Medicine:Periorbital cellulitis
| Periorbital cellulitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Preseptal cellulitis |
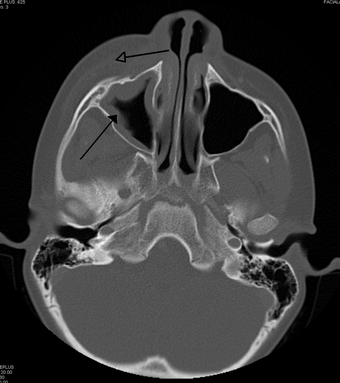 | |
| Periorbital cellulitis caused by a dental infection (also causing maxillary sinusitis) | |
Periorbital cellulitis, or preseptal cellulitis, is an inflammation and infection of the eyelid and portions of skin around the eye anterior to the orbital septum.[1] It may be caused by breaks in the skin around the eye, and subsequent spread to the eyelid; infection of the sinuses around the nose (sinusitis); or from spread of an infection elsewhere through the blood.
Signs and symptoms
Periorbital cellulitis must be differentiated from orbital cellulitis, which is an emergency and requires intravenous (IV) antibiotics. In contrast to orbital cellulitis, patients with periorbital cellulitis do not have bulging of the eye (proptosis), limited eye movement (ophthalmoplegia), pain on eye movement, or loss of vision. If any of these features is present, one must assume that the patient has orbital cellulitis and begin treatment with IV antibiotics. CT scan may be done to delineate the extension of the infection.
Affected individuals may experience: swelling, redness, discharge, pain, shut eye, conjunctival infection, fever (mild), slightly blurred vision, teary eyes, and some reduction in vision.
Typical signs include periorbital erythema, induration, tenderness and warmth.[2]
Causes
Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, other streptococci, and anaerobes are the most common causes, depending on the origin of the infection.[3]
The advent of the Haemophilus influenzae vaccine has dramatically decreased the incidence.[4]
Diagnosis
Tests include blood work (CBC) to rule out infectious cause. Also perform a CT scan, x ray of the anterior skull to view the sinuses, MRI scan and finally a soft tissue ultrasound of the orbital region.
Treatment
Antibiotics are aimed at gram positive bacteria. Medical attention should be sought if symptoms persist beyond 2–3 days.
There is inadequate evidence to draw conclusions about the adjunctive corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of periorbital cellulitis. More research is needed to inform decision making.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Orbital and periorbital cellulitis". HealthAtoZ.com. East Windsor, NJ: OptumHealth. http://www.healthatoz.com/healthatoz/Atoz/common/standard/transform.jsp?requestURI=/healthatoz/Atoz/ency/orbital_and_periorbital_cellulitis.jsp.
- ↑ "Periorbital versus orbital cellulitis". The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 21 (12): 1157–1158. December 2002. doi:10.1097/00006454-200212000-00014. PMID 12488668.
- ↑ "Paediatric pre- and post-septal peri-orbital infections are different diseases. A retrospective review of 262 cases". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 72 (3): 377–383. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.11.013. PMID 18191234.
- ↑ "Preseptal and orbital cellulitis in childhood. A changing microbiologic spectrum". Ophthalmology 105 (10): 1902–5; discussion 1905–6. October 1998. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(98)91038-7. PMID 9787362.
- ↑ "Corticosteroids for periorbital and orbital cellulitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021 (4): CD013535. April 2021. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013535.pub2. PMID 33908631.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |

