Software:TYPE (DOS command)
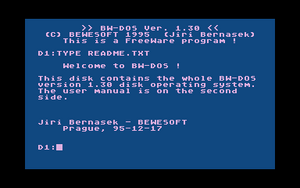 The BW-DOS TYPE command | |
| Developer(s) | Various open-source and commercial developers |
|---|---|
| Operating system | RT-11, OS/8, RSX-11, TOPS-10, TOPS-20, VMS, CP/M, MP/M, CDOS, TRIPOS, HDOS, AmigaDOS, DOS, MSX-DOS, FlexOS, PC-MOS, SpartaDOS X, 4690 OS, OS/2, Windows, AROS, ReactOS, SymbOS |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
| License | PC-MOS: GPLv3 AROS: AROS Public ReactOS: GPLv2 |
In computing, type is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS/4NT and Windows PowerShell used to display the contents of specified files on the computer terminal. The analogous Unix command is cat.
Implementations
The command is available in the operating systems DEC RT-11,[1] OS/8,[2] RSX-11,[3] TOPS-10,[4] TOPS-20,[5] VMS, Digital Research CP/M,[6] MP/M,[7][8] MetaComCo TRIPOS,[9] Heath Company HDOS,[10] AmigaDOS,[11] DOS, FlexOS,[12] TSL PC-MOS,[13] SpartaDOS X,[14] IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS,[15] IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows,[16] ReactOS,[17] AROS,[18] and SymbOS.[19]
The type command is supported by Tim Paterson's SCP 86-DOS.[20] On MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 1 and later.[21] DR DOS 6.0 also includes an implementation of the TYPE command.[22]
It is also available in the open source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox and the EFI shell.[23]
In Windows PowerShell, type is a predefined command alias for the Get-Content Cmdlet which basically serves the same purpose. TYPE originated as an internal command in 86-DOS.
The command-syntax and feature set between operating systems and command shell implementations can differ as can be seen in the following examples.
DEC RT-11
In Digital Equipment Corporation's RT-11, the command accepts up to six input file specifications. Multiple file specifications are separated with commas.
The default filetype is .LST. Wildcards are accepted in place of filenames or filetypes.
Syntax
The command-syntax on RT-11 is:
TYPE[/options] filespecs
COPIES:n– Specify the number of times the file will be typedDELETE– Delete the file after typing itLOG– Log the names of the files typedNEWFILES– Only files dated with the current system date will be typedNOLOG– Suppress the log of the files typedQUERY– Require confirmation before typing each fileWAIT– Wait for user response before proceeding with the type
Examples
TYPE/COPIES:3 REPORT
TYPE/NEWFILES *.LST
DR CP/M, MP/M, FlexOS
In Digital Research CP/M, the command expands tabs and line-feed characters (CTRL-I), assuming tab positions are set at every eighth column.
The command does not support wildcard characters on FlexOS.[12]
Syntax
The command-syntax on CP/M is:
TYPE ufn
Note: ufn = unambiguous file reference
In MP/M, the command has a pause mode. It is specified by entering a 'P' followed by two decimal digits after the filename. The specified number of lines will be displayed and then the command will pause until a carriage return is entered.[7]
Examples
A>TYPE FILE.PLM
A>TYPE B:X.PRN
0A>TYPE CODE.ASM P23
TSL PC-MOS
The Software Link's PC-MOS includes an implementation of TYPE. Like the rest of the operating system, it is licensed under the GPL v3.[24]
It supports an option to display the file content in hexadecimal form.[13]
Syntax
The command-syntax on PC-MOS is:
.TYPE filename [/h]
filename– The name of the file to display/h– Display content in hexadecimal form
Examples
[A:\].TYPE FILE.BIN /h
Microsoft Windows, OS/2, ReactOS
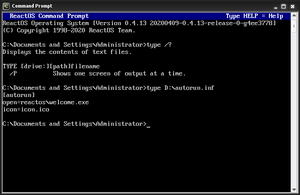
type commandThe command supports wildcard characters. In Microsoft Windows and OS/2 it includes the filename in the output when typing multiple files.
Syntax
The command-syntax on Microsoft Windows and ReactOS is:
type [Drive:][Path]FileName
[Drive:][Path]FileName– This parameter specifies the location and name of the file or files to view. Multiple file names need to be separated with spaces./?– This parameter displays help for the command.
Examples
C:\>type "my report.txt"
C:\>type *.txt
See also
References
- ↑ "RT-11 HELP FILE". http://paleoferrosaurus.com/beta/documents/rt11help.html#TYPE.
- ↑ "Concise Command Language" (CCL)."OS/8 Handbook". April 1974. http://bitsavers.trailing-edge.com/pdf/dec/pdp8/os8/OS8_Handbook_Apr1974.pdf.
- ↑ John F. Pieper (1987). RSX A Guide for Users. Digital Equipment Corporation. ISBN 0-932376-90-8. http://www.rsx11m.com/rsxguide.pdf. Retrieved 2020-09-19.
- ↑ TOPS-10 Operating System Commands Manual. Digital Equipment Corporation. August 1980. http://scandocs.trailing-edge.com/tops10-aa-0916d-tb.pdf. Retrieved 2019-02-17.
- ↑ "TOPS-20 Command manual". http://www.textfiles.com/bitsavers/pdf/dec/pdp10/TOPS20/V6.1/AA-FP65A-TM_tops20CmdsRef.pdf.
- ↑ "Manual". http://www.cpm.z80.de/manuals/cpm22-m.pdf.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Digital Research (July 1981). MP/M - Multi-Programming Monitor Control Program - User's Guide (4 ed.). Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Digital Research. http://www.cpm.z80.de/manuals/mpm1ug01.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ↑ Digital Research (1981-09-25). MP/M-86 Operating System - User's Guide (1 ed.). Pacific Grove, CA, USA: Digital Research. http://bitsavers.informatik.uni-stuttgart.de/pdf/digitalResearch/mpm-86/MPM-86_Users_Guide_Sep81.pdf. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ↑ "Manual". https://www.pagetable.com/docs/amigados_tripos/tripos_manuals.pdf.
- ↑ Heath Company. "Software Reference Manual HDOS SYSTEM Chapter 2 General Operations" (in en). http://sebhc.lesbird.com/documentation/software/HDOS-2/HDOS_Reference_Chapter2.pdf.
- ↑ Rügheimer, Hannes; Spanik, Christian (September 19, 1988). AmigaDOS quick reference. Grand Rapids, Mi : Abacus. ISBN 9781557550491. https://archive.org/details/1988-rugheimer-spanik-amigados-quick-reference.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 FlexOS User's Guide Version 1.3 (1 ed.). Digital Research. November 1986. 1073-2003-001. http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/digitalResearch/flexos/1073-2003_FlexOS_Users_Guide_V1.3_Nov86.pdf. Retrieved 2019-04-23.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "roelandjansen/pcmos386v501". 2 January 2022. https://github.com/roelandjansen/pcmos386v501.
- ↑ SpartaDOS X 4.48 User Guide
- ↑ "Users guide" (PDF). https://archive.org/details/4690OSV6r2UsersGuide/page/n169.
- ↑ "Microsoft TechNet Type article". 11 September 2009. https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb491026.aspx.
- ↑ "reactos/reactos". 3 January 2022. https://github.com/reactos/reactos.
- ↑ "AROS Research Operating System". https://aros.sourceforge.io/documentation/users/shell/index.php.
- ↑ "Data sheet". http://www.symbos.de/appinfo.htm?00025.
- ↑ 86-DOS - Disk Operating System for the 8086 - User's Manual (Preliminary ed.). Seattle, Washington, USA: Seattle Computer Products, Inc.. 1980. http://www.patersontech.com/Dos/docs/86_Dos_usr_03.pdf. Retrieved 2019-07-14. (59 pages)
- ↑ Running MS-DOS Version 6.22 (20th Anniversary Edition), 6th Revised edition. Microsoft Press. 2003. ISBN 0-7356-1812-7.
- ↑ DR DOS 6.0 User Guide Optimisation and Configuration Tips
- ↑ "EFI Shells and Scripting". Intel. http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/efi-shells-and-scripting/.
- ↑ Jansen, Roeland (8 February 2018). "pcmos386v501: PC-MOS/386 v5.01 final release including cdrom driver sources". https://github.com/roelandjansen/pcmos386v501.
Further reading
- Practical Guide to CP/M. Dilithium Press. 1983. ISBN 978-0880560771.
- Kathy Ivens; Brian Proffit (1993). OS/2 Inside & Out. Osborne McGraw-Hill. ISBN 9780078818714.
- John Paul Mueller (2007). Windows Administration at the Command Line for Windows Vista, Windows 2003, Windows XP, and Windows 2000. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0470165799.
External links
 |
