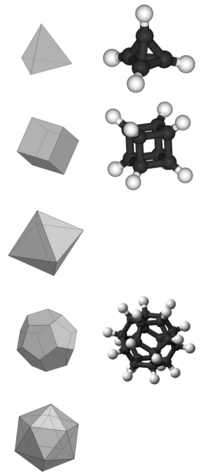
Platonic hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a Platonic hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon whose structure matches one of the five Platonic solids, with carbon atoms replacing its vertices, carbon–carbon bonds replacing its edges, and hydrogen atoms as needed.[1][page needed]
Not all Platonic solids have molecular hydrocarbon counterparts; those that do are the tetrahedron (tetrahedrane), the cube (cubane), and the dodecahedron (dodecahedrane). The possibility and existence of each platonic hydrocarbon is affected by the number of bonds to each carbon vertex and the angle strain between the bonds at each vertex.
Tetrahedrane
Tetrahedrane (C4H4) is a hypothetical compound. It has not yet been synthesized without substituents, but it is predicted to be kinetically stable in spite of its angle strain. Some stable derivatives, including tetra(tert-butyl)tetrahedrane and tetra(trimethylsilyl)tetrahedrane, have been produced.
Cubane
Cubane (C8H8) has been synthesized. Although it has high angle strain, cubane is kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths.
Octahedrane
Angle strain would make an octahedron highly unstable due to inverted tetrahedral geometry at each vertex. There would also be no hydrogen atoms because four edges meet at each corner; thus, the hypothetical octahedrane molecule, with a molecular formula of C6, would be an allotrope of elemental carbon rather than a hydrocarbon. The existence of octahedrane cannot be ruled out completely, although calculations have shown that it is unlikely.[2]
Dodecahedrane
Dodecahedrane (C20H20) was first synthesized in 1982, and has minimal angle strain; the tetrahedral angle is 109.5° and the dodecahedral angle is 108°, only a slight discrepancy.[3]
Icosahedrane
The tetravalency (4-connectedness) of carbon excludes an icosahedron because 5 edges meet at each vertex. True pentavalent carbon is unlikely; methanium, nominally CH+5, usually exists as CH3(H2)+. The hypothetical icosahedral C12+12 lacks hydrogen so it is not a hydrocarbon; it is also an ion.
Both icosahedral and octahedral structures have been observed in boron compounds[2] such as the dodecaborate ion and some of the carbon-containing carboranes.
Other polyhedra
Increasing the number of atoms that comprise the carbon skeleton leads to a geometry that increasingly approximates a sphere, and the space enclosed in the carbon "cage" increases. This trend continues with buckyballs or spherical fullerene (C60). Although not a Platonic hydrocarbon, buckminsterfullerene has the shape of a truncated icosahedron, an Archimedean solid.
The concept can also be extended to regular Euclidean tilings, with the hexagonal tiling producing graphane. A square tiling (which would resemble an infinitely large fenestrane) would suffer from the same problem as octahedrane, and the triangular tiling icosahedrane. No generalisations to hyperbolic tilings seem to be known.
The regular convex 4-polytopes may also have hydrocarbon analogues; hypercubane has been proposed.
References
- ↑ Henning Hopf, Classics in Hydrocarbon Chemistry, Wiley VCH, 2000.[full citation needed]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lewars, Errol G. (2008). Modeling Marvels: Computational Anticipation of Novel molecules. Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 81–82. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6973-4. ISBN 978-1-4020-6972-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=IoFzgBSSCwEC&pg=PA81. Retrieved January 30, 2012.
- ↑ Ternansky, Robert J.; Balogh, Douglas W.; Paquette, Leo A. (1982). "Dodecahedrane". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104 (16): 4503–4504. doi:10.1021/ja00380a040.
 |