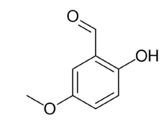
Chemistry:2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde
From HandWiki
Short description: Organic compound and isomer of vanillin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde | |
| Other names
5-Methoxysalicylaldehyde; 2-Formyl-4-methoxyphenol; 6-Hydroxy-m-anisaldehyde
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.149 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow to yellow-green liquid |
| Density | 1.219 g/mL |
| Melting point | 4 °C (39 °F; 277 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.578 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound and an isomer of vanillin.
Synthesis and reactions
The chemical is produced by the Reimer-Tiemann reaction on 4-methoxyphenol with a 79% yield.[1]
It reacts with malononitrile to form 2-imino-6-methoxy-2H-1-benzopyran-3-carbonitrile.[2] It can be reduced by sodium borohydride in ethanol to form 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzyl alcohol.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Wynberg, Hans; Meijer, Egbert W. (2005). The Reimer–Tiemann Reaction. p. 16. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or028.01. ISBN 9780471264187.
- ↑ Dinparast, Leila; Hemmati, Salar; Zengin, Gokhan; Alizadeh, Ali Akbar; Bahadori, Mir Babak; Kafil, Hossein Samadi; Dastmalchi, Siavoush (2019). "Rapid, Efficient, and Green Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives via Knoevenagel Condensation and Investigating Their Biological Effects". ChemistrySelect 4 (31): 9211–9215. doi:10.1002/slct.201901921. ISSN 2365-6549.
- ↑ Cheng, Yan; Ono, Masahiro; Kimura, Hiroyuki; Kagawa, Shinya; Nishii, Ryuichi; Kawashima, Hidekazu; Saji, Hideo (2010). "Fluorinated Benzofuran Derivatives for PET Imaging of β-Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer's Disease Brains". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 1 (7): 321–325. doi:10.1021/ml100082x. ISSN 1948-5875. PMID 24900214.
 |

