Interpreter pattern
In computer programming, the interpreter pattern is a design pattern that specifies how to evaluate sentences in a language.
The basic idea is to have a class for each symbol (terminal or nonterminal) in a specialized computer language. The syntax tree of a sentence in the language is an instance of the composite pattern and is used to evaluate (interpret) the sentence for a client.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
design pattern is one of the twenty-three well-known
GoF design patterns
that describe how to solve recurring design problems to design flexible and reusable object-oriented software, that is, objects that are easier to implement, change, test, and reuse.
What problems can the Interpreter design pattern solve?[1]
- A grammar for a simple language should be defined
- so that sentences in the language can be interpreted.
When a problem occurs very often, it could be considered to represent it as a sentence in a simple language (Domain Specific Languages) so that an interpreter can solve the problem by interpreting the sentence.
For example, when many different or complex search expressions must be specified. Implementing (hard-wiring) them directly into a class is inflexible because it commits the class to particular expressions and makes it impossible to specify new expressions or change existing ones independently from (without having to change) the class.
What solution does the Interpreter design pattern describe?
- Define a grammar for a simple language by defining an
Expressionclass hierarchy and implementing aninterpret()operation. - Represent a sentence in the language by an abstract syntax tree (AST) made up of
Expressioninstances. - Interpret a sentence by calling
interpret()on the AST.
The expression objects are composed recursively into a composite/tree structure that is called
abstract syntax tree (see Composite pattern).
The Interpreter pattern doesn't describe how
to build an abstract syntax tree. This can
be done either manually by a client or automatically by a parser.
See also the UML class and object diagram below.
Uses
- Specialized database query languages such as SQL.
- Specialized computer languages that are often used to describe communication protocols.
- Most general-purpose computer languages actually incorporate several specialized languages[citation needed].
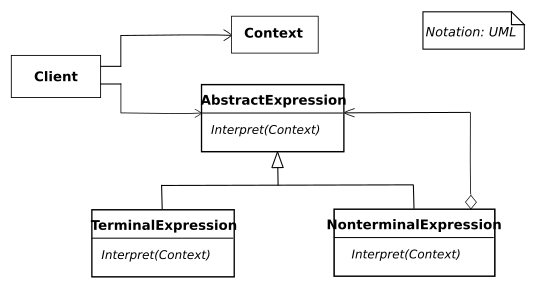
Structure
UML class and object diagram
In the above UML class diagram, the Client class refers to the common AbstractExpression interface for interpreting an expression
interpret(context).
The TerminalExpression class has no children and interprets an expression directly.
The NonTerminalExpression class maintains a container of child expressions
(expressions) and forwards interpret requests
to these expressions.
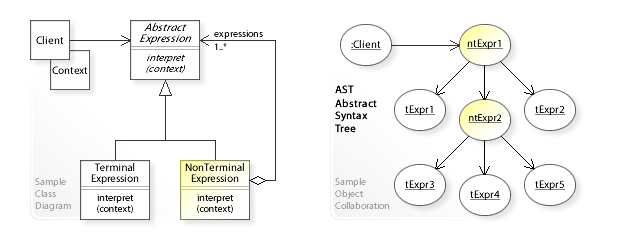
The object collaboration diagram
shows the run-time interactions: The Client object sends an interpret request to the abstract syntax tree.
The request is forwarded to (performed on) all objects downwards the tree structure.
The NonTerminalExpression objects (ntExpr1,ntExpr2) forward the request to their child expressions.
The TerminalExpression objects (tExpr1,tExpr2,…) perform the interpretation directly.
UML class diagram
Example
This C++11 implementation is based on the pre C++98 sample code in the book.
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
class Context;
class BooleanExp {
public:
BooleanExp() = default;
virtual ~BooleanExp() = default;
virtual bool evaluate(Context&) = 0;
virtual BooleanExp* replace(const char*, BooleanExp&) = 0;
virtual BooleanExp* copy() const = 0;
};
class VariableExp;
class Context {
public:
Context() :m() {}
bool lookup(const VariableExp* key) { return m.at(key); }
void assign(VariableExp* key, bool value) { m[key] = value; }
private:
std::map<const VariableExp*, bool> m;
};
class VariableExp : public BooleanExp {
public:
VariableExp(const char* name_) :name(nullptr) {
name = strdup(name_);
}
virtual ~VariableExp() = default;
virtual bool evaluate(Context& aContext) {
return aContext.lookup(this);
}
virtual BooleanExp* replace( const char* name_, BooleanExp& exp ) {
if (0 == strcmp(name_, name)) {
return exp.copy();
} else {
return new VariableExp(name);
}
}
virtual BooleanExp* copy() const {
return new VariableExp(name);
}
VariableExp(const VariableExp&) = delete; // rule of three
VariableExp& operator=(const VariableExp&) = delete;
private:
char* name;
};
class AndExp : public BooleanExp {
public:
AndExp(BooleanExp* op1, BooleanExp* op2)
:operand1(nullptr), operand2(nullptr) {
operand1 = op1;
operand2 = op2;
}
virtual ~AndExp() = default;
virtual bool evaluate(Context& aContext) {
return operand1->evaluate(aContext) && operand2->evaluate(aContext);
}
virtual BooleanExp* replace(const char* name_, BooleanExp& exp) {
return new AndExp(
operand1->replace(name_, exp),
operand2->replace(name_, exp)
);
}
virtual BooleanExp* copy() const {
return new AndExp(operand1->copy(), operand2->copy());
}
AndExp(const AndExp&) = delete; // rule of three
AndExp& operator=(const AndExp&) = delete;
private:
BooleanExp* operand1;
BooleanExp* operand2;
};
int main() {
BooleanExp* expression;
Context context;
VariableExp* x = new VariableExp("X");
VariableExp* y = new VariableExp("Y");
expression = new AndExp(x, y);
context.assign(x, false);
context.assign(y, true);
bool result = expression->evaluate(context);
std::cout << result << '\n';
context.assign(x, true);
context.assign(y, true);
result = expression->evaluate(context);
std::cout << result << '\n';
}
The program output is:
0
1
See also
- Backus–Naur form
- Combinatory logic in computing
- Design Patterns
- Domain-specific language
- Interpreter (computing)
References
External links
- Interpreter implementation in Ruby
- Interpreter implementation in C++
- SourceMaking tutorial
- Interpreter pattern description from the Portland Pattern Repository
 |