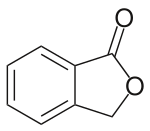
Chemistry:Phthalide
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Benzofuran-1(3H)-one | |
| Other names
Phthalolactone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 134.134 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 75 to 77 °C (167 to 171 °F; 348 to 350 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Phthalide is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C8H6O2. It is a white solid and the simplest benzo lactone. It is prepared from hydroxymethylbenzoic acid.[3]
Phthalides
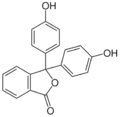
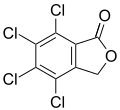
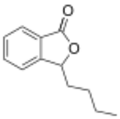
The phthalide core is found a variety of more complex chemical compounds including dyes (such as phenolphthalein), fungicides (such as tetrachlorophthalide, often referred to simply as "phthalide"), and natural oils (such as butylphthalide).
Examples
References
- ↑ Kumar, R. Arun; Maheswari, C. Uma; Ghantasala, Satheesh; Jyothi, C.; Reddy, K. Rajender (2011). "Synthesis of 3H-Quinazolin-4-ones and 4H-3,1-Benzoxazin-4-ones via Benzylic Oxidation and Oxidative Dehydrogenation using Potassium Iodide-tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide". Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis 353 (2+3): 401–410. doi:10.1002/adsc.201000580.
- ↑ Kus, Nermin Simsek (2008). "Some oxidation reactions with molecular oxygen in subcritical water". Asian Journal of Chemistry 20 (2): 1226–1230.
- ↑ J. H. Gardner, C. A. Naylor, Jr (1936). "Phthalide". Organic Syntheses 16: 71. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.016.0071.
 |