Biology:Ascending colon
| Ascending colon | |
|---|---|
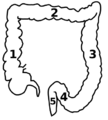
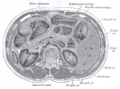
 Drawing of colon seen from front (ascending colon coloured blue) | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Midgut |
| Artery | Right colic artery |
| Vein | Right colic vein |
| Nerve | Celiac ganglia, vagus[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Colon ascendens |
| Anatomical terminology | |
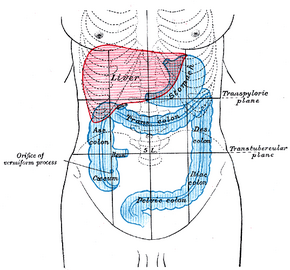
In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the ascending colon is the part of the colon located between the cecum and the transverse colon.
Characteristics and structure
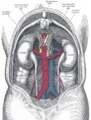
The ascending colon is smaller in calibre than the cecum from where it starts. It passes upward, opposite the colic valve, to the under surface of the right lobe of the liver, on the right of the gall-bladder, where it is lodged in a shallow depression, the colic impression; here it bends abruptly forward and to the left, forming the right colic flexure (hepatic) where it becomes the transverse colon.
It is retained in contact with the posterior wall of the abdomen by the peritoneum, which covers its anterior surface and sides, its posterior surface being connected by loose areolar tissue with the iliacus, quadratus lumborum, aponeurotic origin of transversus abdominis, and with the front of the lower and lateral part of the right kidney.
Sometimes the peritoneum completely invests it and forms a distinct but narrow mesocolon.
It is in relation, in front, with the convolutions of the ileum and the abdominal walls.
Parasympathetic innervation to the ascending colon is supplied by the vagus nerve. Sympathetic innervation is supplied by the thoracic splanchnic nerves.
Location
The ascending colon is on the right side of the body (barring any malformations). The term right colon is hypernymous to ascending colon in precise use; many casual mentions of the right colon chiefly concern the ascending colon.
Additional images
Inner diameters of different sections of the large intestine, with ascending colon (at left) measuring on average 6.6 cm (range 6.0-7.0 cm).[2]
1: Ascending colon
2: Transverse colon
3: Descending colon
4: Sigmoid colon
5: Rectum
See also
- Descending colon
References
- ↑ Nosek, Thomas M.. "Section 6/6ch2/s6ch2_30". Essentials of Human Physiology. http://humanphysiology.tuars.com/program/section6/6ch2/s6ch2_30.htm.
- ↑ "Deficient Pms2, ERCC1, Ku86, CcOI in field defects during progression to colon cancer". J Vis Exp (41). 2010. doi:10.3791/1931. PMID 20689513.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 37:06-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The large intestine."
- largeintestine at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (cecuminside)
 |