Medicine:Gross examination
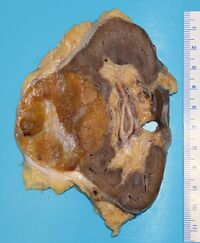
Gross examination or "grossing" is the process by which pathology specimens are inspected with the bare eye to obtain diagnostic information, while being processed for further microscopic examination.
Gross examination of surgical specimens is typically performed by a pathologist, or by a pathologists' assistant working within a pathology practice. Individuals trained in these fields are often able to gather diagnostically critical information in this stage of processing, including the stage and margin status of surgically removed tumors.
The initial step in any examination of a clinical specimen is confirmation of the identity of the patient and the anatomical site from which the specimen was obtained. Sufficient clinical data should be communicated by the clinical team to the pathology team in order to guide the appropriate diagnostic examination and interpretation of the specimen - if such information is not provided, it must be obtained by the examiner prior to processing the specimen.
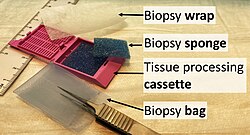
There are usually two end products of the gross examination of a surgical specimen. The first is the gross description, a document which serves as the written record of the examiner's findings, and is included in the final pathology report. The second product is a set of tissue blocks, typically postage stamp-sized portions of tissue sealed in plastic cassettes, which will be processed into slides for microscopic examination. Since only a minority of the tissue from a large specimen can reasonably be subject to microscopic examination, the success of the final histological diagnosis is highly dependent on the skill of the professional performing the gross examination. The gross examiner may sample portions of the specimen for other types of ancillary tests as diagnostically indicated; these include microbiological culture, flow cytometry, cytogenetics, or electron microscopy.
See also
- Timeline of myocardial infarction pathology, including gross examination findings

