Software:pushd and popd
| Original author(s) | Bill Joy |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Various open-source and commercial developers |
| Operating system | Unix, Unix-like, DOS, Windows, ReactOS |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
In computing, pushd and popd are a pair of commands which allow users to quickly switch between the current and previous directory when using the command line. When called, they use a directory stack to sequentially save and retrieve directories visited by the user.[1][2]
They are widely available as builtin commands in many command-line interpreters, such as 4DOS, Bash,[3] C shell, tcsh, Hamilton C shell, KornShell, cmd.exe and PowerShell, and for various operating systems including both Windows and Unix-like systems.
Overview
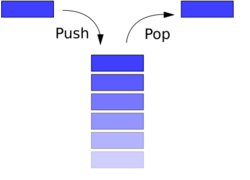
The directory stack underlies the functions of these two commands. It is an array of paths stored as an environment variable in the CLI, which can be viewed using the command dirs in Unix or Get-Location -stack in PowerShell. The current working directory is always at the top of the stack.
The pushd ('push directory') command saves the current working directory to the stack then changes the working directory to the new path input by the user. If pushd is not provided with a path argument, it changes instead to the next directory from the top of the stack,[clarification needed] which can be used to toggle between two directories.
The popd command removes (or 'pops', in the stack analogy) the current path entry from the stack and returns to the path at the top of the stack as the new working directory.[4][5]
The first Unix shell to implement a directory stack was Bill Joy's C shell.[citation needed] The syntax for pushing and popping directories is essentially the same as that used now.[6][7]
Both commands are available in FreeCOM, the command-line interface of FreeDOS.[8]
In Windows PowerShell, pushd is a predefined command alias for the Push-Location cmdlet and popd is a predefined command alias for the Pop-Location cmdlet. Both serve basically the same purpose as the pushd and popd commands.
Examples
Unix-like
[user@server /usr/ports] $ pushd /etc
/etc /usr/ports
[user@server /etc] $ popd
/usr/ports
[user@server /usr/ports] $
Microsoft Windows and ReactOS
C:\Users\root>pushd C:\Users
C:\Users>popd
C:\Users\root>
CMD batch file
@echo off
rem This batch file deletes all .txt files in a specified directory
pushd %1
del *.txt
popd
echo All text files deleted in the %1 directory
Syntax
pushd
pushd [path | ..]
Arguments:
pathThis optional command-line argument specifies the directory to make the current directory. Ifpathis omitted, the path at the top of the directory stack is used, which has the effect of toggling between two directories.
popd
popd
See also
References
- ↑ Pushd - change directory/folder - Windows CMD - SS64.com
- ↑ Popd - Windows CMD - SS64.com
- ↑ Bash Reference Manual: Directory Stack Builtins
- ↑ Microsoft TechNet Pushd article
- ↑ Microsoft TechNet Popd article
- ↑ Chapter 14 – 14.6 The Shells' pushd and popd Commands
- ↑ man tcsh "TCSH(1)". http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?csh+1.
- ↑ FreeCOM - FreeDOS
Further reading
- Frisch, Æleen (2001). Windows 2000 Commands Pocket Reference. O'Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00148-3.
- The Mac OS X Command Line: Unix Under the Hood. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. ISBN 978-0470113851.
External links
 |
