Astronomy:GU Piscium
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation Pisces
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Pisces |
| Right ascension | 01h 12m 35.0519s[1] |
| Declination | 17° 03′ 55.5712″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 12.96 - 13.24 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −1.5±0.5[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 96.642±0.127[1] mas/yr Dec.: −100.704±0.107[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 21.0019 ± 0.0721[1] mas |
| Distance | 155.3 ± 0.5 ly (47.6 ± 0.2 pc) |
| Details | |
| Radius | 0.54±0.04[4] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.75±0.07[4] cgs |
| Temperature | 3250±32[4] K |
| Metallicity | −0.25±0.19[4] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 23.7±2.2[3] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
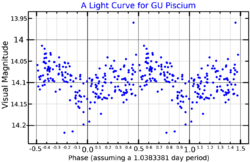
GU Piscium is a star in the constellation Pisces.[5] An RS Canum Venaticorum variable, it ranges from magnitude 12.96 to 13.24 over 1.04 days.[6] It is 48 Parsecs (155 light-years) distant from Earth.[7] This star is also believed to be a member of the AB Doradus moving group with a membership probability of 96.9%.[8]
Planetary system
In 2014, it was found to have a gas giant planet—GU Piscium b—orbiting it.[7]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 9–13 MJ MJ | 2000 | 163,000 | — | — | — |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Riaz, Basmah; Gizis, John E.; Harvin, James (2006). "Identification of New M Dwarfs in the Solar Neighborhood". The Astronomical Journal 132 (2): 866–872. doi:10.1086/505632. Bibcode: 2006AJ....132..866R.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Malo, Lison et al. (2014). "BANYAN. III. Radial Velocity, Rotation, and X-Ray Emission of Low-mass Star Candidates in Nearby Young Kinematic Groups". The Astrophysical Journal 788 (1): 81. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/788/1/81. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...788...81M.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Malo, Lison et al. (2014). "BANYAN. IV. Fundamental Parameters of Low-mass Star Candidates in Nearby Young Stellar Kinematic Groups—Isochronal Age Determination using Magnetic Evolutionary Models". The Astrophysical Journal 792 (1): 37. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/792/1/37. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...792...37M.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "V* GU Psc". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=V%2A+GU+Psc.
- ↑ BSJ (11 November 2011). "GU Piscium". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=36259.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Naud, Marie-Eve et al. (2014). "Discovery of a Wide Planetary-Mass Companion to the Young M3 Star Gu Psc". The Astrophysical Journal 787 (1): 5. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/787/1/5. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...787....5N.
- ↑ Malo, Lison et al. (2013). "Bayesian Analysis to Identify New Star Candidates in Nearby Young Stellar Kinematic Groups". The Astrophysical Journal 762 (2): 88. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/762/2/88. Bibcode: 2013ApJ...762...88M.
 |