Biology:C21orf62
 Generic protein structure example |
C21orf62 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the C21orf62 gene.[2] C21orf62 is found on human chromosome 21, and it is thought to be expressed in tissues of the brain and reproductive organs.[3] Additionally, C21orf62 is highly expressed in ovarian surface epithelial cells during normal regulation, but is not expressed in cancerous ovarian surface epithelial cells.[3]
Gene
Common aliases of C21orf62 are C21orf120, PRED81, and B37.[2] C21orf62 is located on chromosome 21 in humans, and is specifically at the q22.11 position.[4] The C21orf62 gene is 4132 base pairs in length and contains five exons.[2]
mRNA
The mRNA sequence of C21orf62 in humans has one known isoform. This isoform is called uncharacterized protein C21orf62 isoform X1. This isoform is 458 base pairs, or 104 amino acids, in length, and it is significantly shorter than the most observed sequence of C21orf62 in humans. In addition to having an isoform, C21orf62 also has splice variants. All splice variants encode the same gene, but the differences in splice variant sequences occur in the 5' untranslated region of the mRNA sequence.[2]
Protein
General protein characteristics
The C21orf62 protein in humans has a sequence that is 219 amino acids in length.[5] The primary sequence of C21orf62 in humans has a molecular weight of 24.9 kDa and an isoelectric point of 8.[6][7] When it's cleavable signal peptide, which spans amino acids 1-19, is removed, it has a molecular weight of 22.8 kDa and an isoelectric point of 7.8.[6][7][8][9]
Protein composition
C21orf62 in humans has higher cysteine and lower valine concentrations than expected compared to other human proteins. This trend, as showed in Table 1, is the same for other mammals. It does not, however, occur in taxa other than mammalia.[10]
| Genus and Species | Common Name | Organism Clade | % Cysteine | Amino Acid Concentration of Cysteine Compared to Expected | % Valine | Amino Acid Concentration of Valine Compared to Expected | Other Amino Acids with High or Low Concentration Compared to Expected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | Mammalia | 4.6% | High | 3.2% | Low | - |
| Mus musculus | House Mouse | Mammalia | 4.3% | High | 3.5% | Low | Glutamic Acid (1.7%, low) |
| Canis lupus familiaris | Dog | Mammalia | 4.1% | High | 2.7% | Low | Leucine (14.2%, high) |
| Physeter catodon | Sperm Whale | Mammalia | 4.6% | High | 4.1% | Expected | Serine (11.9%, high) |
| Gallus gallus | Chicken | Aves | 3.1% | Expected | 6.7% | Expected | Alanine (2.2%, low)
Glycine (3.1%, low) Proline (1.8%, low) Phenylalanine (7.1%, high) Serine (12.4%, high) Threonine (9.8%) |
| Chelonia mydas | Green Sea Turtle | Reptilia | 3.6% | Expected | 5.8% | Expected | Alanine (1.8%, low)
Serine (11.2%, high) |
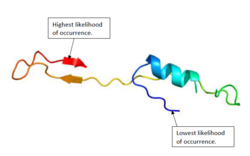
Protein structure
The protein structure of C21orf62 in humans consists of a combination of alpha helices and beta sheets.[11][12] Figure 1 shows a predicted structure of the protein.[1]
Post-translational modifications
C21orf62 has a myristoylation site from amino acid 26–31.[13] It has a sumoylation site from amino acid 132–135.[13][14] Additionally, it has a nuclear export signal from amino acid 98-104.[15]
Expression
Tissue expression
C21orf62 is expressed in human tissues of the brain and reproductive organs.[2]
Expression level
C21orf62 in humans is moderately expressed in the brain, kidneys, pancreas, prostate, testes, and ovaries.[2][16][17]
Regulation of expression
C21orf62 is expressed during blastocyst, fetus, and adult states of human development.[16] It is overexpressed during some tumor states, including pancreatic, gastrointestinal, germ cell, and glioma tumors.[16]
Function
The specific function of C21orf62 in humans is not yet well understood.[2]
Interacting proteins
C21orf62 is thought to potentially interact with nine other proteins.[18] These interactions are shown in Table 2, and they were found through text mining.
| Protein Full Name | Protein Name Symbol | Brief Protein Description[2] |
|---|---|---|
| BCL2 Interacting Protein Like | BNIPL | May function as a bridge molecule that promotes cell death. |
| Thymosin Beta 4, X-linked Pseudogene 4 | TMSB4XP4 | Potentially influences actin polymerization. |
| Synovial Sarcoma X Family Member 4 | SSX4 | May function as a repressor of transcription, and can be useful targets in cancer vaccine-based immunotherapy. |
| Crystallin Beta A2 | CRYBA2 | A major protein in vertebrate eyes that maintains lens transparency and reflective index. |
| Oral Cancer Overexpressed 1 | ORAOV1 | A gene that is frequently overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell cancer. |
| Oligodendrocyte Transcription Factor 1 | OLIG1 | May be expressed during the time from process extension through membrane maintenance in oligodendrocytes. |
| PAX3 and PAX7 Binding Protein 1 | GCFC1 (PAXBP1) | The encoded protein potentially binds to GC-rich DNA sequences. It is suggested that this gene is involved in the regulation of transcription. |
| Relaxin/Insulin Like Family Peptide Receptor 1 and 2 | RXFP1 and RXFP2 | Encoded protein is a receptor for the protein hormone relaxin that influences sperm motility and pregnancy. |
Clinical significance
C21orf62 over or under expression is linked to some types of cancerous cells and tumors.[3][16]
Homology
Paralogs
There are no known paralogs of C21orf62 in humans at this time.[2]
Orthologs
There are currently 193 organisms that are known to be orthologs of C21orf62.[2] The orthologs of C21orf62 are deuterostome animals in the clade Chordata.[2] Table 3 shows a range of C21orf62 orthologs, their NCBI accession numbers, sequence lengths, and sequence identity to the C21orf62 human protein. At this time, C21orf62 is not known to have any protostome or invertebrate orthologs.[2]
| Genus and Species | Common Name | Organism Clade | Estimated Date of Divergence from Humans (Millions of Years Ago)[19] | Accession Number[5] | Amino Acid Sequence Length[5] | Corrected Sequence Identity to Human Protein[20][21] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | mammalia | 0 | NP_001155967.2 | 219 | 100% |
| Mus musculus | House Mouse | mammalia | 90 | NP_083181.1 | 230 | 68.2% |
| Meleagris gallopavo | Wild Turkey | aves | 312 | XP_010721230.1 | 225 | 56.4% |
| Chelonia mydas | Green Sea Turtle | reptilia | 312 | XP_007063646.1 | 224 | 60.8% |
| Xenopus tropicalis | Western Clawed Frog | tetrapoda | 352 | NP_001004889.1 | 207 | 48.9% |
| Latimeria chalumnae | West Indian Ocean Coelacanth | sarcopterygii | 413 | XP_005993681.2 | 237 | 45.0% |
| Ictalurus punctatus | Channel Catfish | actinopterygii | 435 | XP_017326002.1 | 214 | 29.6% |
| Callorhinchus milii | Australian Ghostshark | condrichthyes | 473 | XP_007904174.1 | 222 | 40.4% |
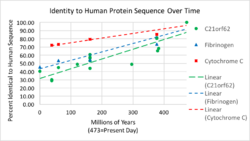
Evolution rate
C21orf62 has an evolution rate that is faster than cytochrome C and fibrinogen. Figure 2 shows the rate of evolution of the C21orf62 gene over the past 473 million years.
External links
- Human C21orf62 genome location and C21orf62 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kelley, Lawrence. "PHYRE2 Protein Fold Recognition Server". http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=help.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 "Home - Gene - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Home - GEO Profiles - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geoprofiles.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "C21orf62 Gene - GeneCards | CU062 Protein | CU062 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C21orf62#localization.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Home - Protein - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kramer, Jack (1990). "AASTATS". Biology Workbench. http://workbench.sdsc.edu/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Toldo, Luca. "PI Isoelectric Point Determination Program". Biology Workbench. http://workbench.sdsc.edu/.
- ↑ "PSORT II server - GenScript". http://www.genscript.com/tools/psort.
- ↑ Charpilloz, Jean-Luc Falcone & Christophe. "TERMINUS - Welcome to terminus" (in en). http://terminus.unige.ch.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Brendel, Volker (1992). "Statistical Analysis of PS". Biology Workbench. http://seqtool.sdsc.edu/. Retrieved 2017-02-06.
- ↑ Pearson, William R. (September 1998). "CHOFAS Analysis". Biology Workbench. http://seqtool.sdsc.edu/. Retrieved 2017-02-06.
- ↑ Pappas, Jr., Georgios J. (1974–1996). "PELE: Protein Structure Prediction". Biology Workbench. http://seqtool.sdsc.edu/. Retrieved 2017-02-06.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Motif Scan" (in en). http://myhits.isb-sib.ch/cgi-bin/motif_scan.
- ↑ The Cucko Workgroup (May 1, 2017). "GPS-SUMO 2.0 Online Service". http://sumosp.biocuckoo.org/online.php.
- ↑ "Analysis and prediction of leucine-rich nuclear export signals". Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 17 (6): 527–36. 2004. doi:10.1093/protein/gzh062. PMID 15314210.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 "Home - UniGene - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/unigene.
- ↑ "The Human Protein Atlas". http://www.proteinatlas.org.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "STRING: functional protein association networks". http://string-db.org/.
- ↑ "TimeTree :: The Timescale of Life". http://timetree.org/.
- ↑ "BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
- ↑ Meyers, E.W., Miller, W. (1989). "ALIGN". CABIOS 4: 11–17. http://seqtool.sdsc.edu/. Retrieved 2017-02-06.
 |

