Biology:Eikenella corrodens
| Eikenella | |
|---|---|
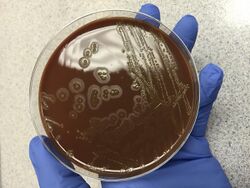
| |
| Eikenella corrodens on chocolate agar after 36 hours. Notice how colonies pit the agar, which is a distinct characteristic of this species. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Eikenella
|
| Species: | E. corrodens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eikenella corrodens (Eiken 1958) Jackson and Goodman 1972 (Approved Lists 1980)
| |
Eikenella corrodens is a Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacillus that can cause severe invasive disease in humans.[1] It was first identified by M. Eiken in 1958, who called it Bacteroides corrodens.[2] E. corrodens is a rare pericarditis associated pathogen.[3] It is a fastidious, slow growing, human commensal bacillus, capable of acting as an opportunistic pathogen and causing abscesses in several anatomical sites, including the liver, lung, spleen, and submandibular region.[4] E. corrodens could independently cause serious infection in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised hosts.[5]
Microbiology
Eikenella corrodens is a pleomorphic bacillus that sometimes appears coccobacillary and typically creates a depression (or "pit") in the agar on which it is growing. Only half produce the pitting of the agar considered characteristic.[citation needed]. It is a slow-growing, facultative anaerobe and a gram-negative bacillus.[6]
It grows in aerobic and anaerobic conditions, but requires an atmosphere enhanced by 3–10% carbon dioxide.[citation needed]
The colonies are small and greyish, they produce a greenish discoloration of the underlying agar, and smell faintly of bleach (hypochlorite).[citation needed]
They are oxidase-positive, catalase-negative, urease-negative, and indole-negative, and reduce nitrate to nitrite.[citation needed]
In 2006, Azakami et al reported that the periodontal pathogen E. corrodens has an ortholog of luxS, the gene required for quorum sensing (QS) signal molecule AI-2 synthesis and that E. corrodens can produce AI-2 signals for cell-to-cell communication. They additionally reported that AI-2 has a role in biofilm formation by E. corrodens.[7] Karim et al reported that this bacterium can produce AI-2 inactivation enzyme during its stationary phase.[8] Karim et al also reported that LuxS-mediated QS may facilitate the maturation and detachment of biofilm formation in E. corrodens, which can lead to progression of periodontal disease.[9]
Medical importance
Eikenella corrodens is a commensal of the human mouth and upper respiratory tract. It is an unusual cause of infection and when it is cultured, it is most usually found mixed with other organisms. Infections most commonly occur in patients with cancers of the head and neck,[10] but can occur in human bite infections, especially "reverse bite", "fight bite", or "clenched fist injuries".[11] It can also cause infections in insulin-dependent diabetics and intravenous drug users who lick their needles ("needle-licker's osteomyelitis").[12] It is one of the HACEK group of infections which are a cause of culture-negative endocarditis. In general, the HACEK organisms are responsible for approximately 3% of all cases of infective endocarditis (IE). IE due to E. corrodens is usually a result of poor oral hygiene and or periodontal infection. Manipulation of the gingival or oral mucosa for dental procedures also can predispose patients to infection since E. corrodens is a constituent of the human oral flora.[13] E. corrodens can coexists and is frequently detected with other pathogens including Staphylococcus and Streptococcus.[14]
Eikenella corrodens infections are typically indolent (the infection does not become clinically evident until a week or more after the injury). They also mimic anaerobic infection in being extremely foul-smelling.[citation needed]
Eikenella corrodens was mentioned in an episode of Forensic Files, in which a hotel employee punched a woman in the mouth, knocking out two of her teeth. Her tooth bacteria caused a major infection in the man's hand.[15]
Treatment
For accurate diagnoses, a high degree of suspicion is required in order to properly attribute an infection to Eikenella corrodens.[16] The identification of E. corrodens may be delayed because of its slow growth in the absence of CO
2.[17] E. corrodens can be treated with penicillins, cephalosporins, or tetracyclines, however due to the resistant nature of the bacteria ongoing and recurring symptoms can be expected despite rigorous and prolonged antibiotic treatment.[18] Submandibular and peritonsillar abscesses caused by E. corrodens can be treated by incision and drainage.[19] Earlier diagnosis and proper drainage surgery with effective antibiotics treatment may improve the prognosis.[20] First-choice drugs for E. corrodens infections should be third-generation cephems, carbapenems, or new quinolones.[21] It is innately resistant to macrolides (e.g., erythromycin), clindamycin, and metronidazole. It is susceptible to fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin) in vitro, but no clinical evidence is available to advocate their use in these infections.[22]
References
- ↑ Wei, Wei; Nie, Hu (December 2019). "Severe purulent pericarditis caused by invasive Eikenella corrodens: Case report and literature review" (in en). BMC Infectious Diseases 19 (1): 657. doi:10.1186/s12879-019-4256-0. ISSN 1471-2334. PMID 31337357.
- ↑ Eiken, M (1958). "Studies on an anaerobic, rodshaped, gram-negative microorganism: Bacteroides corrodens n. sp". Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica 43 (4): 404–16. doi:10.1111/j.1699-0463.1958.tb04677.x. PMID 13594456.
- ↑ Wei, Wei; Nie, Hu (2019-07-23). "Severe purulent pericarditis caused by invasive Eikenella corrodens: Case report and literature review". BMC Infectious Diseases 19 (1): 657. doi:10.1186/s12879-019-4256-0. ISSN 1471-2334. PMID 31337357.
- ↑ Lee, S-H (2003-11-01). "Inflammatory pseudotumour associated with chronic persistent Eikenella corrodens infection: a case report and brief review" (in en). Journal of Clinical Pathology 56 (11): 868–870. doi:10.1136/jcp.56.11.868. ISSN 0021-9746. PMID 14600136.
- ↑ Wei, Wei; Nie, Hu (2019-07-23). "Severe purulent pericarditis caused by invasive Eikenella corrodens: case report and literature review". BMC Infectious Diseases 19 (1): 657. doi:10.1186/s12879-019-4256-0. ISSN 1471-2334. PMID 31337357.
- ↑ Heymann, W. R.; Drezner, D. (August 1997). "Submandibular abscess caused by Eikenella corrodens". Cutis 60 (2): 101–102. ISSN 0011-4162. PMID 9283774. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9283774/.
- ↑ Azakami, Hiroyuki; Teramura, Izumi; Matsunaga, Tetsuro; Akimichi, Hiromi; Noiri, Yuichiro; Ebisu, Shigeyuki; Kato, Akio (2006). "Characterization of autoinducer 2 signal in Eikenella corrodens and its role in biofilm formation". Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 102 (2): 110–7. doi:10.1263/jbb.102.110. PMID 17027872.
- ↑ Karim, Mohammad Minnatul; Nagao, Ayako; Mansur, Fariha Jasin; Matsunaga, Tetsuro; Akakabe, Yoshihiko; Noiri, Yuichiro; Ebisu, Shigeyuki; Kato, Akio et al. (2013). "The Periodontopathogenic Bacterium Eikenella corrodens Produces an Autoinducer-2-Inactivating Enzyme". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 77 (5): 1080–5. doi:10.1271/bbb.130047. PMID 23649272.
- ↑ Karim, Mohammad Minnatul; Hisamoto, Tatsunori; Matsunaga, Tetsuro; Asahi, Yoko; Noiri, Yuichiro; Ebisu, Shigeyuki; Kato, Akio; Azakami, Hiroyuki (2013). "LuxS affects biofilm maturation and detachment of the periodontopathogenic bacterium Eikenella corrodens". Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 116 (3): 313–8. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.03.013. PMID 23639420.
- ↑ Sheng, W.-S.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Hung, C.-C.; Teng, L.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Luh, K.-T. (2001). "Clinical Features of Patients with Invasive Eikenella corrodens Infections and Microbiological Characteristics of the Causative Isolates". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 20 (4): 231–6. doi:10.1007/s100960100477. PMID 11399011.
- ↑ Goldstein, E. J. C. (1992). "Bite Wounds and Infection". Clinical Infectious Diseases 14 (3): 633–8. doi:10.1093/clinids/14.3.633. PMID 1562653.
- ↑ Swisher, Loice A.; Roberts, James R.; Glynn, Martin J. (1994). "Needle licker's osteomyelitis". The American Journal of Emergency Medicine 12 (3): 343–6. doi:10.1016/0735-6757(94)90156-2. PMID 8179747.
- ↑ Das, Md; Badley, Md, A.D.; Cockerill, Md, F.R.; Steckelberg, Md, J.M.; Wilson, Md, W. R. (1997). "Infective endocarditis caused by HACEK microorganisms.". Annual Review of Medicine 48: 25–33. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.48.1.25. PMID 9046942. http://www.educus.com/Journals/9046942?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1. Retrieved 2016-05-17.
- ↑ Udaka, Tsuyoshi; Hiraki, Nobuaki; Shiomori, Teruo; Miyamoto, Hiroshi; Fujimura, Takeyuki; Inaba, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Hideaki (April 2007). "Eikenella corrodens in head and neck infections". The Journal of Infection 54 (4): 343–348. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2005.06.015. ISSN 1532-2742. PMID 16962664. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16962664/.
- ↑ "Punch Line" on IMDb
- ↑ Knudsen, T. D.; Simko, E. J. (February 1995). "Eikenella corrodens: an unexpected pathogen causing a persistent peritonsillar abscess". Ear, Nose, & Throat Journal 74 (2): 114–117. doi:10.1177/014556139507400212. ISSN 0145-5613. PMID 7705229. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7705229/.
- ↑ Lee, S.-H.; Fang, Y.-C.; Luo, J.-P.; Kuo, H.-I.; Chen, H.-C. (November 2003). "Inflammatory pseudotumour associated with chronic persistent Eikenella corrodens infection: a case report and brief review". Journal of Clinical Pathology 56 (11): 868–870. doi:10.1136/jcp.56.11.868. ISSN 0021-9746. PMID 14600136.
- ↑ Knudsen, T. D.; Simko, E. J. (February 1995). "Eikenella corrodens: an unexpected pathogen causing a persistent peritonsillar abscess". Ear, Nose, & Throat Journal 74 (2): 114–117. doi:10.1177/014556139507400212. ISSN 0145-5613. PMID 7705229. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7705229/.
- ↑ Heymann, W. R.; Drezner, D. (August 1997). "Submandibular abscess caused by Eikenella corrodens". Cutis 60 (2): 101–102. ISSN 0011-4162. PMID 9283774. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9283774/.
- ↑ Wei, Wei; Nie, Hu (2019-07-23). "Severe purulent pericarditis caused by invasive Eikenella corrodens: case report and literature review". BMC Infectious Diseases 19 (1): 657. doi:10.1186/s12879-019-4256-0. ISSN 1471-2334. PMID 31337357.
- ↑ Udaka, Tsuyoshi; Hiraki, Nobuaki; Shiomori, Teruo; Miyamoto, Hiroshi; Fujimura, Takeyuki; Inaba, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Hideaki (April 2007). "Eikenella corrodens in head and neck infections". The Journal of Infection 54 (4): 343–348. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2005.06.015. ISSN 1532-2742. PMID 16962664. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16962664/.
- ↑ Sheng, W.-S.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Hung, C.-C.; Teng, L.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Luh, K.-T. (2001). "Clinical Features of Patients with Invasive Eikenella corrodens Infections and Microbiological Characteristics of the Causative Isolates". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 20 (4): 231–6. doi:10.1007/s100960100477. PMID 11399011.
External links
- Eikenella+corrodens at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Eikenella corrodens at the NCBI Taxonomy Browser
Wikidata ☰ Q3039103 entry
 |

