Biology:Fatty acid metabolism regulator protein FadR
| FadR C-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
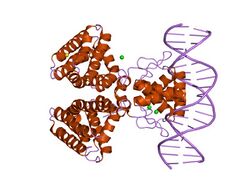 fadr, fatty acid responsive transcription factor from e. coli in complex with fadb operator | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | FadR_C | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07840 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0388 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR008920 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1h9g / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the fatty acid metabolism regulator protein FadR, is a bacterial transcription factor.
Bacteria regulate membrane fluidity by manipulating the relative levels of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids within the phospholipids of their membrane bilayers. In Escherichia coli, the transcription factor, FadR, functions as a switch that co-ordinately regulates the machinery required for fatty acid beta-oxidation and the expression of a key enzyme in fatty acid biosynthesis. This single [repressor controls the transcription of the whole fad regulon.[1] Binding of fadR is specifically inhibited by long chain fatty acyl-CoA compounds.
The crystal structure of FadR reveals a two domain dimeric molecule where the N-terminal winged-helix domain binds DNA, and the C-terminal domain binds acyl-CoA.[1] The binding of acyl-CoA to the C-terminal domain results in a conformational change that affects the DNA binding affinity of the N-terminal domain.[2]
FadR is a member of the GntR family of bacterial transcription regulators. The DNA-binding domain is well conserved for this family, whereas the C-terminal effector-binding domain is more variable, and is consequently used to define the GntR subfamilies.[3] The FadR group is the largest subgroup, and is characterised by an all-helical C-terminal domain composed of 6 to 7 alpha helices.[2]
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 "The FadR.DNA complex. Transcriptional control of fatty acid metabolism in Escherichia coli". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (20): 17373–9. May 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100195200. PMID 11279025.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 "Crystal structure of FadR, a fatty acid-responsive transcription factor with a novel acyl coenzyme A-binding fold". EMBO J. 19 (19): 5167–77. October 2000. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.19.5167. PMID 11013219.
- ↑ "Subdivision of the helix-turn-helix GntR family of bacterial regulators in the FadR, HutC, MocR, and YtrA subfamilies". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (15): 12507–15. April 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110968200. PMID 11756427.
 |

