Astronomy:R Serpentis
From HandWiki
Short description: Variable star in the constellation Serpens
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Serpens |
| Right ascension | 15h 50m 41.73245s[2] |
| Declination | +15° 08′ 01.0810″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.70[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M5-8e[4] |
| B−V color index | 1.500±0.510[3] |
| Variable type | Mira[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 23.8±0.8[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +2.387[2] mas/yr Dec.: −36.699[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.5110 ± 0.2966[2] mas |
| Distance | 930 ± 80 ly (280 ± 20 pc) |
| Details | |
| Radius | ~380[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,704.70[8] L☉ |
| Temperature | 2,780±80[9] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
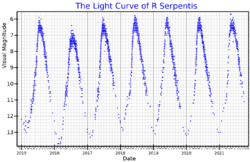
R Serpentis is a Mira variable type star in the equatorial constellation of Serpens. It ranges between apparent magnitude 5.16 and 14.4, and spectral types M5e to M8e, over a period of 356.41 days.[5][11] The variability of this star was discovered in 1826 by Karl Ludwig Harding.[12]
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ Keenan, Philip C. et al. (1974), "Revised Catalog of Spectra of Mira Variables of Types ME and Se", Astrophysical Journal Supplement 28: 271, doi:10.1086/190318, Bibcode: 1974ApJS...28..271K.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Samus', N. N; Kazarovets, E. V; Durlevich, O. V; Kireeva, N. N; Pastukhova, E. N (2017), "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1", Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006), "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system", Astronomy Letters 32 (11): 759–771, doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065, Bibcode: 2006AstL...32..759G.
- ↑ Pasinetti Fracassini, L. E. et al. (February 2001), "Catalogue of Apparent Diameters and Absolute Radii of Stars (CADARS)", Astronomy and Astrophysics 367: 521–524, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000451, Bibcode: 2001A&A...367..521P.
- ↑ McDonald, I. et al. (2012), "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 427 (1): 343–357, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, Bibcode: 2012MNRAS.427..343M.
- ↑ Hofmann, K. -H. et al. (January 2002), "Observations of Mira stars with the IOTA/FLUOR interferometer and comparison with Mira star models", New Astronomy 7 (1): 9–20, doi:10.1016/S1384-1076(01)00085-9, Bibcode: 2002NewA....7....9H.
- ↑ "R Ser". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=R+Ser.
- ↑ Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "R Serpentis". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=34592. Retrieved 22 May 2014.
- ↑ Zsoldos, E. (1994). "Three Early Variable Star Catalogues". Journal for the History of Astronomy 25 (2): 92–98. doi:10.1177/002182869402500202. Bibcode: 1994JHA....25...92Z. http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/full/1994JHA....25...92Z.
 |