Astronomy:OU Puppis
From HandWiki
Short description: Star in the constellation Puppis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Puppis |
| Right ascension | 07h 13m 13.35060s[1] |
| Declination | −45° 10′ 57.8554″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.87[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0pSi[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.07[4] |
| B−V color index | −0.03[4] |
| Variable type | α2 CVn[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +4.30[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −25.166[1] mas/yr Dec.: −87.380[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 17.3622 ± 0.0768[1] mas |
| Distance | 187.9 ± 0.8 ly (57.6 ± 0.3 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 1.11[2] |
| Details[1] | |
| Mass | 2.215 M☉ |
| Radius | 2.232 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 37.05 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.26[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 9,568 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.67 dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 34[7] km/s |
| Age | 382 Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
OU Puppis (OU Pup) is a chemically peculiar class A0 (white main-sequence) star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is about 4.9 and it is approximately 188 light-years away based on parallax.
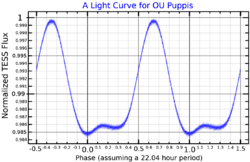
It is an α2 CVn variable, ranging from 4.93 to 4.86 magnitudes with a period of 0.92 of a day.[5] Its spectrum has unusually strong lines of silicon, chromium, and strontium, making it an Ap star.[9]
Unlike the majority of star pairs, the number attached to the Bayer designation 'L' is generally a subscript: L1. Its better-known companion L2 Puppis is similarly represented.[10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ Hoffleit, D.; Warren, W. H. (1995). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Hoffleit+, 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: V/50. Originally Published in: 1964BS....C......0H 5050. Bibcode: 1995yCat.5050....0H.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mermilliod, J. C. (2006). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Homogeneous Means in the UBV System (Mermilliod 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: II/168. Originally Published in: Institut d'Astronomie 2168. Bibcode: 2006yCat.2168....0M.Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ↑ Wilson, R. E. (1953). "General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities". Carnegie Institute Washington D.C. Publication (Carnegie Institution for Science). ISBN 9780598216885. Bibcode: 1953GCRV..C......0W.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015). "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal 804 (2): 146. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804..146D. Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ Renson, P.; Manfroid, J. (May 2009). "Catalogue of Ap, HgMn and Am stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 498 (3): 961–966. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810788. Bibcode: 2009A&A...498..961R. https://zenodo.org/record/890529.
- ↑ Robert Burnham (1978). Burnham's Celestial Handbook: An Observer's Guide to the Universe Beyond the Solar System. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-23673-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=PJzIt3SIlkUC.
 |