Chemistry:Diphenylmethane
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1′-Methylenedibenzene[1] | |
| Other names
Diphenylmethane
Benzylbenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | BnPh, Ph2CH2 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Diphenylmethane |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H12 | |
| Molar mass | 168.234 |
| Appearance | colourless oil |
| Density | 1.006 g/mL |
| Melting point | 22 to 24 °C (72 to 75 °F; 295 to 297 K) |
| Boiling point | 264 °C (507 °F; 537 K) |
| 14 mg/L | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 33 |
| -115.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
| Flash point | > 110 °C; 230 °F; 383 K |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Diphenylmethanol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
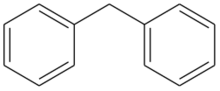
Diphenylmethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CH2 (often abbreviated CH2Ph2). The compound consists of methane wherein two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two phenyl groups. It is a white solid.
Diphenylmethane is a common skeleton in organic chemistry. The diphenylmethyl group is also known as benzhydryl.
Synthesis
It is prepared by the Friedel–Crafts alkylation of benzyl chloride with benzene in the presence of a Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride:[2]
- C6H5CH2Cl + C6H6 → (C6H5)2CH2 + HCl
Reactivity of the C-H bond
The methylene group in diphenylmethane is mildly acidic with a pKa of 32.2, and so can be deprotonated with sodium amide.[3]
- (C6H5)2CH2 + NH2− → (C6H5)2CH− + NH3
The resulting carbanion can be alkylated. For example, treatment with n-bromobutane produces 1,1-diphenylpentane in 92% yield.[4]
- (C6H5)2CH− + CH3CH2CH2CH2Br → (C6H5)2CHCH2CH2CH2CH3 + Br−
Alkylation of various benzhydryl compounds has been demonstrated using the corresponding alkyl halides, both primary (benzyl chloride, β-phenylethyl chloride, and n-octyl bromide) and secondary (benzhydryl chloride, α-phenylethyl chloride, and isopropyl chloride), in yields between 86 and 99%.[3][4]
The acidity of the methylene group in diphenylmethane is due to the weakness of the (C6H5)2CH–H bond, which has a bond dissociation energy of 82 kcal mol−1 (340 kJ mol−1).[5] This is well below the published bond dissociation energies for comparable C–H bonds in propane, where BDE((CH3)2CH–H)=98.6 kcal mol−1, and toluene, where BDE(C6H5CH2–H)=89.7 kcal mol−1.[6][7]
See also
- Benzhydryl compounds
- Toluene, a.k.a. methylbenzene, phenylmethane
- Triphenylmethane
- Tetraphenylmethane
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 452. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ W. W. Hartman and Ross Phillips (1934). "Diphenylmethane". Organic Syntheses 14: 34. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.014.0034.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hauser, Charles R.; Hamrick, Phillip J. (1957). "Alkylation of Diphenylmethane with Alkyl Halides by Sodium Amide. Substitution versus β-Elimination. Relative Acidities of Diphenylmethane and Ammonia". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (12): 3142-3145. doi:10.1021/ja01569a041.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Murphy, William S.; Hamrick, Phillip J.; Hauser, Charles R. (1968). "1,1-Diphenylpentane". Organic Syntheses 48: 80. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.048.0080.
- ↑ Zhang, Xian-Man; Bordwell, Frederick G. (1992). "Homolytic bond dissociation energies of the benzylic carbon-hydrogen bonds in radical anions and radical cations derived from fluorenes, triphenylmethanes, and related compounds". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114 (25): 9787–9792. doi:10.1021/ja00051a010.
- ↑ Blanksby, S. J.; Ellison, G. B. (2003). "Bond Dissociation Energies of Organic Molecules". Accounts of Chemical Research 36 (4): 255–263. doi:10.1021/ar020230d. PMID 12693923.
- ↑ Streitwieser, Andrew; Bergman, Robert G. (2018). "Table of Bond Dissociation Energies". University of California, Berkeley. https://archive.org/details/bergman-r.-g.-streitwieser-a.-table-of-organic-bond-dissociation-energies-2018.
 |

