Biology:Hysterectomy
| Hysterectomy | |
|---|---|
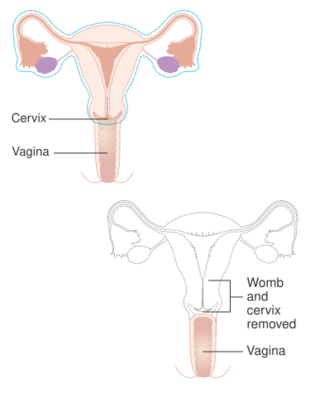 Diagram showing what is removed with a radical hysterectomy | |
| ICD-9-CM | 68.9 |
| MeSH | D007044 |
| MedlinePlus | 002915 |
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. The term “partial” or “total” hysterectomy are lay-terms that incorrectly describe the addition or omission of oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy. These procedures are usually performed by a gynecologist. Removal of the uterus renders the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States.[1] Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as endometriosis, irregular bleeding, and uterine fibroids.[1] It is expected that the frequency of hysterectomies for non-malignant indications will continue to fall given the development of alternative treatment options.[2]
Medical uses

Hysterectomy is a major surgical procedure that has risks and benefits. It affects the hormonal balance and overall health of patients. Because of this, hysterectomy is normally recommended as a last resort after pharmaceutical or other surgical options have been exhausted to remedy certain intractable and severe uterine/reproductive system conditions. There may be other reasons for a hysterectomy to be requested. Such conditions and/or indications include, but are not limited to:[3]
- Endometriosis: growth of the uterine lining outside the uterine cavity. This inappropriate tissue growth can lead to pain and bleeding.[4]
- Adenomyosis: a form of endometriosis, where the uterine lining has grown into and sometimes through the uterine wall musculature. This can thicken the uterine walls and also contribute to pain and bleeding.[5]
- Heavy menstrual bleeding: irregular or excessive menstrual bleeding for greater than a week. It can disturb regular quality of life and may be indicative of a more serious condition.
- Uterine fibroids: benign growths on the uterus wall. These muscular noncancerous tumors can grow in single form or in clusters and can cause extreme pain and bleeding.[6]
- Uterine prolapse: when the uterus sags down due to weakened or stretched pelvic floor muscles potentially causing the uterus to protrude out of the vagina in more severe cases.
- Reproductive system cancer prevention: especially if there is a strong family history of reproductive system cancers (especially breast cancer in conjunction with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation), or as part of recovery from such cancers.[7]
- Gynecologic cancer: depending on the type of hysterectomy, can aid in treatment of cancer or precancer of the endometrium, cervix, or uterus. In order to protect against or treat cancer of the ovaries, would need an oophorectomy.
- Transgender (trans) male affirmation: aids in gender dysphoria, prevention of future gynecologic problems, and transition to obtaining new legal gender documentation.[8]
- Severe developmental disabilities: this treatment is controversial at best. In the United States, specific cases of sterilization due to developmental disabilities have been found by state-level Supreme Courts to violate the patient's constitutional and common-law rights.[9]
- Postpartum: to remove either a severe case of placenta praevia (a placenta that has either formed over or inside the birth canal) or placenta percreta (a placenta that has grown into and through the wall of the uterus to attach itself to other organs), as well as a last resort in case of excessive obstetrical haemorrhage.[10]
- Chronic pelvic pain: should try to obtain pain etiology, although may have no known cause.[11]
Risks and adverse effects
In 1995, the short-term mortality (within 40 days of surgery) was reported at 0.38 cases per 1000 when performed for benign causes. Risks for surgical complications were presence of fibroids, younger age (vascular pelvis with higher bleeding risk and larger uterus), dysfunctional uterine bleeding and parity.[12]
The mortality rate is several times higher when performed in patients who are pregnant, have cancer or other complications.[13]
Long-term effect on all case mortality is relatively small. Women under the age of 45 years have a significantly increased long-term mortality that is believed to be caused by the hormonal side effects of hysterectomy and prophylactic oophorectomy.[14][15] This effect is not limited to pre-menopausal women; even women who have already entered menopause were shown to have experienced a decrease in long-term survivability post-oophorectomy.[16]
Approximately 35% of women after hysterectomy undergo another related surgery within 2 years.[17]
Ureteral injury is not uncommon and occurs in 0.2 per 1,000 cases of vaginal hysterectomy and 1.3 per 1,000 cases of abdominal hysterectomy.[18] The injury usually occurs in the distal ureter close to the infundibulopelvic ligament or as a ureter crosses below the uterine artery, often from blind clamping and ligature placement to control hemorrhage.[19]
Recovery
Hospital stay is 3 to 5 days or more for the abdominal procedure and between 1 and 2 days (but possibly longer) for vaginal or laparoscopically assisted vaginal procedures.[20] After the procedure, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends not inserting anything into the vagina for the first 6 weeks (including inserting tampons or having sex).[21]
Unintended oophorectomy and premature ovarian failure
Removal of one or both ovaries is performed in a substantial number of hysterectomies that were intended to be ovary sparing.[22]
The average onset age of menopause after hysterectomy with ovarian conservation is 3.7 years earlier than average.[23] This has been suggested to be due to the disruption of blood supply to the ovaries after a hysterectomy or due to missing endocrine feedback of the uterus. The function of the remaining ovaries is significantly affected in about 40% of people, some of them even require hormone replacement therapy. Surprisingly, a similar and only slightly weaker effect has been observed for endometrial ablation which is often considered as an alternative to hysterectomy.[24]
A substantial number of women develop benign ovarian cysts after a hysterectomy.[25]
Effects on sexual life and pelvic pain
After hysterectomy for benign indications the majority of patients report improvement in sexual life and pelvic pain. A smaller share of patients report worsening of sexual life and other problems. The picture is significantly different for hysterectomy performed for malignant reasons; the procedure is often more radical with substantial side effects.[26][27] A proportion of patients who undergo a hysterectomy for chronic pelvic pain continue to have pelvic pain after a hysterectomy and develop dyspareunia (painful sexual intercourse).[28]
Premature menopause and its effects
Estrogen levels fall sharply when the ovaries are removed, removing the protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular and skeletal systems. This condition is often referred to as "surgical menopause", although it is substantially different from a naturally occurring menopausal state; the former is a sudden hormonal shock to the body that causes rapid onset of menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, while the latter is a gradually occurring decrease of hormonal levels over a period of years with uterus intact and ovaries able to produce hormones even after the cessation of menstrual periods.[29]
One study showed that risk of subsequent cardiovascular disease is substantially increased for women who had hysterectomy at age 50 or younger. No association was found for women undergoing the procedure after age 50. The risk is higher when ovaries are removed but still noticeable even when ovaries are preserved.[30]
Several other studies have found that osteoporosis (decrease in bone density) and increased risk of bone fractures are associated with hysterectomies.[31][32] This has been attributed to the modulatory effect of estrogen on calcium metabolism and the drop in serum estrogen levels after menopause can cause excessive loss of calcium leading to bone wasting.
Hysterectomies have also been linked with higher rates of heart disease and weakened bones. Those who have undergone a hysterectomy with both ovaries removed typically have reduced testosterone levels as compared to those left intact.[22] Reduced levels of testosterone in women are predictive of height loss, which may occur as a result of reduced bone density,[33] while increased testosterone levels in women are associated with a greater sense of sexual desire.[34]
Oophorectomy before the age of 45 is associated with a fivefold mortality from neurologic and mental disorders.[35]
Urinary incontinence and vaginal prolapse
Urinary incontinence and vaginal prolapse are well known adverse effects that develop with high frequency a very long time after the surgery. Typically, those complications develop 10–20 years after the surgery.[36] For this reason exact numbers are not known, and risk factors are poorly understood. It is also unknown if the choice of surgical technique has any effect. It has been assessed that the risk for urinary incontinence is approximately doubled within 20 years after hysterectomy. One long-term study found a 2.4 fold increased risk for surgery to correct urinary stress incontinence following hysterectomy.[37][38]
The risk for vaginal prolapse depends on factors such as number of vaginal deliveries, the difficulty of those deliveries, and the type of labor.[39] Overall incidence is approximately doubled after hysterectomy.[40]
Adhesion formation and bowel obstruction
The formation of postoperative adhesions is a particular risk after hysterectomy because of the extent of dissection involved as well as the fact the hysterectomy wound is in the most gravity-dependent part of the pelvis into which a loop of bowel may easily fall.[41] In one review, incidence of small bowel obstruction due to intestinal adhesion was found to be 15.6% in non-laparoscopic total abdominal hysterectomies vs. 0.0% in laparoscopic hysterectomies.[42]
Wound infection
Wound infection occurs in approximately 3% of cases of abdominal hysterectomy. The risk is increased by obesity, diabetes, immunodeficiency disorder, use of systemic corticosteroids, smoking, wound hematoma, and preexisting infection such as chorioamnionitis and pelvic inflammatory disease.[43] Such wound infections mainly take the form of either incisional abscess or wound cellulitis. Typically, both confer erythema, but only an incisional abscess confers purulent drainage. The recommended treatment of an incisional abscess after hysterectomy is by incision and drainage, and then coverage by a thin layer of gauze followed by sterile dressing. The dressing should be changed and the wound irrigated with normal saline at least twice each day. In addition, it is recommended to administer an antibiotic active against staphylococci and streptococci, preferably vancomycin when there is a risk of MRSA.[43] The wound can be allowed to close by secondary intention. Alternatively, if the infection is cleared and healthy granulation tissue is evident at the base of the wound, the edges of the incision may be reapproximated, such as by using butterfly stitches, staples or sutures.[43] Sexual intercourse remains possible after hysterectomy. Reconstructive surgery remains an option for women who have experienced benign and malignant conditions.[44] : 1020–1348
Other rare problems
Hysterectomy may cause an increased risk of the relatively rare renal cell carcinoma. The increased risk is particularly pronounced for young women; the risk was lower after vaginally performed hysterectomies.[45] Hormonal effects or injury of the ureter were considered as possible explanations.[46][47] In some cases the renal cell carcinoma may be a manifestation of an undiagnosed hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer syndrome.
Removal of the uterus without removing the ovaries can produce a situation that on rare occasions can result in ectopic pregnancy due to an undetected fertilization that had yet to descend into the uterus before surgery. Two cases have been identified and profiled in an issue of the Blackwell Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology; over 20 other cases have been discussed in additional medical literature.[48] On very rare occasions, sexual intercourse after hysterectomy may cause a transvaginal evisceration of the small bowel.[49] The vaginal cuff is the uppermost region of the vagina that has been sutured closed. A rare complication, it can dehisce and allow the evisceration of the small bowel into the vagina.[50]
Alternatives


Depending on the indication there are alternatives to hysterectomy:
Heavy bleeding
Levonorgestrel intrauterine devices are highly effective at controlling dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) or menorrhagia and should be considered before any surgery.[51]
Menorrhagia (heavy or abnormal menstrual bleeding) may also be treated with the less invasive endometrial ablation which is an outpatient procedure in which the lining of the uterus is destroyed with heat, mechanically or by radio frequency ablation.[52] Endometrial ablation greatly reduces or eliminates monthly bleeding in ninety percent of patients with DUB. It is not effective for patients with very thick uterine lining or uterine fibroids.[53]
Uterine fibroids
Levonorgestrel intrauterine devices are highly effective in limiting menstrual blood flow and improving other symptoms. Side effects are typically very moderate because the levonorgestrel (a progestin) is released in low concentration locally. There is now substantial evidence that Levongestrel-IUDs provide good symptomatic relief for women with fibroids.[54]
Uterine fibroids may be removed and the uterus reconstructed in a procedure called "myomectomy". A myomectomy may be performed through an open incision, laparoscopically, or through the vagina (hysteroscopy).[55]
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a minimally invasive procedure for treatment of uterine fibroids. Under local anesthesia a catheter is introduced into the femoral artery at the groin and advanced under radiographic control into the uterine artery. A mass of microspheres or polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) material (an embolus) is injected into the uterine arteries in order to block the flow of blood through those vessels.[56] The restriction in blood supply usually results in significant reduction of fibroids and improvement of heavy bleeding tendency. The 2012 Cochrane review comparing hysterectomy and UAE did not find any major advantage for either procedure. While UAE is associated with shorter hospital stay and a more rapid return to normal daily activities, it was also associated with a higher risk for minor complications later on. There were no differences between UAE and hysterectomy with regards to major complications.[57]
Uterine fibroids can be removed with a non-invasive procedure called Magnetic Resonance guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS).
Uterine prolapse
Prolapse may also be corrected surgically without removal of the uterus.[58] There are several strategies that can be utilized to help strengthen pelvic floor muscles and prevent the worsening of prolapse. These include, but are not limited to, use of "kegel exercises", vaginal pessary, constipation relief, weight management, and care when lifting heavy objects.[59]
Types

Hysterectomy, in the literal sense of the word, means merely removal of the uterus. However other organs such as ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the cervix are very frequently removed as part of the surgery.[60]
- Radical hysterectomy: complete removal of the uterus, cervix, upper vagina, and parametrium. Indicated for cancer. Lymph nodes, ovaries, and fallopian tubes are also usually removed in this situation, such as in Wertheim's hysterectomy.[61]
- Total hysterectomy: complete removal of the uterus and cervix, with or without oophorectomy.
- Subtotal hysterectomy: removal of the uterus, leaving the cervix in situ.
Subtotal (supracervical) hysterectomy was originally proposed with the expectation that it may improve sexual functioning after hysterectomy, it has been postulated that removing the cervix causes excessive neurologic and anatomic disruption, thus leading to vaginal shortening, vaginal vault prolapse, and vaginal cuff granulations.[62] These theoretical advantages were not confirmed in practice, but other advantages over total hysterectomy emerged. The principal disadvantage is that risk of cervical cancer is not eliminated and women may continue cyclical bleeding (although substantially less than before the surgery). These issues were addressed in a systematic review of total versus supracervical hysterectomy for benign gynecological conditions, which reported the following findings:[63]
- There was no difference in the rates of incontinence, constipation, measures of sexual function, or alleviation of pre-surgery symptoms.
- Length of surgery and amount of blood lost during surgery were significantly reduced during supracervical hysterectomy compared to total hysterectomy, but there was no difference in post-operative transfusion rates.[64]
- Febrile morbidity was less likely and ongoing cyclic vaginal bleeding one year after surgery was more likely after supracervical hysterectomy.
- There was no difference in the rates of other complications, recovery from surgery, or readmission rates.
In the short-term, randomized trials have shown that cervical preservation or removal does not affect the rate of subsequent pelvic organ prolapse.[65]
Supracervical hysterectomy does not eliminate the possibility of having cervical cancer since the cervix itself is left intact and may be contraindicated in women with increased risk of this cancer; regular pap smears to check for cervical dysplasia or cancer are still needed.[66][67]
Technique
Hysterectomy can be performed in different ways. The oldest known technique is vaginal hysterectomy. The first planned hysterectomy was performed by Konrad Langenbeck - Surgeon General of the Hannovarian army, although there are records of vaginal hysterectomy for prolapse going back as far as 50BC.[68]
The first abdominal hysterectomy recorded was by Ephraim McDowell. He performed the procedure in 1809 for a mother of five for a large ovarian mass on her kitchen table.[69]
In modern medicine today, laparoscopic vaginal (with additional instruments passing through ports in small abdominal incisions, close or in the navel) and total laparoscopic techniques have been developed.
Abdominal hysterectomy
Most hysterectomies in the United States are done via laparotomy (abdominal incision, not to be confused with laparoscopy). A transverse (Pfannenstiel) incision is made through the abdominal wall, usually above the pubic bone, as close to the upper hair line of the individual's lower pelvis as possible, similar to the incision made for a caesarean section. This technique allows physicians the greatest access to the reproductive structures and is normally done for removal of the entire reproductive complex.[70] The recovery time for an open hysterectomy is 4–6 weeks and sometimes longer due to the need to cut through the abdominal wall. Historically, the biggest problem with this technique was infections, but infection rates are well-controlled and not a major concern in modern medical practice. An open hysterectomy provides the most effective way to explore the abdominal cavity and perform complicated surgeries. Before the refinement of the vaginal and laparoscopic vaginal techniques, it was also the only possibility to achieve subtotal hysterectomy; meanwhile, the vaginal route is the preferable technique in most circumstances.[71][72]
Vaginal hysterectomy
Vaginal hysterectomy is performed entirely through the vaginal canal and has clear advantages over abdominal surgery such as fewer complications, shorter hospital stays and shorter healing time.[73][74] Abdominal hysterectomy, the most common method, is used in cases such as after caesarean delivery, when the indication is cancer, when complications are expected, or surgical exploration is required.
Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy
With the development of laparoscopic techniques in the 1970s and 1980s, the "laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy" (LAVH) has gained great popularity among gynecologists because compared with the abdominal procedure it is less invasive and the post-operative recovery is much faster. It also allows better exploration and slightly more complicated surgeries than the vaginal procedure. LAVH begins with laparoscopy and is completed such that the final removal of the uterus (with or without removing the ovaries) is via the vaginal canal. Thus, LAVH is also a total hysterectomy; the cervix is removed with the uterus.[75] If the cervix is removed along with the uterus, the upper portion of the vagina is sutured together and called the vaginal cuff.[76]
Laparoscopic-assisted supracervical hysterectomy
The "laparoscopic-assisted supracervical hysterectomy" (LASH) was later developed to remove the uterus without removing the cervix using a morcellator which cuts the uterus into small pieces that can be removed from the abdominal cavity via the laparoscopic ports.[77]
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy
Total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) was developed in the early 90s by Prabhat K. Ahluwalia in Upstate New York.[78] TLH is performed solely through the laparoscopes in the abdomen, starting at the top of the uterus, typically with a uterine manipulator. The entire uterus is disconnected from its attachments using long thin instruments through the "ports". Then all tissue to be removed is passed through the small abdominal incisions.
Other techniques
Supracervical (subtotal) laparoscopic hysterectomy (LSH) is performed similar to the total laparoscopic surgery but the uterus is amputated between the cervix and fundus.[79]
Dual-port laparoscopy is a form of laparoscopic surgery using two 5 mm midline incisions: the uterus is detached through the two ports and removed through the vagina.[80][81]
"Robotic hysterectomy" is a variant of laparoscopic surgery using special remotely controlled instruments that allow the surgeon finer control as well as three-dimensional magnified vision.[82]
-
Uterus prior to hysterectomy
-
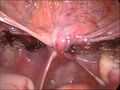
Laparoscopical hysterectomy
-
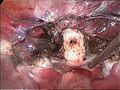
Cervical stump (white) after removal of the uterine corpus at laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy
-
Transvaginal extraction of the uterus in total laparoscopical hysterectomy
-
End of a laparoscopical hysterectomy
Comparison of techniques
Patient characteristics such as the reason for needing a hysterectomy, uterine size, descent of the uterus, presence of diseased tissues surrounding the uterus, previous surgery in the pelvic region, obesity, history of pregnancy, the possibility of endometriosis, or the need for an oophorectomy, will influence a surgeon's surgical approach when performing a hysterectomy.[83][needs update]
Vaginal hysterectomy is recommended over other variants where possible for women with benign diseases.[71][72][83] Vaginal hysterectomy was shown to be superior to LAVH and some types of laparoscopic surgery causing fewer short- and long-term complications, more favorable effect on sexual experience with shorter recovery times and fewer costs.[84][85][86]
Laparoscopic surgery offers certain advantages when vaginal surgery is not possible but also has the disadvantage of significantly longer time required for the surgery.[83][73]
In one 2004 study conducted in the UK comparing abdominal (laparotomic) and laparoscopic techniques, laparoscopic surgery was found to cause longer operation time and a higher rate of major complications while offering much quicker healing.[87] In another study conducted in 2014, laparoscopy was found to be "a safe alternative to laparotomy" in patients receiving total hysterectomy for endometrial cancer. Researchers concluded the procedure "offers markedly improved perioperative outcomes with a lower reoperation rate and fewer postoperative complications when the standard of care shifts from open surgery to laparoscopy in a university hospital".[88]
The abdominal technique is very often applied in difficult circumstances or when complications are expected. Given these circumstances the complication rate and time required for surgery compares very favorably with other techniques, however time required for healing is much longer.[83]
Hysterectomy by abdominal laparotomy is correlated with much higher incidence of intestinal adhesions than other techniques.[42]
Time required for completion of surgery in the eVAL trial is reported as follows:[87]
- abdominal 55.2 minutes average, range 19–155
- vaginal 46.6 minutes average, range 14–168
- laparoscopic (all variants) 82.5 minutes average, range 10–325 (combined data from both trial arms)
Morcellation has been widely used especially in laparoscopic techniques and sometimes for the vaginal technique, but now appears to be associated with a considerable risk of spreading benign or malignant tumors.[89][90] In April 2014, the FDA issued a memo alerting medical practitioners to the risks of power morcellation.[91]
Robotic assisted surgery is presently used in several countries for hysterectomies. Additional research is required to determine the benefits and risks involved, compared to conventional laparoscopic surgery.[92][93]
A 2014 Cochrane review found that robotic assisted surgery may have a similar complication rate when compared to conventional laparoscopic surgery. In addition, there is evidence to suggest that although the surgery make take longer, robotic assisted surgery may result in shorter hospital stays.[92] More research is necessary to determine if robotic assisted hysterectomies are beneficial for people with cancer.[92]
Previously reported marginal advantages of robotic assisted surgery could not be confirmed; only differences in hospital stay and cost remain statistically significant.[94][95][96] In addition, concerns over widespread misleading marketing claims have been raised.[97]
| Technique | Benefits | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal hysterectomy |
|
|
| Vaginal hysterectomy | ||
| Laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy (subtotal hysterectomy) | ||
| Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH) |
|
|
| Total laparoscopic hysterectomy |
|
|
| Single-port laparoscopic hysterectomy / mini laparoscopic hysterectomy |
| |
| Robotic-assisted hysterectomy |
Incidence
Canada
In Canada , the number of hysterectomies between 2008 and 2009 was almost 47,000. The national rate for the same timeline was 338 per 100,000 population, down from 484 per 100,000 in 1997. The reasons for hysterectomies differed depending on whether the woman was living in an urban or rural location. Urban women opted for hysterectomies due to uterine fibroids and rural women had hysterectomies mostly for menstrual disorders.[102]
United States
Hysterectomy is the second most common major surgery among women in the United States (the first is cesarean section). In the 1980s and 1990s, this statistic was the source of concern among some consumer rights groups and puzzlement among the medical community,[103] and brought about informed choice advocacy groups like Hysterectomy Educational Resources and Services (HERS) Foundation, founded by Nora W. Coffey in 1982.
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, of the 617,000 hysterectomies performed in 2004, 73% also involved the surgical removal of the ovaries. There are currently an estimated 22 million women in the United States who have undergone this procedure. Nearly 68 percent were performed for benign conditions such as endometriosis, irregular bleeding and uterine fibroids.[1] Such rates being highest in the industrialized world has led to the controversy that hysterectomies are being largely performed for unwarranted reasons.[104] More recent data suggests that the number of hysterectomies performed has declined in every state in the United States. From 2010 to 2013, there were 12 percent fewer hysterectomies performed, and the types of hysterectomies were more minimally invasive in nature, reflected by a 17 percent increase in laparoscopic procedures.[105]
United Kingdom
In the UK, 1 in 5 women is likely to have a hysterectomy by the age of 60, and ovaries are removed in about 20% of hysterectomies.[106]
Germany
The number of hysterectomies in Germany has been constant for many years. In 2006, 149,456 hysterectomies were performed. Additionally, of these, 126,743 (84.8%) successfully benefitted the patient without incident. Women between the ages of 40 and 49 accounted for 50 percent of hysterectomies, and those between the ages of 50 and 59 accounted for 20 percent.[107] In 2007, the number of hysterectomies decreased to 138,164.[108] In recent years, the technique of laparoscopic or laparoscopically assisted hysterectomies has been raised into the foreground.[109][110]
Denmark
In Denmark , the number of hysterectomies from the 1980s to the 1990s decreased by 38 percent. In 1988, there were 173 such surgeries per 100,000 women, and by 1998 this number had been reduced to 107. The proportion of abdominal supracervical hysterectomies in the same time period grew from 7.5 to 41 percent. A total of 67,096 women underwent hysterectomy during these years.[111]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Plotting the downward trend in traditional hysterectomy | Institute for Healthcare Policy & Innovation". https://ihpi.umich.edu/news/plotting-downward-trend-traditional-hysterectomy.
- ↑ "Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system: uses and controversies". Expert Review of Medical Devices 5 (4): 437–445. July 2008. doi:10.1586/17434440.5.4.437. PMID 18573044.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy" (in en). 2017-02-21. https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/hysterectomy.
- ↑ "Endometriosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Clinical Management". Current Obstetrics and Gynecology Reports 6 (1): 34–41. March 2017. doi:10.1007/s13669-017-0187-1. PMID 29276652.
- ↑ "Uterine Adenomyosis" (in en). https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/uterine-adenomyosis.
- ↑ (in en) Uterine fibroids: Overview. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). 2017-11-16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279535/.
- ↑ "Ovarian Cancer Prevention in High-risk Women". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 60 (4): 738–757. December 2017. doi:10.1097/GRF.0000000000000318. PMID 28957949.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy | Transgender Care". https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/hysterectomy.
- ↑ Washington (state) Protection and Advocacy System. "Growth Attenuation and Sterilization Procedures – "The Ashley Treatment"". Washington, DC: National Disabilities Rights Network. https://purple.ndrn.org/ashley/default.htm.
- ↑ "A 27-year review of obstetric hysterectomy". Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 23 (3): 252–254. May 2003. doi:10.1080/0144361031000098352. PMID 12850853.
- ↑ "Role of hysterectomy in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain". Obstetrics and Gynecology 117 (5): 1175–1178. May 2011. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e31821646e1. PMID 21508759.
- ↑ "Severe complications of hysterectomy: the VALUE study". BJOG 111 (7): 688–694. July 2004. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00174.x. PMID 15198759.
- ↑ "The mortality risk associated with hysterectomy". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 152 (7 Pt 1): 803–808. August 1985. doi:10.1016/s0002-9378(85)80067-3. PMID 4025434.
- ↑ "Prophylactic oophorectomy in premenopausal women and long-term health". Menopause International 14 (3): 111–116. September 2008. doi:10.1258/mi.2008.008016. PMID 18714076.
- ↑ American Urogynecologic Society (May 5, 2015), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation (American Urogynecologic Society), http://www.choosingwisely.org/societies/american-urogynecologic-society/, retrieved June 1, 2015, which cites: * "Prophylactic and risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: recommendations based on risk of ovarian cancer". Obstetrics and Gynecology 117 (2 Pt 1): 404. February 2011. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3182083189. PMID 21252760.
- ↑ "Elective oophorectomy for benign gynecological disorders". Menopause 14 (3 Pt 2): 580–585. 2007. doi:10.1097/gme.0b013e31803c56a4. PMID 17476148.
- ↑ "What We Know about the Long-Term Risks of Hysterectomy for Benign Indication-A Systematic Review". Journal of Clinical Medicine 10 (22): 5335. November 2021. doi:10.3390/jcm10225335. PMID 34830617.
- ↑ "Management of iatrogenic ureteral injury". Therapeutic Advances in Urology 6 (3): 115–124. June 2014. doi:10.1177/1756287214526767. PMID 24883109.
- ↑ Ureteral Trauma at eMedicine
- ↑ "Abdominal hysterectomy". Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/abdominal-hysterectomy/about/pac-20384559.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy" (in en). https://www.acog.org/en/womens-health/faqs/hysterectomy.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "Hysterectomy, oophorectomy, and endogenous sex hormone levels in older women: the Rancho Bernardo Study". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 85 (2): 645–651. February 2000. doi:10.1210/jcem.85.2.6405. PMID 10690870.
- ↑ "The association of hysterectomy and menopause: a prospective cohort study". BJOG 112 (7): 956–962. July 2005. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00696.x. PMID 15957999.
- ↑ "Endometrial resection and ablation techniques for heavy menstrual bleeding". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1 (1): CD001501. January 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001501.pub5. PMID 30667064.
- ↑ "Effect of total abdominal hysterectomy on ovarian blood supply in women of reproductive age". Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine 24 (2): 169–174. February 2005. doi:10.7863/jum.2005.24.2.169. PMID 15661947.
- ↑ "The effect of hysterectomy on sexual functioning". Annual Review of Sex Research 14: 83–113. 2003. PMID 15287159.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy improves sexual response? Addressing a crucial omission in the literature". Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 18 (3): 288–295. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2011.01.012. PMID 21545957.
- ↑ "Chronic pelvic pain: an integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment". Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey 58 (9): 615–623. September 2003. doi:10.1097/01.OGX.0000083225.90017.01. PMID 12972837.
- ↑ "Postmenopausal syndrome". Indian Journal of Psychiatry 57 (Suppl 2): S222–S232. July 2015. doi:10.4103/0019-5545.161483. PMID 26330639.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy and risk of cardiovascular disease: a population-based cohort study". European Heart Journal 32 (6): 745–750. March 2011. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq477. PMID 21186237.
- ↑ "Risk factors for pelvis fracture in older persons". American Journal of Epidemiology 162 (9): 879–886. November 2005. doi:10.1093/aje/kwi295. PMID 16221810.
- ↑ "Risk factors for osteoporosis related to their outcome: fractures". Osteoporosis International 12 (8): 630–638. 2001. doi:10.1007/s001980170062. PMID 11580076.
- ↑ "Low bioavailable testosterone levels predict future height loss in postmenopausal women". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 10 (4): 650–654. April 1995. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650100419. PMID 7610937.
- ↑ "Female hypoactive sexual desire disorder: History and current status". The Journal of Sexual Medicine 3 (3): 408–418. May 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00246.x. PMID 16681466.
- ↑ "Increased mortality for neurological and mental diseases following early bilateral oophorectomy". Neuroepidemiology 33 (1): 32–40. 2009. doi:10.1159/000211951. PMID 19365140.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy and urinary incontinence: a systematic review". Lancet 356 (9229): 535–539. August 2000. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02577-0. PMID 10950229.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy and risk of stress-urinary-incontinence surgery: nationwide cohort study". Lancet 370 (9597): 1494–1499. October 2007. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61635-3. PMID 17964350.
- ↑ "Self-reported bladder function five years post-hysterectomy". Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 25 (5): 469–475. July 2005. doi:10.1080/01443610500235170. PMID 16183583.
- ↑ "Risk factors for vaginal prolapse after hysterectomy". International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 110 (1): 27–30. July 2010. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.01.025. PMID 20362288.
- ↑ "Pelvic organ prolapse surgery following hysterectomy on benign indications". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 198 (5): 572.e1–572.e6. May 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.01.012. PMID 18355787.
- ↑ "Disorders of adhesions or adhesion-related disorder: monolithic entities or part of something bigger--CAPPS?". Seminars in Reproductive Medicine 26 (4): 356–368. July 2008. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1082394. PMID 18756413.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "The incidence and risk factors of post-laparotomy adhesive small bowel obstruction". Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 14 (10): 1619–1628. October 2010. doi:10.1007/s11605-010-1189-8. PMID 20352368.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 43.2 "Diagnosis and Management of Postoperative Infection". The Global Library of Women's Medicine. 2009. doi:10.3843/GLOWM.10032. ISSN 1756-2228. https://www.glowm.com/section_view/heading/Diagnosis%20and%20Management%20of%20Postoperative%20Infection/item/32.
- ↑ Williams gynecology, 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2012. p. 65. ISBN 978-0071716727.
- ↑ "Risk of renal cell carcinoma after hysterectomy". Archives of Internal Medicine 170 (22): 2011–2016. December 2010. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2010.425. PMID 21149759.
- ↑ "Increased risk of renal cell carcinoma subsequent to hysterectomy". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 8 (11): 999–1003. November 1999. PMID 10566555.
- ↑ "Reproductive, menstrual, and other hormone-related factors and risk of renal cell cancer". International Journal of Cancer 123 (9): 2213–2216. November 2008. doi:10.1002/ijc.23750. PMID 18711701.
- ↑ "Early ectopic pregnancy after vaginal hysterectomy. Two case reports". British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 87 (5): 363–365. May 1980. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1980.tb04559.x. PMID 7387935.
- ↑ "[Vaginal evisceration. Report of a case and a literature review]". Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico 81 (6): 349–352. June 2013. PMID 23837301.
- ↑ "Pelvic organ prolapse". Lancet 369 (9566): 1027–1038. March 2007. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60462-0. PMID 17382829.
- ↑ "The levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system as an alternative to hysterectomy in peri-menopausal women". Contraception 75 (6 Suppl): S152–S154. June 2007. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2007.01.003. PMID 17531608.
- ↑ "Endometrial resection and ablation versus hysterectomy for heavy menstrual bleeding". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021 (2): CD000329. February 2021. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000329.pub4. PMID 33619722.
- ↑ "5 operations you don't want to get – and what to do instead". CNN. July 27, 2007. https://www.cnn.com/2007/HEALTH/07/27/healthmag.surgery/.
- ↑ "Intrauterine device use among women with uterine fibroids: a systematic review". Contraception 82 (1): 41–55. July 2010. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2010.02.011. PMID 20682142.
- ↑ A Gynecologist's Second Opinion: The Questions & Answers You Need to Take Charge of Your Health (revised ed.). Plume. 2002. pp. 89–92, 105–150. http://www.gynsecondopinion.com#why.
- ↑ "Uterine artery embolization for treatment of symptomatic fibroids; a single institution experience". Hippokratia 18 (3): 258–261. 2014. PMID 25694762.
- ↑ "Uterine artery embolization for symptomatic uterine fibroids". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (12): CD005073. December 2014. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005073.pub4. PMID 25541260.
- ↑ "Having Prolapse, Cystocele and Rectocele Fixed Without Hysterectomy". Women's Health. wdxcyber.com. https://www.wdxcyber.com/nurine08.htm.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy" (in en). 2017-02-21. https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/hysterectomy.
- ↑ "Complete Hysterectomy" (in en). 2011-02-02. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/complete-hysterectomy.
- ↑ encyclopedia.com > Wertheim's hysterectomy Citing: "Wertheim's hysterectomy". A Dictionary of Nursing. 2008. Encyclopedia.com. (October 13, 2010).
- ↑ "Long-Term Outcomes of the Total or Supracervical Hysterectomy (TOSH) Trial". Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery 16 (1): 49–57. January 2010. doi:10.1097/SPV.0b013e3181cec343. PMID 22229107.
- ↑ "Total versus subtotal hysterectomy for benign gynaecological conditions". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (4): CD004993. April 2012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004993.pub3. PMID 22513925.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy-a comparison of approaches". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International 107 (20): 353–359. May 2010. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2010.0353. PMID 20539807.
- ↑ "Outcomes after total versus subtotal abdominal hysterectomy". The New England Journal of Medicine 347 (17): 1318–1325. October 2002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa013336. PMID 12397189.
- ↑ American Academy of Family Physicians (April 2012). "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation (American Academy of Family Physicians). http://choosingwisely.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/5things_12_factsheet_Amer_Acad_Fam_Phys.pdf. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
- ↑ Consumer Reports; American Academy of Family Physicians (May 2012). "Pap tests: When you need them—and when you don't". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation (Consumer Reports). http://consumerhealthchoices.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/ChoosingWiselyPapTestsAAFP.pdf. Retrieved August 17, 2012.
- ↑ "Vaginal Hysterectomy". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554482/. Retrieved 2022-10-31.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy: Then and Now - Oxford Women's Health". https://www.oxfordwomenshealth.co.nz/blog/hysterectomy-then-and-now.html.
- ↑ "The transverse-vertical incision (Alazzam hybrid incision)". Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery 407 (3): 1303–1309. May 2022. doi:10.1007/s00423-021-02404-5. PMID 35226178.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 "Subtotal hysterectomy and myomectomy - vaginally". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology 25 (2): 133–152. April 2011. doi:10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2010.11.003. PMID 21185235.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 "Vaginal route: a gynaecological route for much more than hysterectomy". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology 25 (2): 115–132. April 2011. doi:10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2010.12.005. PMID 21349773.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 "Methods of hysterectomy: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". BMJ 330 (7506): 1478. June 2005. doi:10.1136/bmj.330.7506.1478. PMID 15976422.
- ↑ "Surgical approach to hysterectomy for benign gynaecological disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2023 (8): CD003677. August 2023. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003677.pub6. PMID 37642285.
- ↑ "Surgery - Foundation for Women's Cancer" (in en-US). Foundation for Women's Cancer. http://www.foundationforwomenscancer.org/types-of-gynecologic-cancers/uterine/surgery/.
- ↑ "Vaginal cuff dehiscence: risk factors and management". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 206 (4): 284–288. April 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2011.08.026. PMID 21974989.
- ↑ "Feasibility of myomatous tissue extraction in laparoscopic surgery by contained in - bag morcellation: A retrospective single arm study". International Journal of Surgery 62: 22–27. February 2019. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.12.013. PMID 30639472.
- ↑ "Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy". The Journal of the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists 3 (4, Supplement): S1–S2. August 1996. doi:10.1016/S1074-3804(96)80129-0. PMID 9074073.
- ↑ "Laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy compared to total hysterectomy". JSLS 13 (3): 370–375. 2009. PMID 19793479.
- ↑ "A Novel Approach to Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Using Only Two 5mm Ports: Initial Clinical Experience". Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 17 (6): S87. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2010.08.381.
- ↑ "Dual Port Hysterectomy: A Novel Technique and Initial Experience". Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 19 (6): S86. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2012.08.620.
- ↑ "Robotic surgery: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007339.htm.
- ↑ 83.00 83.01 83.02 83.03 83.04 83.05 83.06 83.07 83.08 83.09 83.10 83.11 83.12 83.13 83.14 83.15 83.16 83.17 83.18 83.19 83.20 83.21 83.22 83.23 83.24 83.25 "Surgical approach to hysterectomy for benign gynaecological disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015 (8): CD003677. August 2015. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003677.pub5. PMID 26264829.
- ↑ "Laparoscopic hysterectomy--is there a benefit?". The New England Journal of Medicine 335 (7): 512–513. August 1996. doi:10.1056/NEJM199608153350712. PMID 8672159.
- ↑ "Laparoscopic Hysterectomy and Health Care in America – Finding the Balance Between Costs and Outcomes". https://www.obgyn.net/surgical-gynecology/laparoscopic-hysterectomy-and-health-care-america.
- ↑ "[Hysterectomy for benign lesions in the north of France: epidemiology and postoperative events]". Journal de Gynecologie, Obstetrique et Biologie de la Reproduction 30 (2): 151–159. April 2001. PMID 11319467.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 "The eVALuate study: two parallel randomised trials, one comparing laparoscopic with abdominal hysterectomy, the other comparing laparoscopic with vaginal hysterectomy". BMJ 328 (7432): 129–0. January 2004. doi:10.1136/bmj.37984.623889.F6. PMID 14711749.
- ↑ "Comparison of reoperation rates, perioperative outcomes in women with endometrial cancer when the standard of care shifts from open surgery to laparoscopy". Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 290 (6): 1215–1220. December 2014. doi:10.1007/s00404-014-3347-9. PMID 25009071.
- ↑ "Peritoneal dissemination complicating morcellation of uterine mesenchymal neoplasms". PLOS ONE 7 (11): e50058. 2012. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050058. PMID 23189178. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...750058S.
- ↑ "Parasitic myomas after laparoscopic surgery: an emerging complication in the use of morcellator? Description of four cases". Fertility and Sterility 96 (2): e90–e96. August 2011. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.05.095. PMID 21719004.
- ↑ "Safety Communications – UPDATED Laparoscopic Uterine Power Morcellation in Hysterectomy and Myomectomy: FDA Safety Communication" (in en). Center for Devices and Radiological Health. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm424443.htm.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 92.2 92.3 92.4 92.5 92.6 92.7 "Robot-assisted surgery in gynaecology". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (4): CD011422. April 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011422.pub2. PMID 30985921.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 93.2 "Robot-assisted surgery in gynaecology". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (4): CD011422. April 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011422.pub2. PMID 30985921.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 "Robotically assisted vs laparoscopic hysterectomy among women with benign gynecologic disease". JAMA 309 (7): 689–698. February 2013. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.186. PMID 23423414.
- ↑ "Total laparoscopic hysterectomy versus da Vinci robotic hysterectomy: is using the robot beneficial?". Journal of Gynecologic Oncology 22 (4): 253–259. December 2011. doi:10.3802/jgo.2011.22.4.253. PMID 22247802.
- ↑ "Minimally Invasive Hysterectomy: An Analysis of Different Techniques". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 58 (4): 732–739. December 2015. doi:10.1097/GRF.0000000000000149. PMID 26457851.
- ↑ "The commercialization of robotic surgery: unsubstantiated marketing of gynecologic surgery by hospitals". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 207 (3): 174.e1–174.e7. September 2012. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2012.06.050. PMID 22835493.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy in very obese and morbidly obese patients: a systematic review with cumulative analysis of comparative studies". Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 292 (4): 723–738. October 2015. doi:10.1007/s00404-015-3680-7. PMID 25773357.
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 99.2 99.3 99.4 99.5 99.6 99.7 "Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy and Laparoscopic-Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy". Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America 43 (3): 463–478. September 2016. doi:10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.005. PMID 27521879.
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 100.2 100.3 100.4 "Laparoscopic subtotal hysterectomy: evidence and techniques". Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology 20 (4): 424–434. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2013.01.009. PMID 23510954.
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 "Total versus subtotal hysterectomy for benign gynaecological conditions". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (4): CD004993. April 2012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004993.pub3. PMID 22513925.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy rates falling: report". CBC News. 2010-05-27. https://www.cbc.ca/news/technology/hysterectomy-rates-falling-report-1.903774.
- ↑ Kolata, Gina (1988-09-20). "Rate of Hysterectomies Puzzles Experts". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/1988/09/20/science/rate-of-hysterectomies-puzzles-experts.html.
- ↑ Masters, Coco (2006-07-01). "Are Hysterectomies Too Common?". Time (magazine). http://content.time.com/time/health/article/0,8599,1644050,00.html. Retrieved 2007-07-17.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy Procedures Pacing A Downward Trend" (in en). 23 January 2018. https://labblog.uofmhealth.org/rounds/plotting-downward-trend-traditional-hysterectomy.
- ↑ Khastgir, Gautam; Studd, John (1998). Hysterectomy and HRT. Taylor & Francis. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-85317-408-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=v-ENVtKsRhUC&q=hysterectomy+incidence&pg=PA1.
- ↑ Wolfrum, Christine (1 June 2008). "Vorschnelle Schnitte". Apotheken Umschau. Baierbrunn: Wort & Bild Verlag.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy-a comparison of approaches". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International 107 (20): 353–359. May 2010. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2010.0353. PMID 20539807.
- ↑ "Laparoscopic hysterectomy: challenges and limitations". Minimally Invasive Therapy & Allied Technologies 14 (3): 145–159. 2005. doi:10.1080/13645700510034010. PMID 16754157.
- ↑ "Die laparoskopisch assistierte vaginale Hysterektomie – Sinn oder Unsinn?". Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde 67 (6): 628–632. 2007. doi:10.1055/s-2007-965243.
- ↑ "Hysterectomy on benign indication in Denmark 1988-1998. A register based trend analysis". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 80 (3): 267–272. March 2001. doi:10.1080/j.1600-0412.2001.080003267.x. PMID 11207494.
External links
- Hysterectomy at Curlie
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia Hysterectomy
- Oncolex.org features live footage videos showing radical hysterctomies
- Hudson's FTM Resource Guide, "FTM Gender Reassignment Surgery
 |