Physics:Fine structure
In atomic physics, the fine structure describes the splitting of the spectral lines of atoms due to electron spin and relativistic corrections to the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation. It was first measured precisely for the hydrogen atom by Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley in 1887,[1][2] laying the basis for the theoretical treatment by Arnold Sommerfeld, introducing the fine-structure constant.[3]
Background
Gross structure
The gross structure of line spectra is the structure predicted by the quantum mechanics of non-relativistic electrons with no spin. For a hydrogenic atom, the gross structure energy levels only depend on the principal quantum number n. However, a more accurate model takes into account relativistic and spin effects, which break the degeneracy of the energy levels and split the spectral lines. The scale of the fine structure splitting relative to the gross structure energies is on the order of (Zα)2, where Z is the atomic number and α is the fine-structure constant, a dimensionless number equal to approximately 1/137.
Relativistic corrections
The fine structure energy corrections can be obtained by using perturbation theory. To perform this calculation one must add three corrective terms to the Hamiltonian: the leading order relativistic correction to the kinetic energy, the correction due to the spin–orbit coupling, and the Darwin term coming from the quantum fluctuating motion or zitterbewegung of the electron.
These corrections can also be obtained from the non-relativistic limit of the Dirac equation, since Dirac's theory naturally incorporates relativity and spin interactions.
The hydrogen atom
This section discusses the analytical solutions for the hydrogen atom as the problem is analytically solvable and is the base model for energy level calculations in more complex atoms.
Kinetic energy relativistic correction
The gross structure assumes the kinetic energy term of the Hamiltonian takes the same form as in classical mechanics, which for a single electron means [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{H}^0 = \frac{p^{2}}{2m_e} + V }[/math] where V is the potential energy, [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] is the momentum, and [math]\displaystyle{ m_e }[/math] is the electron rest mass.
However, when considering a more accurate theory of nature via special relativity, we must use a relativistic form of the kinetic energy, [math]\displaystyle{ T = \sqrt{p^2 c^2 + m_e^2 c^4} - m_e c^2 = m_e c^2 \left[ \sqrt{1 + \frac{p^{2}}{m_e^2 c^2}}-1\right] }[/math] where the first term is the total relativistic energy, and the second term is the rest energy of the electron ([math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] is the speed of light). Expanding the square root for large values of [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math], we find [math]\displaystyle{ T = \frac{p^2}{2m_e} - \frac{p^4}{8m_e^3 c^2} + \cdots }[/math]
Although there are an infinite number of terms in this series, the later terms are much smaller than earlier terms, and so we can ignore all but the first two. Since the first term above is already part of the classical Hamiltonian, the first order correction to the Hamiltonian is [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{H}' = -\frac{p^{4}}{8m_e^{3}c^{2}} }[/math]
Using this as a perturbation, we can calculate the first order energy corrections due to relativistic effects. [math]\displaystyle{ E_n^{(1)} = \left\langle\psi^0\right\vert \mathcal{H}' \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle = -\frac{1}{8m_e^3c^2} \left\langle\psi^0\right\vert p^4 \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle = -\frac{1}{8m_e^3c^2} \left\langle\psi^0\right\vert p^2 p^2 \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ \psi^{0} }[/math] is the unperturbed wave function. Recalling the unperturbed Hamiltonian, we see [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \mathcal{H}^0 \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle &= E_n \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle \\ \left(\frac{p^2}{2m_e} + V\right)\left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle &= E_n \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle \\ p^2 \left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle &= 2m_e(E_n - V)\left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle \end{align} }[/math]
We can use this result to further calculate the relativistic correction: [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} E_n^{(1)} &= -\frac{1}{8m_e^3 c^2}\left\langle\psi^0\right\vert p^2 p^2 \left\vert\psi^{0}\right\rangle \\[1ex] &= -\frac{1}{8m_e^3 c^2}\left\langle\psi^0\right\vert (2m_e)^2 (E_n - V)^2\left\vert\psi^0\right\rangle \\[1ex] &= -\frac{1}{2m_ec^2}\left(E_n^2 - 2E_n\langle V\rangle + \left\langle V^2\right\rangle \right) \end{align} }[/math]
For the hydrogen atom, [math]\displaystyle{ V(r) = \frac{-e^2}{4\pi \varepsilon_0 r}, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \left\langle \frac{1}{r} \right\rangle = \frac{1}{a_0 n^2}, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \left\langle \frac{1}{r^2} \right\rangle = \frac{1}{(\ell + 1/2) n^3 a_0^2}, }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ e }[/math] is the elementary charge, [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_0 }[/math] is the vacuum permittivity, [math]\displaystyle{ a_0 }[/math] is the Bohr radius, [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is the principal quantum number, [math]\displaystyle{ \ell }[/math] is the azimuthal quantum number and [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] is the distance of the electron from the nucleus. Therefore, the first order relativistic correction for the hydrogen atom is [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} E_{n}^{(1)} &= -\frac{1}{2m_ec^2}\left(E_n^2 + 2E_n\frac{e^2}{4\pi \varepsilon_0}\frac{1}{a_0 n^2} + \frac{1}{16\pi^2 \varepsilon_0^2}\frac{e^4}{\left(\ell + \frac{1}{2}\right) n^3 a_0^2}\right) \\ &= -\frac{E_n^2}{2m_ec^2}\left(\frac{4n}{\ell + \frac{1}{2}} - 3\right) \end{align} }[/math] where we have used: [math]\displaystyle{ E_n = - \frac{e^2}{8 \pi \varepsilon_0 a_0 n^2} }[/math]
On final calculation, the order of magnitude for the relativistic correction to the ground state is [math]\displaystyle{ -9.056 \times 10^{-4}\ \text{eV} }[/math].
Spin–orbit coupling
For a hydrogen-like atom with [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math] protons ([math]\displaystyle{ Z = 1 }[/math] for hydrogen), orbital angular momentum [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf L }[/math] and electron spin [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf S }[/math], the spin–orbit term is given by: [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{H}_\mathrm{SO} = \left(\frac{Ze^2}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\right) \left(\frac{g_s - 1}{2m_e^2 c^2}\right)\frac{\mathbf{L} \cdot \mathbf{S}}{r^3} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ g_s }[/math] is the spin g-factor.
The spin–orbit correction can be understood by shifting from the standard frame of reference (where the electron orbits the nucleus) into one where the electron is stationary and the nucleus instead orbits it. In this case the orbiting nucleus functions as an effective current loop, which in turn will generate a magnetic field. However, the electron itself has a magnetic moment due to its intrinsic angular momentum. The two magnetic vectors, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{B} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol\mu_s }[/math] couple together so that there is a certain energy cost depending on their relative orientation. This gives rise to the energy correction of the form [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta E_{\mathrm{SO}} = \xi (r) \mathbf L \cdot \mathbf S }[/math]
Notice that an important factor of 2 has to be added to the calculation, called the Thomas precession, which comes from the relativistic calculation that changes back to the electron's frame from the nucleus frame.
Since [math]\displaystyle{ \left\langle \frac{1}{r^3} \right\rangle = \frac{Z^3}{n^3 a_0^3} \frac{1}{\ell \left(\ell + \frac{1}{2}\right) (\ell + 1)} }[/math]
by Kramers–Pasternack relations and [math]\displaystyle{ \left\langle \mathbf L \cdot \mathbf S \right\rangle = \frac{\hbar^2}{2} \left[j(j + 1) - \ell(\ell + 1) - s(s + 1)\right] }[/math]
the expectation value for the Hamiltonian is: [math]\displaystyle{ \left\langle \mathcal{H}_{\mathrm{SO}} \right\rangle = \frac{E_n{}^2}{m_e c^2} ~n~ \frac{j(j + 1) - \ell(\ell + 1) - \frac{3}{4}}{\ell \left( \ell + \frac{1}{2}\right) (\ell + 1) } }[/math]
Thus the order of magnitude for the spin–orbital coupling is: [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{Z^4}{n^3 \left(j + \frac{1}{2}\right)} 10^{-5}\text{ eV} }[/math]
When weak external magnetic fields are applied, the spin–orbit coupling contributes to the Zeeman effect.
Darwin term
There is one last term in the non-relativistic expansion of the Dirac equation. It is referred to as the Darwin term, as it was first derived by Charles Galton Darwin, and is given by: [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \mathcal{H}_{\text{Darwin}} &= \frac{\hbar^2}{8m_e^2 c^2}\,4\pi\left(\frac{Ze^2}{4\pi \varepsilon_0}\right) \delta^3{\left(\mathbf r\right)} \\ \langle \mathcal{H}_{\text{Darwin}} \rangle &= \frac{\hbar^2}{8m_e^2 c^2}\,4\pi\left(\frac{Ze^2}{4\pi \varepsilon_0}\right)| \psi(0)|^2 \\[3pt] \psi (0) &= \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ for } \ell \gt 0 \\ \frac{1}{\sqrt{4\pi}} \, 2 \left( \frac {Z}{n a_0} \right)^\frac{3}{2} & \text{ for } \ell = 0 \end{cases}\\[2pt] \mathcal{H}_{\text{Darwin}} &= \frac{2n}{m_e c^2}\,E_n^2 \end{align} }[/math]
The Darwin term affects only the s orbitals. This is because the wave function of an electron with [math]\displaystyle{ \ell \gt 0 }[/math] vanishes at the origin, hence the delta function has no effect. For example, it gives the 2s orbital the same energy as the 2p orbital by raising the 2s state by 9.057×10−5 eV.
The Darwin term changes potential energy of the electron. It can be interpreted as a smearing out of the electrostatic interaction between the electron and nucleus due to zitterbewegung, or rapid quantum oscillations, of the electron. This can be demonstrated by a short calculation.[4]
Quantum fluctuations allow for the creation of virtual electron-positron pairs with a lifetime estimated by the uncertainty principle [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta t \approx \hbar/\Delta E \approx \hbar/mc^2 }[/math]. The distance the particles can move during this time is [math]\displaystyle{ \xi \approx c\Delta t \approx \hbar/mc = \lambda_c }[/math], the Compton wavelength. The electrons of the atom interact with those pairs. This yields a fluctuating electron position [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf r + \boldsymbol \xi }[/math]. Using a Taylor expansion, the effect on the potential [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math] can be estimated: [math]\displaystyle{ U(\mathbf r + \boldsymbol\xi) \approx U(\mathbf r) + \xi\cdot\nabla U(\mathbf r) + \frac 1 2 \sum_{i,j} \xi_i \xi_j \partial_i \partial_j U(\mathbf r) }[/math]
Averaging over the fluctuations [math]\displaystyle{ \boldsymbol \xi }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \overline\xi = 0, \quad \overline{\xi_i\xi_j} = \frac 1 3 \overline{\boldsymbol\xi^2} \delta_{ij}, }[/math]
gives the average potential [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{U\left(\mathbf r + \boldsymbol\xi\right)} = U{\left(\mathbf r\right)} + \frac{1}{6} \overline{\boldsymbol\xi^2} \nabla^2 U\left(\mathbf r\right). }[/math]
Approximating [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{\boldsymbol\xi^2} \approx \lambda_c^2 }[/math], this yields the perturbation of the potential due to fluctuations: [math]\displaystyle{ \delta U \approx \frac16 \lambda_c^2 \nabla^2 U = \frac{\hbar^2}{6m_e^2c^2}\nabla^2 U }[/math]
To compare with the expression above, plug in the Coulomb potential: [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla^2 U = -\nabla^2 \frac{Z e^2}{4\pi\varepsilon_0 r} = 4\pi \left(\frac{Z e^2}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\right) \delta^3(\mathbf r) \quad\Rightarrow\quad \delta U \approx \frac{\hbar^2}{6m_e^2c^2} 4\pi \left(\frac{Z e^2}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\right) \delta^3(\mathbf r) }[/math]
This is only slightly different.
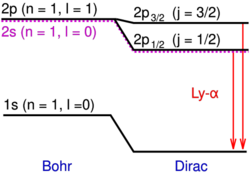
Another mechanism that affects only the s-state is the Lamb shift, a further, smaller correction that arises in quantum electrodynamics that should not be confused with the Darwin term. The Darwin term gives the s-state and p-state the same energy, but the Lamb shift makes the s-state higher in energy than the p-state.
Total effect
The full Hamiltonian is given by [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{H}=\mathcal{H}_\text{Coulomb} + \mathcal{H}_{\text{kinetic}}+\mathcal{H}_{\mathrm{SO}}+\mathcal{H}_{\text{Darwin}}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{H}_\text{Coulomb} }[/math] is the Hamiltonian from the Coulomb interaction.
The total effect, obtained by summing the three components up, is given by the following expression:[5] [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta E = \frac{E_{n}(Z\alpha)^{2}}{n}\left( \frac{1}{j + \frac{1}{2}} - \frac{3}{4n} \right)\,, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ j }[/math] is the total angular momentum quantum number ([math]\displaystyle{ j = 1/2 }[/math] if [math]\displaystyle{ \ell = 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ j = \ell \pm 1/2 }[/math] otherwise). It is worth noting that this expression was first obtained by Sommerfeld based on the old Bohr theory; i.e., before the modern quantum mechanics was formulated.
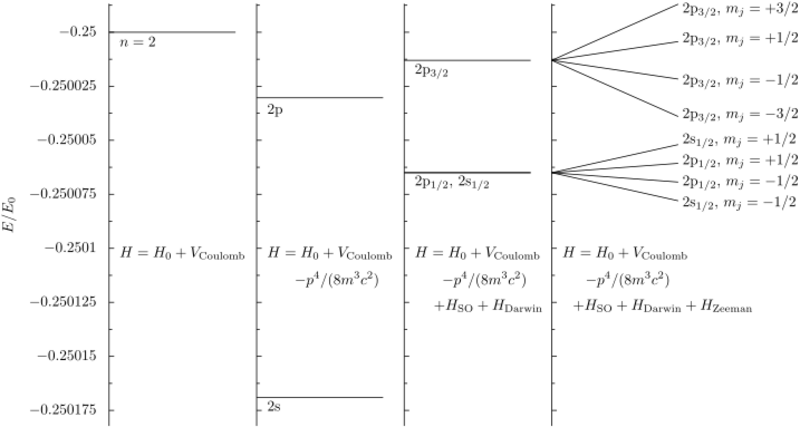
Exact relativistic energies
The total effect can also be obtained by using the Dirac equation. In this case, the electron is treated as non-relativistic. The exact energies are given by[6] [math]\displaystyle{ E_{j\,n} = -m_\text{e}c^2\left[1 - \left(1 + \left[\frac{\alpha}{n - j - \frac{1}{2} + \sqrt{\left(j + \frac{1}{2}\right)^2 - \alpha^2}}\right]^2\right)^{-\frac{1}{2}}\right]. }[/math]
This expression, which contains all higher order terms that were left out in the other calculations, expands to first order to give the energy corrections derived from perturbation theory. However, this equation does not contain the hyperfine structure corrections, which are due to interactions with the nuclear spin. Other corrections from quantum field theory such as the Lamb shift and the anomalous magnetic dipole moment of the electron are not included.
See also
References
- ↑ A.A. Michelson; E. W. Morley (1887). "On a method of making the wave-length of sodium light the actual practical standard of length". American Journal of Science 34: 427. https://archive.org/details/americanjourna3341887newh/page/427.
- ↑ A.A. Michelson; E. W. Morley (1887). "On a method of making the wave-length of sodium light the actual practical standard of length". Philosophical Magazine 24: 463. https://archive.org/details/s5philosophicalm24lond/page/463.
- ↑ A.Sommerfeld (July 1940). "Zur Feinstruktur der Wasserstofflinien. Geschichte und gegenwärtiger Stand der Theorie" (in german). Naturwissenschaften 28 (27): 417–423. doi:10.1007/BF01490583.
- ↑ Zelevinsky, Vladimir (2011), Quantum Physics Volume 1: From Basics to Symmetries and Perturbations, WILEY-VCH, ISBN 978-3-527-40979-2
- ↑ Berestetskii, V. B.; E. M. Lifshitz; L. P. Pitaevskii (1982). Quantum electrodynamics. Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3371-0.
- ↑ Sommerfeld, Arnold (1919). Atombau und Spektrallinien'. Braunschweig: Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn. ISBN 3-87144-484-7. German English
- Griffiths, David J. (2004). Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-805326-X. https://archive.org/details/introductiontoel00grif_0.
- Liboff, Richard L. (2002). Introductory Quantum Mechanics. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-8053-8714-5.
External links
 |


