Chemistry:α-Eucaine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Alpha-Eucaine |
| Other names | α-Eucaine; Eucaine A |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
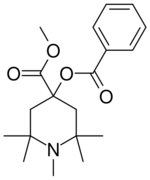
| Formula | C19H27NO4 |
| Molar mass | 333.428 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
α-Eucaine (alpha-eucaine) is a drug that was previously used as a local anesthetic.[1] It was designed as an analog of cocaine and was one of the first synthetic chemical compounds to find general use as an anesthetic.[2]
Synthesis
The Aldol condensation between two equivalents of acetone gives Mesityl oxide [141-79-7] (1) (isophorone is a side-product of this reaction). Ammonolysis of mesityl oxide formed diacetonamine [625-04-7] (2). The reaction of this product with acetone then gives 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidone [826-36-8] (3). N-methylation of the secondary amine gives 1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidin-4-one [5554-54-1] (4). Cyanohydrin formation gives CID:434556 (5). Esterification of the tertiary alcohol with benzoyl chloride gives (6). Pinner reaction of the nitrile with EtOH/H+ affords alpha-eucaine (7).
See also
- Eucaine, or β-eucaine, a related local anesthetic
References
- ↑ Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. 31 October 2005. pp. 127–9. ISBN 978-0-470-01552-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=jglFsz5EJR8C&pg=PA127.
- ↑ The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology. Elsevier. 12 May 2014. pp. 213–4. ISBN 978-1-4832-2192-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=DvbJCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA213.
- ↑ "THE IDENTIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF α- AND β-EUCAINE. 1". Journal of the American Chemical Society 23 (12): 885–893. December 1901. doi:10.1021/ja02038a002. https://zenodo.org/record/2044259.
 |

