Astronomy:MZ Puppis
From HandWiki
Short description: Red supergiant star in the constellation of Puppis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Puppis |
| Right ascension | 08h 04m 16.19s[2] |
| Declination | −32° 40′ 29.4″[2] |
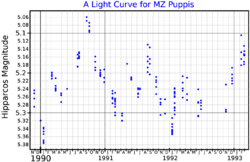
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.20 - 5.44[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Red supergiant |
| Spectral type | M1Iab-Ib[4] |
| Variable type | LC?[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +35.90[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −5.736[2] mas/yr Dec.: +6.830[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.8126 ± 0.1013[2] mas |
| Distance | approx. 4,000 ly (approx. 1,200 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.8[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 14[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 400[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 26,550 - 28,580[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | −0.92[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,745±170[8] K |
| Age | 25[10] Myr |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
MZ Puppis is a red supergiant star in the constellation of Puppis. It has a radius of 400 R☉.[8]
References
- ↑ "Hipparcos Tools Interactive Data Access". ESA. https://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/hipparcos/interactive-data-access.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1: B/gcvs. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989). "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 71: 245. doi:10.1086/191373. Bibcode: 1989ApJS...71..245K.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Melnik, A. M.; Dambis, A. K. (2020). "Distance scale for high-luminosity stars in OB associations and in field with Gaia DR2. Spurious systematic motions". Astrophysics and Space Science 365 (7): 112. doi:10.1007/s10509-020-03827-0. Bibcode: 2020Ap&SS.365..112M.
- ↑ Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3". Astronomy & Astrophysics 657: A7. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202142146. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2022A&A...657A...7K.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Messineo, M.; Brown, A. G. A. (2019). "A Catalog of Known Galactic K-M Stars of Class I Candidate Red Supergiants in Gaia DR2". The Astronomical Journal 158 (1): 20. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab1cbd. Bibcode: 2019AJ....158...20M.
- ↑ Stassun, Keivan G. et al. (September 2018). "The TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List". The Astronomical Journal 156 (3): 102. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aad050. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2018AJ....156..102S.
- ↑ Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (January 2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 410 (1): 190–200. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T.
 |