Chemistry:Indoline
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydro-1H-indole | |
| Other names
2,3-Dihydroindole
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 111915 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9N | |
| Molar mass | 119.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.063 g/mL |
| Melting point | −21 °C (−6 °F; 252 K) |
| Boiling point | 220 to 221 °C (428 to 430 °F; 493 to 494 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Fisher Scientific |
| Flash point | 92.8 °C (199.0 °F; 365.9 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related aromatics
|
carbazole, indole, isoindoline, oxindole |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
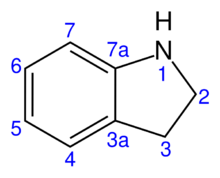
Indoline is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formulation C8H9N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound is based on the indole structure, but the 2-3 bond is saturated. By oxidation/dehydrogenation it can be converted to indoles.[1][2]
Indoline can be produced from the reaction of indole, zinc and 85% phosphoric acid.[3] It was used to make Indocaine.
References
- ↑ Template:Katritzky2nd
- ↑ Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850346-6. https://archive.org/details/organicchemistry00clay_0.
- ↑ Dolby, Lloyd J.; Gribble, Gordon W. (1966). "A convenient preparation of indoline". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 3 (2): 124–125. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570030202. ISSN 0022-152X.
 |

