Medicine:Spastic ataxia-corneal dystrophy syndrome
From HandWiki
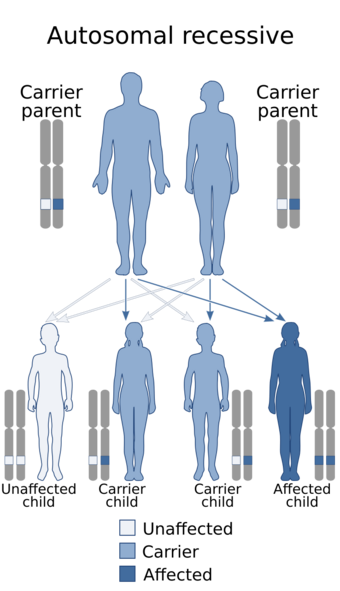
Spastic ataxia-corneal dystrophy syndrome (also known as Bedouin spastic ataxia syndrome) is an autosomally resessive disease. It has been found in an inbred Bedouin family.[1] It was first described in 1986. A member of the family who was first diagnosed with this disease also had Bartter syndrome. It was concluded by its first descriptors Mousa-Al et al. that the disease is different from a disease known as corneal-cerebellar syndrome that had been found in 1985.[2]
Symptoms include spastic ataxia, cataracts, macular corneal dystrophy and nonaxial myopia. Mental development is normal.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Orphanet: Spastic ataxia-corneal dystrophy syndrome". October 2006. http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=en&Expert=2572.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "OMIM Entry - 271320 - SPINOCEREBELLAR DEGENERATION WITH MACULAR CORNEAL DYSTROPHY, CONGENITAL CATARACTS, AND MYOPIA". 21 October 2014. http://www.omim.org/entry/271320.
Further reading
- "Autosomally inherited recessive spastic ataxia, macular corneal dystrophy, congenital cataracts, myopia and vertically oval temporally tilted discs. Report of a Bedouin family—a new syndrome". J. Neurol. Sci. 76 (1): 105–21. 1986. doi:10.1016/0022-510x(86)90145-0. PMID 3465874.
- Ahmad S. Teebi (30 July 2010). Genetic Disorders Among Arab Populations. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-642-05080-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=HDIa0tyllqgC&pg=PA366.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |