Medicine:Foix–Chavany–Marie syndrome
| Foix–Chavany–Marie syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Facio-pharyngo-glosso-masticatory diplegia |
 | |
| Operculum (brain) | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Foix–Chavany–Marie Syndrome (FCMS), also known as bilateral opercular syndrome, is a neuropathological disorder characterized by paralysis of the facial, tongue, pharynx, and masticatory muscles of the mouth that aid in chewing.[1][unreliable source?] The disorder is primarily caused by thrombotic and embolic strokes, which cause a deficiency of oxygen in the brain. As a result, bilateral lesions may form in the junctions between the frontal lobe and temporal lobe, the parietal lobe and cortical lobe, or the subcortical region of the brain.[2][3][unreliable source?] FCMS may also arise from defects existing at birth that may be inherited or nonhereditary. Symptoms of FCMS can be present in a person of any age and it is diagnosed using automatic-voluntary dissociation assessment, psycholinguistic testing, neuropsychological testing, and brain scanning. Treatment for FCMS depends on the onset, as well as on the severity of symptoms, and it involves a multidisciplinary approach.
Classification
There are two forms (also referred to as "classifications") of FCMS; bilateral and unilateral. The bilateral form is most common (also referred to as the "classical form") and is caused by the formation of lesions on both sides of the anterior or posterior region of the operculum. In contrast, the unilateral form is rare and is caused by the formation of lesions on one side of the anterior or posterior region of the operculum.[1] Lesions located in the anterior regions of the operculum are associated with motor deficits and anarthria, a total absence of the ability to form speech or language. Lesions located in the posterior regions of the operculum are associated with parietal opercular functions.[2] The two classifications of FCMS were established based on the location of the lesion, stroke, and trauma affecting the brain. Classifying FCMS based solely upon lesions yields five specific subtypes of FCMS currently known to fall into the bilateral and unilateral categories:[1][3]
- Bilateral anterior opercular syndrome (lesion in both the anterior or in the frontal operculum)
- Opercular-subopercular syndrome (lesions in the opercular cortex on one side and the subopercular lesion in the contralateral side).
- Subopercular syndrome (lesions in the subcortical corticobulbar projections only).
- Unilateral anterior syndrome involving the frontal operculum.
- Posterior syndrome involving the junction between the frontal and the parietal lobe of the operculum.
Bilateral
The bilateral form of FCMS (also known as facio-labio-pharyngo-glosso-laryngo-brachial paralysis) is consistent with the classic presentation of bilateral corticobulbar involvement. It is characterized by well-preserved automatic and reflex movements. It is caused by lesions in the cortical or subcortical region of the anterior opercular area surrounding the insula formingFoix–Chavany– the gyri of the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes.[4]
Unilateral
The unilateral operculum syndrome is a very rare form of FCMS caused by the formation of unilateral lesions. In this form of FCMS, the unaffected hemisphere of the brain compensates for the unilateral lesion. Usually, this occurs when the unaffected region is the individual's dominant hemisphere.[1]
Symptoms
An individual affected with FCMS develops disabilities associated with voluntary movements using the facial, lingual, pharyngeal, and masticatory muscles. However, the reflexive and autonomic functions of these muscles groups are usually intact. Common symptoms include drooling, an inability to elevate and depress the mandible, difficulty chewing, inability of protruding tongue, swallowing, and loss of speech.[3][1][4]
Classification of the disorder is distinguished by the location of the lesions formed, which causes certain symptoms to be present or amplified. FCMS caused by the formation of bilateral lesions causes paralysis of the facial, lingual, pharyngeal, and masticatory muscles. This form of FCMS involves voluntary-autonomic dissociation and an inability to form speech. The formation of bilateral lesions confined to the posterior operculum has a distinct symptom of word deafness, an inability to understand language.
FCMS caused by the formation of lesions unilaterally causes muteness of speech and upper motor neuron cranial nerve paresis, muscular weakness. The formation of unilateral lesions confined to the posterior operculum has distinct symptoms that includes sensory loss in the hand and face contralateral to the location of the lesion.[4]
Causes
Foix–Chavany–Marie syndrome is primarily caused by multiple strokes and lesions. However, less common causes that can eventually produce lesions to the operculum resulting in the FCMS syndrome include the following; tumors, trauma, encephalitis, neurodegenerative diseases, and vasculitis. Viral infections, such as Herpes and HIV can also cause FCMS. Moreover, any lesion in the cortical or sub-cortical region affecting the corticobulbar pathways will produce FCMS.[1]
Cerebrovascular disease
Strokes are one of the most common causes of Foix–Chavany–Marie syndrome. The type of strokes associated with this syndrome include embolic and thrombotic strokes. Strokes affecting the middle cerebral artery and the branches that pass through or near the operculum are characteristic of FCMS.[1]
Central nervous system infection
Symptoms of infections specifically HIV and herpes simplex encephalitis can cause FCMS. Numerous lesions can develop with HIV infections, which likely result in the development of FCMS.[1][5]
Epilepsy
Epilepsy symptoms such as seizures can spread discharges that cause FCMS. This causation results in the only reversible development of FCMS as it is the only cause that allows full recuperation from speech, swallowing, and mastication difficulties when treated.[3] This causation is most commonly seen in children with FCMS.[3]
Unusual Causes
- Tumors
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- Moyamoya disease
- Vasculitis[6]
- Trauma
Mechanism
FCMS is primarily originates from damages in the posterior region of the inferior frontal gyrus and inferior region of the precentral gyrus.[6] Anatomically, the word operculum is defined as the cortices encompassing the insula, which includes the pre and post-central, inferior-frontal, supramarginal, angular inferior parietal, and superior temporal convolutions.[1] Parts of the brain such as Heschl's gyrus, Brodmann's area, Broca's area, Wernicke's area are amongst the most relevant in the operculum. These areas are responsible for auditory functions for language and speech.[7]
FCMS, sometimes called cortical pseudobulbar palsy, is characterized by lesions affected both sides of the operculum. These lesions typically damage the cranial nerves leading to both motor and sensory deficits. The cranial nerves that are impaired include the following; Cranial Nerve (CN) V (the trigeminal nerve), CN VII (the facial nerve), CN IX (the glossopharyngeal nerve), CN X (the vagus nerve), and CN XII (the hypoglossal nerve). Cerebral malformation, namely unilateral schizencephaly in association with contralateral polymicrogyria symmetrically in the perisylvian area is another known characteristic of FCMS. Moreover, another deformation found with FCMS includes the failure of opercularization caused by the underdevelopment of the anterior part of the opercula found in the fetal brain in the 32nd week.[7]
Neuropathology
The anatomic basisFoix–Chavany– for the automatic voluntary dissociation is characterized by the following. Neurons that lie adjacently in the operculum project supranuclear fibers to the cranial nuclei for the voluntary movement of facial, pharyngeal, lingual, and masticatory muscles. Emotional movement of these muscles is controlled by alternative pathways that run from the amygdala and lateral hypothalamus to the brainstem via the medial forebrain bundle and dorsal longitudinal fasciculus.[8]
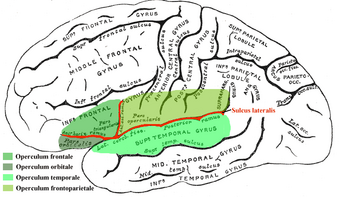
The opercular cortex surrounding the insula is separated by two anatomical components: the ascending rami of the lateral sulcus and the posterior rami into three different sections of the operculum.[3]
- Frontal operculum formed by posterior part of the inferior frontal gyrus.
- Fronto-parietal opercula formed by the lowermost part of the precentral and postcentral gyrus and the anterior and lowermost part of the inferior parietal lobule.
- Temporal opercula formed by the superior temporal gyrus.[3]
Diagnosis
Criteria
FCMS shares similar characteristics with the following disorders: catatonia, akinetic mutism, orobuccal apraxia, Broca's aphasia, pseudobulbar palsy, bulbar palsy secondary to myasthenia gravis, Guillain–Barré syndrome, and brainstem strokes.[1]
In determining a diagnosis between with catatonia, akinetic mutism, and FCMS, a person must demonstrate their ability to perform voluntary function of the limbs. Patients with catatonia or akinetic mutism are not able to perform voluntary commands that involve the use of limbs, while patients with FCMS still possess voluntary usage of limbs.[1] If a person can demonstrate ability in voluntary usage of limbs, catatonia and akinetic mutism are most likely ruled out from the diagnosis.
In determining a diagnosis between Broca's aphasia and FCMS, a person must demonstrate their ability in voluntary movement of cranial musculature. People with Broca's aphasia may not exhibit a complete loss of voluntary movement facial muscles, pharyngeal muscles, laryngeal muscles, brachial muscles, tongue muscles, and muscles of the mouth that aid in chewing. These voluntary functions may still be present, to varying degrees. People with FCMS do not possess this ability. For people with FCMS, voluntary movement of cranial musculature is completely absent.[1]
In determining a diagnosis between pseudobulbar palsy, a person must demonstrate whether or not muteness is present, as well as the ability to move the facial, buccal, lingual, and pharyngeal muscles. People with pseudobulbar palsy exhibit, to varying degrees, an ability in these functions, while patients with FCMS do not.[1]
Techniques
There are three general classes of tests utilized by physicians when determining a diagnosis for FCMS: (1) automatic-voluntary dissociation assessment, (2) psycholinguistic testing, and (3) neuropsychological testing.[9] In addition, brain scanning techniques are utilized to observe whether ischemic abnormalities or lesions are present within the operculum region of the cortices.
Automatic-voluntary dissociation assessment
FCMS is largely characterized by the paralysis of voluntary movement in facial, lingual, pharyngeal, and masticatory muscles, while automatic, involuntary functions of these four muscle groups remain.[3] Automatic functions are performed by inducing involuntary reflexes, such as palatal, laryngeal, blink, and gag reflexes. Other involuntary functions that are tested include spontaneous smiling, laughter, and yawning.[10] Patients with the disorder are able to these functions under automatic, involuntary reflex. An individual's ability to perform these functions voluntarily are tested determined through a series of commands by the physician. Typically, individuals with the disorder are not able to perform any of these functions upon command. Dissociation between automatic and voluntary dissociation is indicated by an individual's ability to perform the involuntary, automatic functions, and their inability to perform the same actions, voluntary.
Psycholinguistic testing
Psycholinguistics pertain to the psychological and neurobiological components that allow humans to acquire, utilize, comprehend, and produce language. The tests most commonly used for psycholinguistic testing include the Dutch version of Aachen aphasia test, syntactic comprehension test, and the Token test.[10] Psycholinguistics allow physicians to narrow down and rule out other disorders that may be similar to FCMS when diagnosing a patient.
Neuropsychological testing
Neuropsychology is the study of neurobiology and psychology. Neuropsychological tests are utilized for the purpose of observing an individual's abilities in cognitive functioning, reasoning, and memories.[10] The tests most commonly used for neuropsychological testing include WAIS-III, Stroop test, Bourdon Wiersma test, and the Rey–Osterrieth complex figure test. These tests allow physicians to evaluate the degree to which the bilateral lesions in the operculum have been affected, and allow for the determination of proper treatment.
Imaging
Scanning techniques include EEG, SPECT, MRI, and CT brain scanning.[1][2] These additional techniques are useful in determining what type of lesion the patient has, and allows physicians to determine more effective ways in treating the patient.

Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is one of the best techniques that can detect the lesions in the brain of the FCMS that some of the times are missed by just using a Computer-Tomography Scan. Also, this type of imaging can reveal right frontal lobes contusions encompassing the anterior operculum, the premotor area, and the association area.[10]
CT scan
This computer-tomography type of imaging is one of the most used in any clinical environment and although it can detect some of the brain areas affected by a stroke or a trauma it does not provide the same acuity as the magnetic resonance imaging. CT scans can also reveal, in patients with the syndrome, the bilateral cortical infarcts located in the posterior frontal region involving the opercular areas.[3]
SPECT
The single photon emission computed tomography of the brain can show uptake area in the right frontal lobe and normal uptake are in the left hemisphere.[10] This type of imaging can give a more detailed view of a specific region of the brain.
Other techniques
An electroencephalography (EEG) is also used in patients with the FCMS and it can reveal focal slowing and epileptic discharges from left fronto-temporal regions.[3]
Management
Treatment of Foix–Chavany–Marie syndrome depends on the onset of symptoms and involves a multidisciplinary approach. Drugs are used in neurological recovery depending on the etiological classification of FCMS. FCMS caused by epilepsy, specifically resulting in the development of lesions in the bilateral and subcortical regions of the brain can be treated using antiepileptic drugs to reverse abnormal EEG changes and induce complete neurological recovery.[3] In addition, a hemispherectomy can be performed to reverse neurological deficits and control the seizures. This procedure can result in a complete recovery from epileptic seizures.[3] Physical therapy is also used to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Classical FCMS resulting in the decline of ones ability to speak and swallow can be treated using neuromuscular electrical stimulation and traditional dysphagia therapy. Speech therapy further targeting dysphagia can strengthen oral musculature using modified feeding techniques and postures. Therapeutic feedings include practicing oral and lingual movements using ice chips.[1] In addition, different procedures can be performed by a neurosurgeon to alleviate some symptoms.
See also
- Pseudobulbar palsy
- Operculum
- Corticobulbar tracts
- Wernicke's aphasia
- Broca's aphasia
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Bakar, M; Kirshner, HS; Niaz, F (1998). "The opercular-subopercular syndrome: four cases with review of the literature.". Behavioural Neurology 11 (2): 97–103. doi:10.1155/1998/423645. PMID 11568407.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Starkstein, SE; Berthier, M; Leiguarda, R (July 1988). "Bilateral opercular syndrome and crossed aphemia due to a right insular lesion: a clinicopahological study.". Brain and Language 34 (2): 253–61. doi:10.1016/0093-934X(88)90137-X. PMID 3401694.[unreliable source?][non-primary source needed]
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 Lekhjung, Thapa; Raju, Paudel; PVS, Rana (2010). "Opercular syndrome: Case reports and review of literature". Neurology Asia 15 (2): 145–152. http://www.neurology-asia.org/articles/20102_145.pdf.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Desai, SD; Patel, D; Bharani, S; Kharod, N (May 2013). "Opercular syndrome: A case report and review.". Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences 8 (2): 123–5. doi:10.4103/1817-1745.117842. PMID 24082930.
- ↑ Johanna C. van der Poel, PhD, Charles A. Haenggeli, MD, and Wouterina C.G. Overweg-Plandsoen, PhD (1995). "Operculum Syndrome: Unusual Feature of Herpes Simplex Encephalitis". Pediatric Neurology 12 (3): 246–249. doi:10.1016/0887-8994(95)00005-z. PMID 7619193.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Milanlioglu, A; Aydın, MN; Gökgül, A; Hamamcı, M; Erkuzu, MA; Tombul, T (2013). "Ischemic bilateral opercular syndrome.". Case Reports in Medicine 2013: 513572. doi:10.1155/2013/513572. PMID 23476665.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Szabó, N; Hegyi, A; Boda, M; Páncsics, M; Pap, C; Zágonyi, K; Romhányi, E; Túri, S et al. (May 2009). "Bilateral operculum syndrome in childhood.". Journal of Child Neurology 24 (5): 544–50. doi:10.1177/0883073808327841. PMID 19196875.
- ↑ Ohtomo, R; Iwata, A; Tsuji, S (January 2014). "Unilateral opercular infarction presenting with Foix-Chavany-Marie Syndrome.". Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 23 (1): 179–81. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2012.08.015. PMID 23040957.
- ↑ Theys, Tom; Van Cauter, Sofie; Kho, Kuan H.; Vijverman, Anne-Catherine; Peeters, Ronald R.; Sunaert, Stefan; van Loon, Johannes (2013-02-01). "Neural correlates of recovery from Foix-Chavany-Marie syndrome". Journal of Neurology 260 (2): 415–420. doi:10.1007/s00415-012-6641-0. ISSN 1432-1459. PMID 22893305.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Nitta, N; Shiino, A; Sakaue, Y; Nozaki, K (August 2013). "Foix-Chavany-Marie syndrome after unilateral anterior opercular contusion: a case report.". Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 115 (8): 1539–41. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.12.036. PMID 23369402.[non-primary source needed]
Further reading
- Ole Daniel Enersen. "Foix-Chavany-Marie syndrome". Who Named It?. http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/1527.html.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |