Medicine:Ablepharon macrostomia syndrome
| Ablepharon macrostomia syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | AMS |
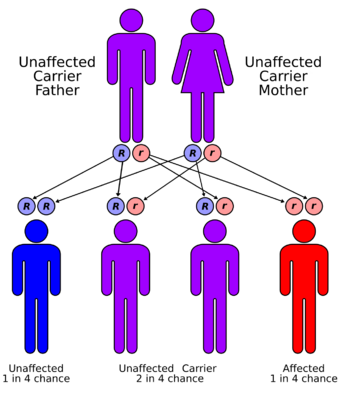 | |
| Ablepharon macrostomia syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance | |
Ablepharon macrostomia syndrome (AMS) is an extremely rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by malformations of the skull, skin, fingers and genitals.[1] Affected individuals may also have malformations of the nipples and abdominal wall.
Younger individuals might experience language difficulties, and in some instances mental retardation is known.[2]
Symptoms
- Absent/short eyelids
- Absent eyebrows
- Absent eyelashes
- External ear abnormalities
- Alopecia
Genetics
It has been suggested that AMS is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.[1][3] This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Treatment usually involves plastic and reconstructive surgery. Surgery may be needed to correct undescended testes or hernias.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Ablepharon-macrostomia syndrome: first report of familial occurrence". Am. J. Med. Genet. 94 (4): 281–3. October 2000. doi:10.1002/1096-8628(20001002)94:4<281::AID-AJMG3>3.0.CO;2-S. PMID 11038439.
- ↑ "Ablepharon macrostomia syndrome". Retrieved 2009-11-24.
- ↑ NORD - National Organization for Rare Disorders, Inc
External links
| Classification |
|---|

