Chemistry:N-Methylpiperazine
From HandWiki
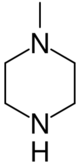
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methylpiperazine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2920 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 100.165 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | −6 °C (21 °F; 267 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 138 °C (280 °F; 411 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | FischerSci |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H312, H314, H317, H330, H331, H332 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P284, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P311, P312, P320, P321, P322 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Piperazine, 4-methylpyridine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
N-Methylpiperazine is a heterocyclic organic compound.
Uses
N-Methylpiperazine is a common building block used in organic synthesis.[2] For example, N-methylpiperazine is used in the manufacture of various pharmaceutical drugs including cyclizine,[3] meclizine, and sildenafil.
The lithium salt, lithium N-methylpiperazide, is used as a reagent in organic synthesis for protection of aryl aldehydes.[4]
Synthesis
Industrially, N-methylpiperazine is produced by reacting diethanolamine and methylamine at 250 bar and 200 °C.[5][6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "1-Methylpiperazine". Chemistry Dashboard. Environmental Protection Agency. https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/dsstoxdb/results?search=DTXSID4021898.
- ↑ "1-methylpiperazine". European Chemicals Agency. https://echa.europa.eu/brief-profile/-/briefprofile/100.003.309.
- ↑ Vardanyan, Ṛuben & Hruby, Victor J.. Synthesis of Essential Drugs. p. 226.
- ↑ Comins, Daniel L.; Joseph, Sajan P. (2001). "Lithium N-Methylpiperazide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rl128. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ "Preparation of N-Methylpiperazine" US patent 4845218, issued 1989-07-04
- ↑ "Catalytic synthesis of N-methylpiperazine from diethanolamine and methylamine by cyclodehydration reaction". Indian Journal of Chemical Technology 1 (November): 359–360. 1994. http://nopr.niscair.res.in/bitstream/123456789/31280/1/IJCT%201%286%29%20359-360.pdf.
 |


