Chemistry:Hydroxymethylbilane
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,3′,3′′,3′′′-[3,8,13,18-Tetrakis(carboxymethyl)-19-(hydroxymethyl)-5,10,15,22,23,24-hexahydro-21H-biline-2,7,12,17-tetrayl]tetrapropanoic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3,3′,3′′,3′′′-[14,33,53,73-Tetrakis(carboxymethyl)-15-(hydroxymethyl)-11H,31H,51H,71H-1,7(2),3,5(2,5)-tetrapyrrolaheptaphane-13,34,54,74-tetrayl]tetrapropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1209089 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | hydroxymethylbilane |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C40H46N4O17 | |
| Molar mass | 854.81 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
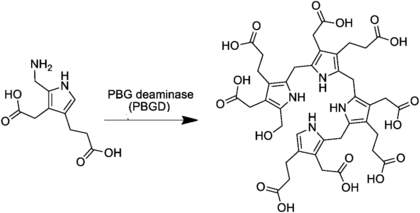
Hydroxymethylbilane, also known as preuroporphyrinogen, is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms during the synthesis of porphyrins, a group of critical substances that include haemoglobin, myoglobin, and chlorophyll. The name is often abbreviated as HMB.
Structure
The compound is a substituted bilane, a chain of four pyrrole rings interconnected by methylene bridges –CH
2–. The chain starts with a hydroxymethyl group –CH
2–OH and ends with an hydrogen, in place of the respective methylene bridges. The other two carbon atoms of each pyrrole cycle are connected to an acetic acid group –CH
2–COOH and a propionic acid group –CH
2–CH
2–COOH, in that order.[1]
Metabolism
HMB is generated from four molecules of porphobilinogen by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase:[2]
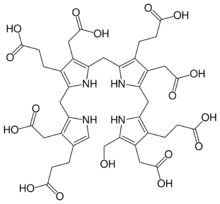
The enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase closes the chain to form uroporphyrinogen III:[2]
Uroporphyrinogen III is a porphyrinogen, which is a class of compounds with the hexahydroporphine macrocycle. In the absence of the enzyme, the compound undergoes spontaneous cyclization and becomes uroporphyrinogen I.[3][4]
References
- ↑ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221. ISBN 978-0470048672.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G. (2011). Biochemistry (4. ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-57095-1.
- ↑ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221. ISBN 978-0470048672.
- ↑ Sassa, S.; Kappas, A. (2000). "Molecular aspects of the inherited porphyrias". Journal of Internal Medicine 247 (2): 169–178. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2796.2000.00618.x. PMID 10692079.
 |