Astronomy:47 Capricorni
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Capricornus |
| Right ascension | 21h 46m 16.26887s[2] |
| Declination | −09° 16′ 33.3799″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.00[3] (5.90 - 6.14)[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | giant |
| Spectral type | M2III[5] |
| B−V color index | 1.629±0.010[3] |
| Variable type | SRb[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +19.80±0.89[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +18.731[2] mas/yr Dec.: +8.387[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.7933 ± 0.2052[2] mas |
| Distance | 1,170 ± 90 ly (360 ± 30 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.76[3] |
| Details | |
| Radius | 102+11 −10[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,940±162[2] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,784+188 −186[2] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
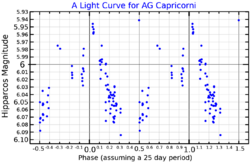
47 Capricorni is a variable star located around 1,170[2] light years from the Sun in the southern constellation Capricornus,[7] near the northern border with Aquarius. It has the variable star designation of AG Capricorni and a Bayer designation of c2 Capricorni;[8] 47 Capricorni is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a dim, red-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude that varies between 5.90 and 6.14. The star is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +20 km/s.[6]
This is an aging red giant star with a stellar classification of M2III.[5] It is a semiregular variable star of subtype SRb with a period of 30.592 days and a maximum brightness of 5.9 magnitude.[4] With the supply of hydrogen at its core exhausted, the star has expanded to around 102[2] times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 1,940[2] times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,784 K.[2]
References
- ↑ "Hipparcos Tools Interactive Data Access". ESA. https://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/hipparcos/interactive-data-access.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999). "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars". Michigan Spectral Survey 5. Bibcode: 1999MSS...C05....0H.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Famaey, B. et al. (2009). "Spectroscopic binaries among Hipparcos M giants,. I. Data, orbits, and intrinsic variations". Astronomy and Astrophysics 498 (2): 627. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810698. Bibcode: 2009A&A...498..627F.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "47 Cap". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=47+Cap.
- ↑ Kostjuk, N. D. (2002). "HD 207005". HD-DM-GC-HR-HIP-Bayer-Flamsteed Cross Index. Institute of Astronomy of Russian Academy of Sciences; CDS. http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR-5?-out.add=.&-source=IV/27A/catalog&recno=3684. IV/27A
 |