Hopf algebra
In mathematics, a Hopf algebra, named after Heinz Hopf, is a structure that is simultaneously an (unital associative) algebra and a (counital coassociative) coalgebra, with these structures' compatibility making it a bialgebra, and that moreover is equipped with an antiautomorphism satisfying a certain property. The representation theory of a Hopf algebra is particularly nice, since the existence of compatible comultiplication, counit, and antipode allows for the construction of tensor products of representations, trivial representations, and dual representations.
Hopf algebras occur naturally in algebraic topology, where they originated and are related to the H-space concept, in group scheme theory, in group theory (via the concept of a group ring), and in numerous other places, making them probably the most familiar type of bialgebra. Hopf algebras are also studied in their own right, with much work on specific classes of examples on the one hand and classification problems on the other. They have diverse applications ranging from condensed-matter physics and quantum field theory[1] to string theory[2] and LHC phenomenology.[3]
Formal definition
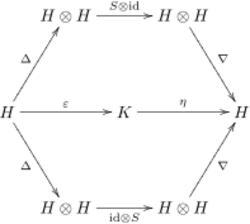
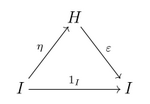
Formally, a Hopf algebra is an (associative and coassociative) bialgebra H over a field K together with a K-linear map S: H → H (called the antipode) such that the following diagram commutes:
Here Δ is the comultiplication of the bialgebra, ∇ its multiplication, η its unit and ε its counit. In the sumless Sweedler notation, this property can also be expressed as
- [math]\displaystyle{ S(c_{(1)})c_{(2)}=c_{(1)}S(c_{(2)})=\varepsilon(c)1\qquad\mbox{ for all }c\in H. }[/math]
As for algebras, one can replace the underlying field K with a commutative ring R in the above definition.[4]
The definition of Hopf algebra is self-dual (as reflected in the symmetry of the above diagram), so if one can define a dual of H (which is always possible if H is finite-dimensional), then it is automatically a Hopf algebra.[5]
Structure constants
Fixing a basis [math]\displaystyle{ \{e_k\} }[/math] for the underlying vector space, one may define the algebra in terms of structure constants for multiplication:
- [math]\displaystyle{ e_i\nabla e_j = \sum_k \mu^k_{\;ij} e_k }[/math]
for co-multiplication:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta e_i = \sum_{j,k} \nu^{\;jk}_i e_j\otimes e_k }[/math]
and the antipode:
- [math]\displaystyle{ S e_i = \sum_j \tau_i^{\;j} e_j }[/math]
Associativity then requires that
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mu^k_{\;ij}\mu^m_{\;kn}=\mu^k_{\;jn}\mu^m_{\;ik} }[/math]
while co-associativity requires that
- [math]\displaystyle{ \nu_k^{\;ij}\nu_i^{\;mn}=\nu_k^{\;mi}\nu_i^{\;nj} }[/math]
The connecting axiom requires that
- [math]\displaystyle{ \nu_k^{\;ij}\tau_j^{\;m}\mu^n_{\;pm}=\nu_k^{\;jm}\tau_j^{\,\;i}\mu^n_{\;pm} }[/math]
Properties of the antipode
The antipode S is sometimes required to have a K-linear inverse, which is automatic in the finite-dimensional case[clarification needed], or if H is commutative or cocommutative (or more generally quasitriangular).
In general, S is an antihomomorphism,[6] so S2 is a homomorphism, which is therefore an automorphism if S was invertible (as may be required).
If S2 = idH, then the Hopf algebra is said to be involutive (and the underlying algebra with involution is a *-algebra). If H is finite-dimensional semisimple over a field of characteristic zero, commutative, or cocommutative, then it is involutive.
If a bialgebra B admits an antipode S, then S is unique ("a bialgebra admits at most 1 Hopf algebra structure").[7] Thus, the antipode does not pose any extra structure which we can choose: Being a Hopf algebra is a property of a bialgebra.
The antipode is an analog to the inversion map on a group that sends g to g−1.[8]
Hopf subalgebras
A subalgebra A of a Hopf algebra H is a Hopf subalgebra if it is a subcoalgebra of H and the antipode S maps A into A. In other words, a Hopf subalgebra A is a Hopf algebra in its own right when the multiplication, comultiplication, counit and antipode of H are restricted to A (and additionally the identity 1 of H is required to be in A). The Nichols–Zoeller freeness theorem of Warren Nichols and Bettina Zoeller (1989) established that the natural A-module H is free of finite rank if H is finite-dimensional: a generalization of Lagrange's theorem for subgroups.[9] As a corollary of this and integral theory, a Hopf subalgebra of a semisimple finite-dimensional Hopf algebra is automatically semisimple.
A Hopf subalgebra A is said to be right normal in a Hopf algebra H if it satisfies the condition of stability, adr(h)(A) ⊆ A for all h in H, where the right adjoint mapping adr is defined by adr(h)(a) = S(h(1))ah(2) for all a in A, h in H. Similarly, a Hopf subalgebra A is left normal in H if it is stable under the left adjoint mapping defined by adl(h)(a) = h(1)aS(h(2)). The two conditions of normality are equivalent if the antipode S is bijective, in which case A is said to be a normal Hopf subalgebra.
A normal Hopf subalgebra A in H satisfies the condition (of equality of subsets of H): HA+ = A+H where A+ denotes the kernel of the counit on A. This normality condition implies that HA+ is a Hopf ideal of H (i.e. an algebra ideal in the kernel of the counit, a coalgebra coideal and stable under the antipode). As a consequence one has a quotient Hopf algebra H/HA+ and epimorphism H → H/A+H, a theory analogous to that of normal subgroups and quotient groups in group theory.[10]
Hopf orders
A Hopf order O over an integral domain R with field of fractions K is an order in a Hopf algebra H over K which is closed under the algebra and coalgebra operations: in particular, the comultiplication Δ maps O to O⊗O.[11]
Group-like elements
A group-like element is a nonzero element x such that Δ(x) = x⊗x. The group-like elements form a group with inverse given by the antipode.[12] A primitive element x satisfies Δ(x) = x⊗1 + 1⊗x.[13][14]
Examples
| Depending on | Comultiplication | Counit | Antipode | Commutative | Cocommutative | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| group algebra KG | group G | Δ(g) = g ⊗ g for all g in G | ε(g) = 1 for all g in G | S(g) = g−1 for all g in G | if and only if G is abelian | yes | |
| functions f from a finite[lower-alpha 1] group to K, KG (with pointwise addition and multiplication) | finite group G | Δ(f)(x,y) = f(xy) | ε(f) = f(1G) | S(f)(x) = f(x−1) | yes | if and only if G is abelian | |
| Representative functions on a compact group | compact group G | Δ(f)(x,y) = f(xy) | ε(f) = f(1G) | S(f)(x) = f(x−1) | yes | if and only if G is abelian | Conversely, every commutative involutive reduced Hopf algebra over C with a finite Haar integral arises in this way, giving one formulation of Tannaka–Krein duality.[15] |
| Tensor algebra T(V) | vector space V | Δ(x) = x ⊗ 1 + 1 ⊗ x, x in V, Δ(1) = 1 ⊗ 1 | ε(x) = 0 | S(x) = −x for all x in 'T1(V) (and extended to higher tensor powers) | If and only if dim(V)=0,1 | yes | symmetric algebra and exterior algebra (which are quotients of the tensor algebra) are also Hopf algebras with this definition of the comultiplication, counit and antipode |
| Universal enveloping algebra U(g) | Lie algebra g | Δ(x) = x ⊗ 1 + 1 ⊗ x for every x in g (this rule is compatible with commutators and can therefore be uniquely extended to all of U) | ε(x) = 0 for all x in g (again, extended to U) | S(x) = −x | if and only if g is abelian | yes | |
| Sweedler's Hopf algebra H=K[c, x]/c2 = 1, x2 = 0 and xc = −cx. | K is a field with characteristic different from 2 | Δ(c) = c ⊗ c, Δ(x) = c ⊗ x + x ⊗ 1, Δ(1) = 1 ⊗ 1 | ε(c) = 1 and ε(x) = 0 | S(c) = c−1 = c and S(x) = −cx | no | no | The underlying vector space is generated by {1, c, x, cx} and thus has dimension 4. This is the smallest example of a Hopf algebra that is both non-commutative and non-cocommutative. |
| ring of symmetric functions[16] | in terms of complete homogeneous symmetric functions hk (k ≥ 1):
Δ(hk) = 1 ⊗ hk + h1 ⊗ hk−1 + ... + hk−1 ⊗ h1 + hk ⊗ 1. |
ε(hk) = 0 | S(hk) = (−1)k ek | yes | yes |
Note that functions on a finite group can be identified with the group ring, though these are more naturally thought of as dual – the group ring consists of finite sums of elements, and thus pairs with functions on the group by evaluating the function on the summed elements.
Cohomology of Lie groups
The cohomology algebra (over a field [math]\displaystyle{ K }[/math]) of a Lie group [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] is a Hopf algebra: the multiplication is provided by the cup product, and the comultiplication
- [math]\displaystyle{ H^*(G,K) \rightarrow H^*(G\times G,K) \cong H^*(G,K)\otimes H^*(G,K) }[/math]
by the group multiplication [math]\displaystyle{ G\times G\to G }[/math]. This observation was actually a source of the notion of Hopf algebra. Using this structure, Hopf proved a structure theorem for the cohomology algebra of Lie groups.
Theorem (Hopf)[17] Let [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] be a finite-dimensional, graded commutative, graded cocommutative Hopf algebra over a field of characteristic 0. Then [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] (as an algebra) is a free exterior algebra with generators of odd degree.
Quantum groups and non-commutative geometry
All examples above are either commutative (i.e. the multiplication is commutative) or co-commutative (i.e.[18] Δ = T ∘ Δ where the twist map[19] T: H ⊗ H → H ⊗ H is defined by T(x ⊗ y) = y ⊗ x). Other interesting Hopf algebras are certain "deformations" or "quantizations" of those from example 3 which are neither commutative nor co-commutative. These Hopf algebras are often called quantum groups, a term that is so far only loosely defined. They are important in noncommutative geometry, the idea being the following: a standard algebraic group is well described by its standard Hopf algebra of regular functions; we can then think of the deformed version of this Hopf algebra as describing a certain "non-standard" or "quantized" algebraic group (which is not an algebraic group at all). While there does not seem to be a direct way to define or manipulate these non-standard objects, one can still work with their Hopf algebras, and indeed one identifies them with their Hopf algebras. Hence the name "quantum group".
Representation theory
Let A be a Hopf algebra, and let M and N be A-modules. Then, M ⊗ N is also an A-module, with
- [math]\displaystyle{ a(m\otimes n):=\Delta(a)(m \otimes n)=(a_1\otimes a_2)(m\otimes n)=(a_1 m \otimes a_2 n) }[/math]
for m ∈ M, n ∈ N and Δ(a) = (a1, a2). Furthermore, we can define the trivial representation as the base field K with
- [math]\displaystyle{ a(m):=\epsilon(a)m }[/math]
for m ∈ K. Finally, the dual representation of A can be defined: if M is an A-module and M* is its dual space, then
- [math]\displaystyle{ (af)(m):=f(S(a)m) }[/math]
where f ∈ M* and m ∈ M.
The relationship between Δ, ε, and S ensure that certain natural homomorphisms of vector spaces are indeed homomorphisms of A-modules. For instance, the natural isomorphisms of vector spaces M → M ⊗ K and M → K ⊗ M are also isomorphisms of A-modules. Also, the map of vector spaces M* ⊗ M → K with f ⊗ m → f(m) is also a homomorphism of A-modules. However, the map M ⊗ M* → K is not necessarily a homomorphism of A-modules.
Related concepts
Graded Hopf algebras are often used in algebraic topology: they are the natural algebraic structure on the direct sum of all homology or cohomology groups of an H-space.
Locally compact quantum groups generalize Hopf algebras and carry a topology. The algebra of all continuous functions on a Lie group is a locally compact quantum group.
Quasi-Hopf algebras are generalizations of Hopf algebras, where coassociativity only holds up to a twist. They have been used in the study of the Knizhnik–Zamolodchikov equations.[20]
Multiplier Hopf algebras introduced by Alfons Van Daele in 1994[21] are generalizations of Hopf algebras where comultiplication from an algebra (with or without unit) to the multiplier algebra of tensor product algebra of the algebra with itself.
Hopf group-(co)algebras introduced by V. G. Turaev in 2000 are also generalizations of Hopf algebras.
Weak Hopf algebras
Weak Hopf algebras, or quantum groupoids, are generalizations of Hopf algebras. Like Hopf algebras, weak Hopf algebras form a self-dual class of algebras; i.e., if H is a (weak) Hopf algebra, so is H*, the dual space of linear forms on H (with respect to the algebra-coalgebra structure obtained from the natural pairing with H and its coalgebra-algebra structure). A weak Hopf algebra H is usually taken to be a
- finite-dimensional algebra and coalgebra with coproduct Δ: H → H ⊗ H and counit ε: H → k satisfying all the axioms of Hopf algebra except possibly Δ(1) ≠ 1 ⊗ 1 or ε(ab) ≠ ε(a)ε(b) for some a,b in H. Instead one requires the following:
- [math]\displaystyle{ (\Delta(1) \otimes 1)(1 \otimes \Delta(1)) = (1 \otimes \Delta(1))(\Delta(1) \otimes 1) = (\Delta \otimes \mbox{Id})\Delta(1) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \epsilon(abc) = \sum \epsilon(ab_{(1)})\epsilon(b_{(2)}c) = \sum \epsilon(ab_{(2)})\epsilon(b_{(1)}c) }[/math]
- for all a, b, and c in H.
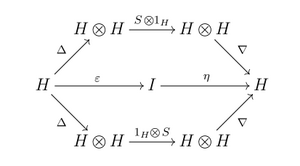
- H has a weakened antipode S: H → H satisfying the axioms:
- [math]\displaystyle{ S(a_{(1)})a_{(2)} = 1_{(1)} \epsilon(a 1_{(2)}) }[/math] for all a in H (the right-hand side is the interesting projection usually denoted by ΠR(a) or εs(a) with image a separable subalgebra denoted by HR or Hs);
- [math]\displaystyle{ a_{(1)}S(a_{(2)}) = \epsilon(1_{(1)}a)1_{(2)} }[/math] for all a in H (another interesting projection usually denoted by ΠR(a) or εt(a) with image a separable algebra HL or Ht, anti-isomorphic to HL via S);
- [math]\displaystyle{ S(a_{(1)})a_{(2)}S(a_{(3)}) = S(a) }[/math] for all a in H.
- Note that if Δ(1) = 1 ⊗ 1, these conditions reduce to the two usual conditions on the antipode of a Hopf algebra.
The axioms are partly chosen so that the category of H-modules is a rigid monoidal category. The unit H-module is the separable algebra HL mentioned above.
For example, a finite groupoid algebra is a weak Hopf algebra. In particular, the groupoid algebra on [n] with one pair of invertible arrows eij and eji between i and j in [n] is isomorphic to the algebra H of n x n matrices. The weak Hopf algebra structure on this particular H is given by coproduct Δ(eij) = eij ⊗ eij, counit ε(eij) = 1 and antipode S(eij) = eji. The separable subalgebras HL and HR coincide and are non-central commutative algebras in this particular case (the subalgebra of diagonal matrices).
Early theoretical contributions to weak Hopf algebras are to be found in[22] as well as[23]
Hopf algebroids
See Hopf algebroid
Analogy with groups
Groups can be axiomatized by the same diagrams (equivalently, operations) as a Hopf algebra, where G is taken to be a set instead of a module. In this case:
- the field K is replaced by the 1-point set
- there is a natural counit (map to 1 point)
- there is a natural comultiplication (the diagonal map)
- the unit is the identity element of the group
- the multiplication is the multiplication in the group
- the antipode is the inverse
In this philosophy, a group can be thought of as a Hopf algebra over the "field with one element".[24]
Hopf algebras in braided monoidal categories
The definition of Hopf algebra is naturally extended to arbitrary braided monoidal categories.[25][26] A Hopf algebra in such a category [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,I,\alpha,\lambda,\rho,\gamma) }[/math] is a sextuple [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta,\Delta,\varepsilon,S) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] is an object in [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math], and
- [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla:H\otimes H\to H }[/math] (multiplication),
- [math]\displaystyle{ \eta:I\to H }[/math] (unit),
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta:H\to H\otimes H }[/math] (comultiplication),
- [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon:H\to I }[/math] (counit),
- [math]\displaystyle{ S:H\to H }[/math] (antipode)
— are morphisms in [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math] such that
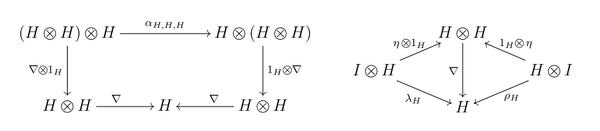
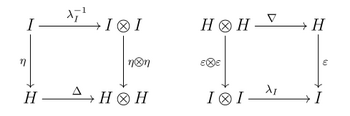
- 1) the triple [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta) }[/math] is a monoid in the monoidal category [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,I,\alpha,\lambda,\rho,\gamma) }[/math], i.e. the following diagrams are commutative:[lower-alpha 2]
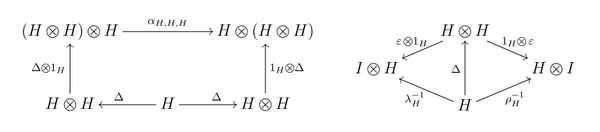
- 2) the triple [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\Delta,\varepsilon) }[/math] is a comonoid in the monoidal category [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,I,\alpha,\lambda,\rho,\gamma) }[/math], i.e. the following diagrams are commutative:[lower-alpha 2]
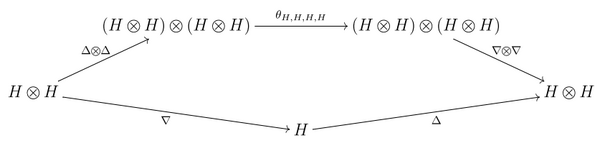
- 3) the structures of monoid and comonoid on [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] are compatible: the multiplication [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla }[/math] and the unit [math]\displaystyle{ \eta }[/math] are morphisms of comonoids, and (this is equivalent in this situation) at the same time the comultiplication [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta }[/math] and the counit [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon }[/math] are morphisms of monoids; this means that the following diagrams must be commutative:
- where [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda_I:I\otimes I\to I }[/math] is the left unit morphism in [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math], and [math]\displaystyle{ \theta }[/math] the natural transformation of functors [math]\displaystyle{ (A\otimes B)\otimes (C\otimes D)\stackrel{\theta}{\rightarrowtail} (A\otimes C)\otimes (B\otimes D) }[/math] which is unique in the class of natural transformations of functors composed from the structural transformations (associativity, left and right units, transposition, and their inverses) in the category [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math].
The quintuple [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta,\Delta,\varepsilon) }[/math] with the properties 1),2),3) is called a bialgebra in the category [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,I,\alpha,\lambda,\rho,\gamma) }[/math];
- 4) the diagram of antipode is commutative:
The typical examples are the following.
- Groups. In the monoidal category [math]\displaystyle{ (\text{Set},\times,1) }[/math] of sets (with the cartesian product [math]\displaystyle{ \times }[/math] as the tensor product, and an arbitrary singletone, say, [math]\displaystyle{ 1=\{\varnothing\} }[/math], as the unit object) a triple [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta) }[/math] is a monoid in the categorical sense if and only if it is a monoid in the usual algebraic sense, i.e. if the operations [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla(x,y)=x\cdot y }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \eta(1) }[/math] behave like usual multiplication and unit in [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] (but possibly without the invertibility of elements [math]\displaystyle{ x\in H }[/math]). At the same time, a triple [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\Delta,\varepsilon) }[/math] is a comonoid in the categorical sense iff [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta }[/math] is the diagonal operation [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta(x)=(x,x) }[/math] (and the operation [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon }[/math] is defined uniquely as well: [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon(x)=\varnothing }[/math]). And any such a structure of comonoid [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\Delta,\varepsilon) }[/math] is compatible with any structure of monoid [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta) }[/math] in the sense that the diagrams in the section 3 of the definition always commute. As a corollary, each monoid [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta) }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ (\text{Set},\times,1) }[/math] can naturally be considered as a bialgebra [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta,\Delta,\varepsilon) }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ (\text{Set},\times,1) }[/math], and vice versa. The existence of the antipode [math]\displaystyle{ S:H\to H }[/math] for such a bialgebra [math]\displaystyle{ (H,\nabla,\eta,\Delta,\varepsilon) }[/math] means exactly that every element [math]\displaystyle{ x\in H }[/math] has an inverse element [math]\displaystyle{ x^{-1}\in H }[/math] with respect to the multiplication [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla(x,y)=x\cdot y }[/math]. Thus, in the category of sets [math]\displaystyle{ (\text{Set},\times,1) }[/math] Hopf algebras are exactly groups in the usual algebraic sense.
- Classical Hopf algebras. In the special case when [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,s,I) }[/math] is the category of vector spaces over a given field [math]\displaystyle{ K }[/math], the Hopf algebras in [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,s,I) }[/math] are exactly the classical Hopf algebras described above.
- Functional algebras on groups. The standard functional algebras [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal C}(G) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal E}(G) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal O}(G) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal P}(G) }[/math] (of continuous, smooth, holomorphic, regular functions) on groups are Hopf algebras in the category (Ste,[math]\displaystyle{ \odot }[/math]) of stereotype spaces,[27]
- Group algebras. The stereotype group algebras [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal C}^\star(G) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal E}^\star(G) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal O}^\star(G) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ {\mathcal P}^\star(G) }[/math] (of measures, distributions, analytic functionals and currents) on groups are Hopf algebras in the category (Ste,[math]\displaystyle{ \circledast }[/math]) of stereotype spaces.[27] These Hopf algebras are used in the duality theories for non-commutative groups.[28]
See also
- Quasitriangular Hopf algebra
- Algebra/set analogy
- Representation theory of Hopf algebras
- Ribbon Hopf algebra
- Superalgebra
- Supergroup
- Anyonic Lie algebra
- Sweedler's Hopf algebra
- Hopf algebra of permutations
- Milnor–Moore theorem
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ The finiteness of G implies that KG ⊗ KG is naturally isomorphic to KGxG. This is used in the above formula for the comultiplication. For infinite groups G, KG ⊗ KG is a proper subset of KGxG. In this case the space of functions with finite support can be endowed with a Hopf algebra structure.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Here [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha_{H,H,H}:(H\otimes H)\otimes H\to H\otimes (H\otimes H) }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda_H:I\otimes H\to H }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_H:H\otimes I\to H }[/math] are the natural transformations of associativity, and of the left and the right units in the monoidal category [math]\displaystyle{ (C,\otimes,I,\alpha,\lambda,\rho,\gamma) }[/math].
Citations
- ↑ Haldane, F. D. M.; Ha, Z. N. C.; Talstra, J. C.; Bernard, D.; Pasquier, V. (1992). "Yangian symmetry of integrable quantum chains with long-range interactions and a new description of states in conformal field theory". Physical Review Letters 69 (14): 2021–2025. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.69.2021. PMID 10046379. Bibcode: 1992PhRvL..69.2021H.
- ↑ Plefka, J.; Spill, F.; Torrielli, A. (2006). "Hopf algebra structure of the AdS/CFT S-matrix". Physical Review D 74 (6): 066008. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.74.066008. Bibcode: 2006PhRvD..74f6008P.
- ↑ Abreu, Samuel; Britto, Ruth; Duhr, Claude; Gardi, Einan (2017-12-01). "Diagrammatic Hopf algebra of cut Feynman integrals: the one-loop case" (in en). Journal of High Energy Physics 2017 (12): 90. doi:10.1007/jhep12(2017)090. ISSN 1029-8479. Bibcode: 2017JHEP...12..090A.
- ↑ Underwood 2011, p. 55
- ↑ Underwood 2011, p. 62
- ↑ Dăscălescu, Năstăsescu & Raianu (2001). "Prop. 4.2.6". Hopf Algebra: An Introduction. p. 153. https://books.google.com/books?id=pBJ6sbPHA0IC&pg=PA153&dq=%22is+an+antimorphism+of+algebras%22.
- ↑ Dăscălescu, Năstăsescu & Raianu (2001). "Remarks 4.2.3". Hopf Algebra: An Introduction. p. 151. https://books.google.com/books?id=pBJ6sbPHA0IC&pg=PA151&dq=%22the+antipode+is+unique%22.
- ↑ Quantum groups lecture notes
- ↑ Nichols, Warren D. (1989), "A Hopf algebra freeness theorem", American Journal of Mathematics 111 (2): 381–385, doi:10.2307/2374514
- ↑ Montgomery 1993, p. 36
- ↑ Underwood 2011, p. 82
- ↑ Hazewinkel, Michiel; Gubareni, Nadezhda Mikhaĭlovna; Kirichenko, Vladimir V. (2010). Algebras, Rings, and Modules: Lie Algebras and Hopf Algebras. Mathematical surveys and monographs. 168. American Mathematical Society. p. 149. ISBN 978-0-8218-7549-0.
- ↑ Mikhalev, Aleksandr Vasilʹevich; Pilz, Günter, eds (2002). The Concise Handbook of Algebra. Springer-Verlag. p. 307, C.42. ISBN 978-0792370727.
- ↑ Abe, Eiichi (2004). Hopf Algebras. Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics. 74. Cambridge University Press. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-521-60489-5.
- ↑ Hochschild, G (1965), Structure of Lie groups, Holden-Day, pp. 14–32
- ↑ See Hazewinkel, Michiel (January 2003). "Symmetric Functions, Noncommutative Symmetric Functions, and Quasisymmetric Functions". Acta Applicandae Mathematicae 75 (1–3): 55–83. doi:10.1023/A:1022323609001.
- ↑ Hopf, Heinz (1941). "Über die Topologie der Gruppen–Mannigfaltigkeiten und ihre Verallgemeinerungen" (in de). Ann. of Math.. 2 42 (1): 22–52. doi:10.2307/1968985.
- ↑ Underwood 2011, p. 57
- ↑ Underwood 2011, p. 36
- ↑ Montgomery 1993, p. 203
- ↑ Van Daele, Alfons (1994). "Multiplier Hopf algebras". Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 342 (2): 917–932. doi:10.1090/S0002-9947-1994-1220906-5. https://www.ams.org/tran/1994-342-02/S0002-9947-1994-1220906-5/S0002-9947-1994-1220906-5.pdf.
- ↑ Böhm, Gabriella; Nill, Florian; Szlachanyi, Kornel (1999). "Weak Hopf Algebras". J. Algebra 221 (2): 385–438. doi:10.1006/jabr.1999.7984.
- ↑ Nikshych, Dmitri; Vainerman, Leonid (2002). "Finite groupoids and their applications". in Montgomery, S.; Schneider, H.-J.. New directions in Hopf algebras. 43. Cambridge: M.S.R.I. Publications. pp. 211–262. ISBN 9780521815123. https://books.google.com/books?id=I3IK9U5Co_0C&pg=PA211.
- ↑ Group = Hopf algebra « Secret Blogging Seminar, Group objects and Hopf algebras, video of Simon Willerton.
- ↑ Turaev & Virelizier 2017, 6.2.
- ↑ Akbarov 2009, p. 482.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Akbarov 2003, 10.3.
- ↑ Akbarov 2009.
References
- Dăscălescu, Sorin; Năstăsescu, Constantin; Raianu, Șerban (2001), Hopf Algebras. An introduction, Pure and Applied Mathematics, 235 (1st ed.), Marcel Dekker, ISBN 978-0-8247-0481-0.
- Cartier, Pierre (2007), "A Primer of Hopf Algebras", in Cartier, P.; Moussa, P.; Julia, B. et al., Frontiers in Number Theory, Physics, and Geometry, II, Berlin: Springer, pp. 537–615, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-30308-4_12, ISBN 978-3-540-30307-7
- Fuchs, Jürgen (1992), Affine Lie algebras and quantum groups. An introduction with applications in conformal field theory, Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-48412-1
- Heinz Hopf, Uber die Topologie der Gruppen-Mannigfaltigkeiten und ihrer Verallgemeinerungen, Annals of Mathematics 42 (1941), 22–52. Reprinted in Selecta Heinz Hopf, pp. 119–151, Springer, Berlin (1964). MR4784, Zbl 0025.09303
- Montgomery, Susan (1993), Hopf algebras and their actions on rings, Regional Conference Series in Mathematics, 82, Providence, Rhode Island: American Mathematical Society, ISBN 978-0-8218-0738-5
- Street, Ross (2007), Quantum groups: A Path To Current Algebra, Australian Mathematical Society Lecture Series, 19, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-69524-4.
- Sweedler, Moss E. (1969), Hopf algebras, Mathematics Lecture Note Series, W. A. Benjamin, Inc., New York, ISBN 9780805392548, https://books.google.com/books?id=8FnvAAAAMAAJ
- Underwood, Robert G. (2011), An introduction to Hopf algebras, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-72765-3
- Turaev, Vladimir; Virelizier, Alexis (2017), Monoidal Categories and Topological Field Theory, Progress in Mathematics, 322, Springer, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-49834-8, ISBN 978-3-319-49833-1, https://proxylibrary.hse.ru:2084/book/10.1007/978-3-319-49834-8.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2003). "Pontryagin duality in the theory of topological vector spaces and in topological algebra". Journal of Mathematical Sciences 113 (2): 179–349. doi:10.1023/A:1020929201133.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2009). "Holomorphic functions of exponential type and duality for Stein groups with algebraic connected component of identity". Journal of Mathematical Sciences 162 (4): 459–586. doi:10.1007/s10958-009-9646-1.
 |