any fi the degree of the resulting polynomial may double with each quantifier. In order to prevent this, we must introduce a new reduction operator R which will reduce the degrees of the polynomial without changing their behavior on Boolean inputs.
So now before we arithmetize we introduce a new expression:
or put another way:
Now for every i ≤ k we define the function fi. We also define to be the polynomial p(x1, ..., xm) which is obtained by arithmetizing φ. Now in order to keep the degree of the polynomial low, we define fi in terms of fi+1:
Now we can see that the reduction operation R, doesn't change the degree of the polynomial. Also it is important to see that the Rx operation doesn't change the value of the function on boolean inputs. So f0 is still the truth value of ψ, but the Rx value produces a result that is linear in x. Also after any we add in ψ′ in order to reduce the degree down to 1 after arithmetizing .
Now let's describe the protocol. If n is the length of ψ, all arithmetic operations in the protocol are over a field of size at least n4 where n is the length of ψ.
- Phase 0: P → V: P sends f0 to V. V checks that f0= 1 and rejects if not.
- Phase 1: P → V: P sends f1(z) to V. V uses coefficients to evaluate f1(0) and f1(1). Then it checks that the polynomial's degree is at most n and that the following identities are true:
- If either fails then reject.
- Phase i: P → V: P sends as a polynomial in z. r1 denotes the previously set random values for
V uses coefficients to evaluate and . Then it checks that the polynomial degree is at most n and that the following identities are true:
If either fails then reject.
V → P: V picks a random r in F and sends it to P. (If then this r replaces the previous r).
Goto phase i + 1 where P must persuade V that is correct.
- Phase k + 1: V evaluates . Then it checks if If they are equal then V accepts, otherwise V rejects.
This is the end of the protocol description.
If ψ is true then V will accept when P follows the protocol. Likewise if is a malicious prover which lies, and if ψ is false, then will need to lie at phase 0 and send some value for f0. If at phase i, V has an incorrect value for then and will likely also be incorrect, and so forth. The probability for to get lucky on some random r is at most the degree of the polynomial divided by the field size: . The protocol runs through O(n2) phases, so the probability that gets lucky at some phase is ≤ 1/n. If is never lucky, then V will reject at phase k+1.
Since we have now shown that both IP ⊆ PSPACE and PSPACE ⊆ IP, we can conclude that IP = PSPACE as desired. Moreover, we have shown that any IP algorithm may be taken to be public-coin, since the reduction from PSPACE to IP has this property.
Variants
There are a number of variants of IP which slightly modify the definition of the interactive proof system. We summarize some of the better-known ones here.
dIP
A subset of IP is the deterministic Interactive Proof class, which is similar to IP but has a deterministic verifier (i.e. with no randomness). This class is equal to NP.
Perfect Completeness
An equivalent definition of IP replaces the condition that the interaction succeeds with high probability on strings in the language with the requirement that it always succeeds:
This seemingly stronger criterion of "perfect completeness" does not change the complexity class IP, since any language with an interactive proof system may be given an interactive proof system with perfect completeness.[4]
MIP
In 1988, Goldwasser et al. created an even more powerful interactive proof system based on IP called MIP in which there are two independent provers. The two provers cannot communicate once the verifier has begun sending messages to them. Just as it's easier to tell if a criminal is lying if he and his partner are interrogated in separate rooms, it's considerably easier to detect a malicious prover trying to trick the verifier if there is another prover it can double-check with. In fact, this is so helpful that Babai, Fortnow, and Lund were able to show that MIP = NEXPTIME, the class of all problems solvable by a nondeterministic machine in exponential time, a very large class. Moreover, all languages in NP have zero-knowledge proofs in an MIP system, without any additional assumptions; this is only known for IP assuming the existence of one-way functions.
IPP
IPP (unbounded IP) is a variant of IP where we replace the BPP verifier by a PP verifier. More precisely, we modify the completeness and soundness conditions as follows:
- Completeness: if a string is in the language, the honest verifier will be convinced of this fact by an honest prover with probability at least 1/2.
- Soundness: if the string is not in the language, no prover can convince the honest verifier that it is in the language, except with probability less than 1/2.
Although IPP also equals PSPACE, IPP protocols behaves quite differently from IP with respect to oracles: IPP=PSPACE with respect to all oracles, while IP ≠ PSPACE with respect to almost all oracles.[5]
QIP
QIP is a version of IP replacing the BPP verifier by a BQP verifier, where BQP is the class of problems solvable by quantum computers in polynomial time. The messages are composed of qubits.[6] In 2009, Jain, Ji, Upadhyay, and Watrous proved that QIP also equals PSPACE,[7] implying that this change gives no additional power to the protocol. This subsumes a previous result of Kitaev and Watrous that QIP is contained in EXPTIME because QIP = QIP[3], so that more than three rounds are never necessary.[8]
compIP
Whereas IPP and QIP give more power to the verifier, a compIP system (competitive IP proof system) weakens the completeness condition in a way that weakens the prover:
- Completeness: if a string is in the language L, the honest verifier will be convinced of this fact by an honest prover with probability at least 2/3. Moreover, the prover will do so in probabilistic polynomial time given access to an oracle for the language L.
Essentially, this makes the prover a BPP machine with access to an oracle for the language, but only in the completeness case, not the soundness case. The concept is that if a language is in compIP, then interactively proving it is in some sense as easy as deciding it. With the oracle, the prover can easily solve the problem, but its limited power makes it much more difficult to convince the verifier of anything. In fact, compIP isn't even known or believed to contain NP.
On the other hand, such a system can solve some problems believed to be hard. Somewhat paradoxically, though such a system is not believed to be able to solve all of NP, it can easily solve all NP-complete problems due to self-reducibility. This stems from the fact that if the language L is not NP-hard, the prover is substantially limited in power (as it can no longer decide all NP problems with its oracle).
Additionally, the graph nonisomorphism problem (which is a classical problem in IP) is also in compIP, since the only hard operation the prover has to do is isomorphism testing, which it can use the oracle to solve. Quadratic non-residuosity and graph isomorphism are also in compIP.[9] Note, Quadratic non-residuosity (QNR) is likely an easier problem than graph isomorphism as QNR is in UP intersect co-UP.[10]
Notes
- ↑ Lund, C.; Fortnow, L.; Karloff, H.; Nisan, N. (1990). "Algebraic methods for interactive proof systems". Proceedings [1990] 31st Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. IEEE Comput. Soc. Press. pp. 2–10. doi:10.1109/fscs.1990.89518. ISBN 0-8186-2082-X.
- ↑ Shamir, Adi. "Ip= pspace." Journal of the ACM 39.4 (1992): 869-877.
- ↑ Chang Richard (1994). "The random oracle hypothesis is false". Journal of Computer and System Sciences 49 (1): 24–39. doi:10.1016/s0022-0000(05)80084-4.
- ↑ Furer Martin, Goldreich Oded, Mansour Yishay, Sipser Michael, Zachos Stathis (1989). "On Completeness and Soundness in Interactive Proof Systems". Advances in Computing Research: A Research Annual 5: 429–442.
- ↑ R. Chang, B. Chor, Oded Goldreich, J. Hartmanis, J. Håstad, D. Ranjan, and P. Rohatgi. The random oracle hypothesis is false. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 49(1):24-39. 1994.
- ↑ J. Watrous. PSPACE has constant-round quantum interactive proof systems. Proceedings of IEEE FOCS'99, pp. 112-119. 1999.
- ↑ Rahul Jain; Zhengfeng Ji; Sarvagya Upadhyay; John Watrous (2009). "QIP = PSPACE". arXiv:0907.4737 [quant-ph].
- ↑ A. Kitaev and J. Watrous. Parallelization, amplification, and exponential time simulation of quantum interactive proof systems. Proceedings of the 32nd ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 608-617. 2000.
- ↑ Shafi Goldwasser and Mihir Bellare. The Complexity of Decision versus Search. SIAM Journal on Computing, Volume 23, No. 1. February 1994.
- ↑ "A note on quadratic residuosity and UP". Information Processing Letters 92 (3): 127–131. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.ipl.2004.06.015.
References
- Babai, L. Trading group theory for randomness. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Symposium on the Theory of Computation . ACM, New York, 1985, pp. 421–429.
- Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali, and Charles Rackoff. The Knowledge complexity of interactive proof-systems. Proceedings of 17th ACM Symposium on the Theory of Computation, Providence, Rhode Island. 1985, pp. 291–304. Extended abstract
- Shafi Goldwasser and Michael Sipser. Private coins versus public coins in interactive proof systems. Proceedings of the 18th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computation. ACM, New York, 1986, pp. 59–68.
- Rahul Jain, Zhengfeng Ji, Sarvagya Upadhyay, John Watrous. QIP = PSPACE. [1]
- Lund, C., Fortnow, L., Karloff, H., Nisan, N. Algebraic methods for interactive proof systems. In Proceedings of 31st Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science. IEEE, New York, 1990, pp. 2–90.
- Adi Shamir. IP = PSPACE. Journal of the ACM, volume 39, issue 4, p. 869–877. October 1992.
- Alexander Shen. IP=PSpace: Simplified Proof. J.ACM, v. 39(4), pp. 878–880, 1992.
- Complexity Zoo: IP, MIP, IPP, QIP, QIP(2), compIP, frIP
 |
