Chemistry:3-Bromobenzaldehyde
From HandWiki
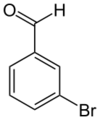
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Bromobenzaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5BrO | |
| Molar mass | 185.020 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid. |
| Density | 1.587 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | 18 to 21 °C (64 to 70 °F; 291 to 294 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 233 to 236 °C (451 to 457 °F; 506 to 509 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
4-Bromobenzaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
3-Bromobenzaldehyde is an isomer of bromobenzaldehyde. It is a colorless viscous liquid.
3-Bromobenzaldehyde can be prepared from 3-nitrobenzaldehyde.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "3-Bromobenzaldehyde". Sigma-Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/b57206?lang=en.
- ↑ Johannes S. Buck and Walter S. Ide (1933). "m-Chlorobenzaldehyde". Organic Syntheses 13: 28. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.013.0028.
 |

