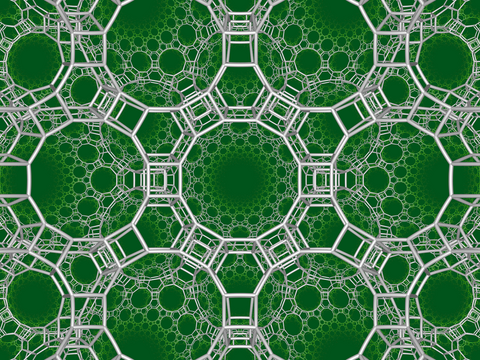
Triangular tiling honeycomb
| Triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | Hyperbolic regular honeycomb Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,6,3} h{6,3,6} h{6,3[3]} ↔ {3[3,3]} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| Cells | {3,6} |
| Faces | triangle {3} |
| Edge figure | triangle {3} |
| Vertex figure | hexagonal tiling |
| Dual | Self-dual |
| Coxeter groups | , [3,6,3] , [6,3[3]] , [3[3,3]] |
| Properties | Regular |
The triangular tiling honeycomb is one of 11 paracompact regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycombs) in hyperbolic 3-space. It is called paracompact because it has infinite cells and vertex figures, with all vertices as ideal points at infinity. It has Schläfli symbol {3,6,3}, being composed of triangular tiling cells. Each edge of the honeycomb is surrounded by three cells, and each vertex is ideal with infinitely many cells meeting there. Its vertex figure is a hexagonal tiling.
A geometric honeycomb is a space-filling of polyhedral or higher-dimensional cells, so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical tiling or tessellation in any number of dimensions.
Honeycombs are usually constructed in ordinary Euclidean ("flat") space, like the convex uniform honeycombs. They may also be constructed in non-Euclidean spaces, such as hyperbolic uniform honeycombs. Any finite uniform polytope can be projected to its circumsphere to form a uniform honeycomb in spherical space.
Symmetry
It has two lower reflective symmetry constructions, as an alternated order-6 hexagonal tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ↔
↔ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , and as
, and as ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() from
from ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , which alternates 3 types (colors) of triangular tilings around every edge. In Coxeter notation, the removal of the 3rd and 4th mirrors, [3,6,3*] creates a new Coxeter group [3[3,3]],
, which alternates 3 types (colors) of triangular tilings around every edge. In Coxeter notation, the removal of the 3rd and 4th mirrors, [3,6,3*] creates a new Coxeter group [3[3,3]], ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , subgroup index 6. The fundamental domain is 6 times larger. By Coxeter diagram there are 3 copies of the first original mirror in the new fundamental domain:
, subgroup index 6. The fundamental domain is 6 times larger. By Coxeter diagram there are 3 copies of the first original mirror in the new fundamental domain: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ↔
↔ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Related Tilings
It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic infinite-order apeirogonal tiling, {∞,∞}, with infinite apeirogonal faces, and with all vertices on the ideal surface.
Related honeycombs
The triangular tiling honeycomb is a regular hyperbolic honeycomb in 3-space, and one of eleven paracompact honeycombs.
There are nine uniform honeycombs in the [3,6,3] Coxeter group family, including this regular form as well as the bitruncated form, t1,2{3,6,3}, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() with all truncated hexagonal tiling facets.
with all truncated hexagonal tiling facets.
The honeycomb is also part of a series of polychora and honeycombs with triangular edge figures.
Rectified triangular tiling honeycomb
| Rectified triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | r{3,6,3} h2{6,3,6} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | r{3,6} {6,3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} hexagon {6} |
| Vertex figure |  triangular prism |
| Coxeter group | , [3,6,3] , [6,3[3]] , [3[3,3]] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive |
The rectified triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has trihexagonal tiling and hexagonal tiling cells, with a triangular prism vertex figure.
, has trihexagonal tiling and hexagonal tiling cells, with a triangular prism vertex figure.
Symmetry
A lower symmetry of this honeycomb can be constructed as a cantic order-6 hexagonal tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ↔
↔ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . A second lower-index construction is
. A second lower-index construction is ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ↔
↔ ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Truncated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Truncated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | t{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | t{3,6} {6,3} |
| Faces | hexagon {6} |
| Vertex figure | 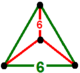 tetrahedron |
| Coxeter group | , [3,6,3] , [3,3,6] |
| Properties | Regular |
The truncated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , is a lower-symmetry form of the hexagonal tiling honeycomb,
, is a lower-symmetry form of the hexagonal tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . It contains hexagonal tiling facets with a tetrahedral vertex figure.
. It contains hexagonal tiling facets with a tetrahedral vertex figure.
Bitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Bitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | 2t{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | t{6,3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} dodecagon {12} |
| Vertex figure | 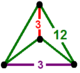 tetragonal disphenoid |
| Coxeter group | , 3,6,3 |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, cell-transitive |
The bitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has truncated hexagonal tiling cells, with a tetragonal disphenoid vertex figure.
, has truncated hexagonal tiling cells, with a tetragonal disphenoid vertex figure.
Cantellated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Cantellated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | rr{3,6,3} or t0,2{3,6,3} s2{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | rr{6,3} r{6,3} 40px {}×{3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} hexagon {6} |
| Vertex figure | 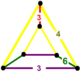 wedge |
| Coxeter group | , [3,6,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The cantellated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has rhombitrihexagonal tiling, trihexagonal tiling, and triangular prism cells, with a wedge vertex figure.
, has rhombitrihexagonal tiling, trihexagonal tiling, and triangular prism cells, with a wedge vertex figure.
Symmetry
It can also be constructed as a cantic snub triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , a half-symmetry form with symmetry [3+,6,3].
, a half-symmetry form with symmetry [3+,6,3].
Cantitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Cantitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | tr{3,6,3} or t0,1,2{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | tr{6,3} t{6,3} 40px {}×{3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} hexagon {6} dodecagon {12} |
| Vertex figure | 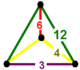 mirrored sphenoid |
| Coxeter group | , [3,6,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The cantitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has truncated trihexagonal tiling, truncated hexagonal tiling, and triangular prism cells, with a mirrored sphenoid vertex figure.
, has truncated trihexagonal tiling, truncated hexagonal tiling, and triangular prism cells, with a mirrored sphenoid vertex figure.
Runcinated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Runcinated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,3{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | {3,6} {}×{3} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} |
| Vertex figure | 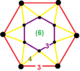 hexagonal antiprism |
| Coxeter group | , 3,6,3 |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive |
The runcinated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has triangular tiling and triangular prism cells, with a hexagonal antiprism vertex figure.
, has triangular tiling and triangular prism cells, with a hexagonal antiprism vertex figure.
Runcitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Runcitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | t0,1,3{3,6,3} s2,3{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagrams | |
| Cells | t{3,6} rr{3,6} 40px {}×{3} 40px {}×{6} |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} hexagon {6} |
| Vertex figure | isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid |
| Coxeter group | , [3,6,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
The runcitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has hexagonal tiling, rhombitrihexagonal tiling, triangular prism, and hexagonal prism cells, with an isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid vertex figure.
, has hexagonal tiling, rhombitrihexagonal tiling, triangular prism, and hexagonal prism cells, with an isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid vertex figure.
Symmetry
It can also be constructed as a runcicantic snub triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , a half-symmetry form with symmetry [3+,6,3].
, a half-symmetry form with symmetry [3+,6,3].
Omnitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb
| Omnitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | t0,1,2,3{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | tr{3,6} {}×{6} |
| Faces | square {4} hexagon {6} dodecagon {12} |
| Vertex figure | 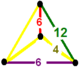 phyllic disphenoid |
| Coxeter group | , 3,6,3 |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive |
The omnitruncated triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has truncated trihexagonal tiling and hexagonal prism cells, with a phyllic disphenoid vertex figure.
, has truncated trihexagonal tiling and hexagonal prism cells, with a phyllic disphenoid vertex figure.
Runcisnub triangular tiling honeycomb
| Runcisnub triangular tiling honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Paracompact scaliform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | s3{3,6,3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Cells | r{6,3} {}x{3} 40px {3,6} 40px tricup |
| Faces | triangle {3} square {4} hexagon {6} |
| Vertex figure | |
| Coxeter group | , [3+,6,3] |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, non-uniform |
The runcisnub triangular tiling honeycomb, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , has trihexagonal tiling, triangular tiling, triangular prism, and triangular cupola cells. It is vertex-transitive, but not uniform, since it contains Johnson solid triangular cupola cells.
, has trihexagonal tiling, triangular tiling, triangular prism, and triangular cupola cells. It is vertex-transitive, but not uniform, since it contains Johnson solid triangular cupola cells.
See also
- Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
- Regular tessellations of hyperbolic 3-space
- Paracompact uniform honeycombs
References
- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. ISBN 0-486-61480-8. (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
- The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays (1999), Dover Publications, LCCN 99-35678, ISBN 0-486-40919-8 (Chapter 10, Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space) Table III
- Jeffrey R. Weeks The Shape of Space, 2nd edition ISBN 0-8247-0709-5 (Chapter 16-17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I, II)
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, 1966
- N.W. Johnson: Geometries and Transformations, (2018) Chapter 13: Hyperbolic Coxeter groups
 |