Software:Resource Monitor
From HandWiki
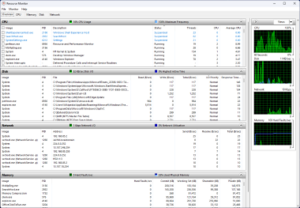 Resource Monitor running under Windows 11 | |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | January 30, 2007 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64 and ARM |
| Type | System resources utility |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
Resource Monitor, a utility in Windows Vista and later, displays information about the use of hardware (CPU, memory, disk, and network) and software (file handles and modules) resources in real time.[1] Users can launch Resource Monitor by executing resmon.exe (perfmon.exe in Windows Vista).
The Vista and later Resource Monitor heavily leverages the Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) facilities introduced in Windows 7;[2] the counter setup (event tracing session) used by the Resource Monitor can provide logging as well.[3]
Features
The Resource Monitor window includes five tabs:[4]
- Overview
- CPU
- displays column lists of Processes, Services, Associated Handles and Associated Modules; charts of CPU Usage (separate for every core)
- Memory
- displays overall Physical Memory consumption and separate consumption of every Process; charts of Used Physical Memory, Commit Charge and Hard Faults/sec
- Disk
- displays Processes with Disk Activity and Storage; charts of Disk Usage (KB/sec) and Disk Queue Length
- Network
- displays Processes with Network Activity, TCP Connections and Listening Ports; charts of Network Usage (separate for every adapter) and TCP Connections
Ways to start the application
- Choose Start→Type to search "Resource Monitor".
- Start Windows Task Manager→select Performance tab→Click the "Open Resource Monitor" link at the lower left corner.
- Choose Start→All Programs→Accessories→System Tools→Resource Monitor.
- %windir%\system32\perfmon.exe /res
- %windir%\system32\resmon.exe
See also
- Activity Monitor in macOS
- System Monitor was available on Windows 95, 95 OSR, 95 OSR2, 98, 98SE, ME
- Performance Monitor introduced in Windows NT
References
- ↑ Tulloch, Mitch; Northrup, Tony; Honeycutt, Jerry; Wilson, Ed (October 7, 2009). Windows 7 Resource Kit. Pearson Education (published 2009). ISBN 9780735642775. https://books.google.com/books?id=Q5xCAwAAQBAJ. Retrieved June 3, 2014. "The Resource Overview screen of the Reliability and Performance Monitor Control Panel item in Windows Vista has become a separate tool in Windows 7 called Resource Monitor [...]."
- ↑ Waterman, Michael (November 4, 2013). "Getting Started with Performance Tracing Part 1 Event Tracing for Windows Demystified". TechNet. Microsoft. http://blogs.technet.com/b/michw/archive/2013/11/04/getting-started-with-performance-tracing-part-1-event-tracing-for-windows-demystified.aspx.
- ↑ "How to pull the information that Resource Monitor (ResMon.exe) provides?". TechNet. Microsoft. January 4, 2011. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/archive/blogs/yongrhee/how-to-pull-the-information-that-resource-monitor-resmon-exe-provides.
- ↑ Phelps, Justin (October 14, 2011). "How to Use Resource Monitor". PC World. IDG. http://www.pcworld.com/article/241677/how_to_use_resource_monitor.html.
 |
