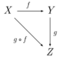Stereotype algebra
In functional analysis and related areas of mathematics, stereotype algebras are topological algebras defined as stereotype spaces with a (unital and associative) multiplication satisfying the condition of separate uniform continuity on compact sets.
Definition
There are two equivalent ways to define stereotype algebra.
- An abstract definition: a (projective[1]) stereotype algebra[2][3] is a monoid in the monoidal category (Ste,,) of stereotype spaces with the tensor product .
- An analytic definition: let be a stereotype space (over the field of complex numbers[4]) and suppose it is endowed with a bilinear operation that turns into a unital and associative algebra (over the field ). Then is called a (projective) stereotype algebra[2][5][6][7] if the multiplication is a continuous bilinear map in the stereotype sense, i.e. if for each compact set and for each neighbourhood of zero there is a neighbourhood of zero such that [8]
A morphism of stereotype algebras and is a continuous unital[9] homomorphism .
Stereotype algebras form a subclass in the class of separately continuous topological algebras.
Examples
- 1. All Fréchet algebras are stereotype. In particular, all Banach algebras are stereotype.[10]
- 2. For each stereotype space the stereotype space of operators , , is a stereotype algebra with respect to the operation of composition.[10]
- 3. The main examples of functional algebras[10] in Analysis and Geometry are stereotype algebras:
- the algebra of continuous functions on a paracompact locally compact topological space with the topology of uniform convergence on compact sets ,
- the algebra of smooth functions on a smooth manifold with the topology of uniform convergence with all derivatives on compact sets ,
- the algebra of holomorphic functions on a Stein manifold with the topology of uniform convergence on compact sets ,
- the algebra of polynomials (regular functions) on an affine algebraic variety with the strongest locally convex topology.
- 4. Stereotype group algebras. In the case when the space in the previous examples has a structure of a topological group, the dual stereotype spaces to the functional algebras on are stereotype algebras with respect to the operation of convolution:[10]
- the algebra of Radon measures with compact support on a locally compact group ,[11]
- the algebra of distributions with compact support on a real Lie group ,
- the algebra of holomorphic functionals on a Stein group[12] ,
- the algebra of currents on an affine algebraic group .
- In contrast to the other models of group algebras in functional analysis, the stereotype group algebras possess the universal property[13][14] and the structure of Hopf algebra[15].
Stereotype modules
A stereotype space is called a left stereotype module over a stereotype algebra , if a bilinear operation is defined that turns into a left module over , and this operation is a continuous bilinear map in the stereotype sense: for each compact set and for each neighbourhood of zero there is a neighbourhood of zero such that
and at the same time for each compact set and for each neighbourhood of zero there is a neighbourhood of zero such that
The notion of a right stereotype module over a stereotype algebra is defined by analogy.
The theory of stereotype algebras allows to simplify the formulations in the theory of topological algebras and to bring this field closer to abstract algebra. The following two results (which do not hold for general jointly or separately continuous algebras) are typical illustrations.[16]
Theorem.[17] A stereotype space with a structure of left (right) module over a stereotype algebra is a stereotype module over if and only if the operation of multiplication (respectively, ) defines a continuous map (a representation) .[18]
Theorem.[19] For each stereotype algebra the categories Ste and Ste of left and right stereotype modules over are enriched categories over the monoidal category (Ste,,) of stereotype spaces.
Applications
The notion of stereotype algebra is used in the generalizations[20] of the Pontryagin duality theory to the classes of non-commutative groups based on the notion of envelope: the holomorphic, the smooth and the continuous envelopes of stereotype algebras lead respectively to the constructions of the holomorphic, the smooth and the continuous dualities in big geometric disciplines – complex geometry, differential geometry, and topology – for certain classes of (not necessarily commutative) topological groups considered in these disciplines (affine algebraic groups, and some classes of Lie groups and Moore groups).[21][22][20][23]
See also
- Stereotype space
- Topological algebra
- Fréchet algebra
- Banach algebra
- C*-algebra
- Operator algebra
Notes
- ↑ There is another notion, an injective stereotype algebra, which is defined as a monoid in the monoidal category (Ste,,) of stereotype spaces with the dual tensor product, . The class of these algebras is much narrower.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Akbarov 2003, p. 271.
- ↑ Akbarov 2005.
- ↑ ...or the field of real numbers
- ↑ Akbarov 2009, p. 483.
- ↑ Akbarov 2016, p. 147.
- ↑ Akbarov 2017, p. 594. sfn error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFAkbarov2017 (help)
- ↑ The requirement on in the analytic definition of stereotype algebra can be equivalently expressed as follows: for each compact set and for each net tending to zero in , the nets and tend to zero in uniformly on :
- ↑ A homomorphism is said to be unital if it preserves unit: .
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Akbarov 2003, p. 272.
- ↑ If is an infinite locally compact group then the algebra of measures on is not a Fréchet algebra. In the case when is compact, is a Smith space. If is -compact, then is a Brauner space.
- ↑ A Stein group is a complex Lie group which is a Stein manifold.
- ↑ I.e. the homomorphisms of stereotype algebras are in one-to-one correspondence with the continuous representations of the group , and the same is true for the algebras , and with the smooth, holomorphic and polynomial representations of the corresponding groups.
- ↑ Akbarov 2003, p. 275.
- ↑ Akbarov 2009, p. 507.
- ↑ Other illustrations are the already mentioned universality property for the stereotype group algebrasAkbarov 2003, p. 275 and the structure of Hopf algebra on themAkbarov 2009, p. 507.
- ↑ Akbarov 2003, p. 283.
- ↑ Here is the stereotype space of operators .
- ↑ Akbarov 2003, p. 289.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Akbarov 2017. sfn error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFAkbarov2017 (help)
- ↑ Akbarov 2009.
- ↑ Akbarov 2016.
- ↑ Kuznetsova 2013.
References
- Akbarov, S.S. (2022). Stereotype spaces and algebras. De Gruyter Expositions in Mathematics. De Gruyter. ISBN 9783110780918. https://www.degruyter.com/document/isbn/9783110780918/html.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2003). "Pontryagin duality in the theory of topological vector spaces and in topological algebra". Journal of Mathematical Sciences 113 (2): 179–349. doi:10.1023/A:1020929201133.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2005). "Pontryagin duality and topological algebras". Banach Center Publications 67: 55–71. doi:10.4064/bc67-0-5. http://webmail.impan.gov.pl/cgi-bin/bc/pdf?bc67-0-05.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2009). "Holomorphic functions of exponential type and duality for Stein groups with algebraic connected component of identity". Journal of Mathematical Sciences 162 (4): 459–586. doi:10.1007/s10958-009-9646-1.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2016). "Envelopes and refinements in categories, with applications to functional analysis". Dissertationes Mathematicae 513: 1–188. doi:10.4064/dm702-12-2015. https://www.impan.pl/en/publishing-house/journals-and-series/dissertationes-mathematicae/all/513.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2017). "Continuous and smooth envelopes of topological algebras. Part 1". Journal of Mathematical Sciences 227 (5): 531–668. doi:10.1007/s10958-017-3599-6.
- Akbarov, S.S. (2017). "Continuous and smooth envelopes of topological algebras. Part 2". Journal of Mathematical Sciences 227 (6): 669–789. doi:10.1007/s10958-017-3600-4.
- Kuznetsova, Y. (2013). "A duality for Moore groups". Journal of Operator Theory 69 (2): 101–130. doi:10.7900/jot.2011mar17.1920. Bibcode: 2009arXiv0907.1409K.