Astronomy:MX Puppis
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation Puppis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Puppis |
| Right ascension | 08h 13m 29.51720s[1] |
| Declination | −35° 53′ 58.2662″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.60 - 4.92[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B1.5 IVe[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.98[4] |
| B−V color index | −0.11[4] |
| Variable type | γ Cas[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +35.00[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −7.30[1] mas/yr Dec.: +9.75[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.51 ± 0.16[1] mas |
| Distance | 930 ± 40 ly (280 ± 10 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −2.97[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 10.1[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 6.5[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 28,840[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.41[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 32,870[10] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 145[10] km/s |
| Age | 22.5[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
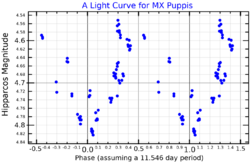
MX Puppis (MX Pup) is a class B1.5IV[3] (blue subgiant) star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude varies irregularly between magnitude 4.6 and 4.9 and it is classified as a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable.[2] It is approximately 930 light years away based on parallax.[1]
MX Puppis was first found to be a variable star by Alan William James Cousins in 1959.[11] It was given its variable star designation in 1972.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Slettebak, A. (1982). "Spectral types and rotational velocities of the brighter Be stars and A-F type shell stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 50: 55. doi:10.1086/190820. Bibcode: 1982ApJS...50...55S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 2237. Bibcode: 2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 410 (1): 190–200. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.410..190T. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Balona, L. A.; Ozuyar, D. (2020). "Pulsation among TESS a and B stars and the Maia variables". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 493 (4): 5871. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa670. Bibcode: 2020MNRAS.493.5871B.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Zorec, J.; Frémat, Y.; Domiciano De Souza, A.; Royer, F.; Cidale, L.; Hubert, A.-M.; Semaan, T.; Martayan, C. et al. (2016). "Critical study of the distribution of rotational velocities of Be stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics 595: A132. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628760. Bibcode: 2016A&A...595A.132Z.
- ↑ Cousins, A. W. J. (1959). "Measures of Bright Southern Stars on the UBV System". Monthly Notes of the Astron. Soc. Southern Africa 18: 47. Bibcode: 1959MNSSA..18...47C. https://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/pdf/1959MNSSA..18...47C. Retrieved 10 October 2024.
- ↑ Kukarkin, B. V.; Kholopov, P. N.; Kukarkina, N. P.; Perova, N. B. (September 1972). "58th Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 717: 1. Bibcode: 1972IBVS..717....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/0701/0717.pdf. Retrieved 10 October 2024.
- ↑ Hubert, A. M.; Floquet, M. (July 1998). "Investigation of the variability of bright Be stars using Hipparcos photometry". Astronomy and Astrophysics 335: 565–572. Bibcode: 1998A&A...335..565H. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1998A&A...335..565H. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
 |