Biology:MROH9
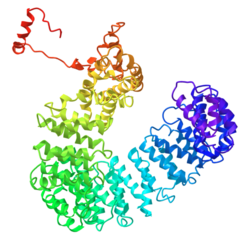
 Generic protein structure example |
Maestro heat-like repeat-containing protein family member 9 (MROH9) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MROH9 gene.[1] The word ‘maestro’ itself is an acronym, standing for male-specific transcription in the developing reproductive organs (MRO). MRO genes belong to the MROH family, which includes MROH9.[2]
Gene
MROH9 is also known as C1orf129 and ARMC11 (armadillo repeat-containing 11).[3][4] The genomic location is on chromosome 1 (1q24.3) on its plus end, spanning 129,232 base pairs.
Transcript
The MROH9 gene is encoded by an mRNA transcript that is 3,102 nucleotides in length. mRNA transcript variant 1 (NM_001163629.2), which encodes protein isoform 1 (NP_001157101.1), is the longest transcript encoding the longest, highest-quality isoform.[1] Transcript variant 2 is found to have a shorter, more distant C-terminus, and an alternative 3’ coding region and 3’ UTR compared to variant 1. Transcript variant 1 has 23 exons, making up a coding sequence that is 2,586 nucleotides long.[1]
Protein
The dominant isoform protein that the MROH9 encodes is isoform 1, with a length of 861 amino acids.[3] Table 1 displays some of the other common protein isoforms of the MROH9.
| Isoform | Accession number | Length (a.a.) | Exons | Domains |
| 1 | NP_001157101.1 | 861 | 23 | 5 HEATs, 2 HEAT repeats |
| 2 | NP_079339.2 | 573 | 15 | 5 HEATs |
| X1 | XP_011508307.1 | 811 | 21 | 3 HEAT repeats |
| X2 | XP_011508308.1 | 803 | 20 | none |
| X3 | XP_011508309.1 | 546 | 12 | 3 HEAT repeats |
Table 1: Information about the different isoforms of the MROH9 gene
The isoforms of the MROH9 gene and their respective lengths and exon numbers.[3][6]
Domains
Of the 11 MROH genes in the family, all of their respective proteins contain HEAT repeats, a type of protein structural motif made up of a short loop linking two alpha helices. HEAT repeats, structurally related to armadillo repeats, are known to form superhelical structures involved in intracellular transport.[2] Protein isoform 1 encoded by the MROH9 gene has 5 HEAT regions and 2 HEAT repeats; the quantity of these vary across the different isoforms, as seen in the table.[citation needed]
Structure

The secondary structure of human MROH9 protein isoform 1 has 49 alpha helices with no apparent sheets or coils.[1] The I-TASSER result displaying the tertiary structure with the highest probability score is pictured at the top of the page, and this structure was seen across orthologs, as well.[8]
Regulation
Gene level
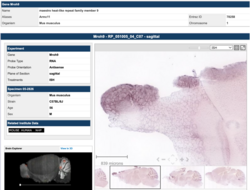
The encoded transcript of MRO genes were found in one study to exhibit “sexual dimorphic expression during murine gonadal development.” The researchers also found increased expression of MRO genes in human testicular tissue, and a particular cytoplasmic expression pattern of the protein in testicular germ cells.[2]
RNAseq data from NCBI Gene shows that MROH9 in humans is only consistently expressed in the lungs and no other tissue, though it shows notable expression in the intestines, stomach, and male/female gonads in almost all of the sets.[3] Low probability scores imply that this gene might be expressed at very low levels. Microarray-assessed tissue expression pattern data from confirms that expression is higher in the lungs, though very low across all other various tissues. Conditional expression pattern data shows that MROH9 is not particularly expressed in any one condition over the other.[3]
The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas confirm the gene’s expression in lung, intestine, and gonad tissue. MROH9 expression specifically correlates with a cluster that specializes in cilium organization and cilia cells. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas also shows that the gene shows significant levels of expression in the olfactory bulb region of the brain. Since the lung, gonads, intestines, and nose all require cilia cells to function, it is possible that the MROH9 gene confers the function of such tissues.[9]
Protein level
Subcellular localization of the MROH9 isoform 1 protein is predicted to be within the cytoplasm.[10] This is consistent across strict and distant orthologs, too, as the MROH9 protein shows cytoplasmic subcellular localization across most mammalian taxons. However, predicted data report that the protein could be important in the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.[10]
Predicted post-translational modifications reported by MyHits Motif Scan show that the MROH9 protein may have 27 phosphorylation sites, 7 N-linked glycosylation sites, and 4 myristoylation sites. However, considering that the probability scores are very low and that this protein is most probably located in the cytoplasm - meaning that it does not travel across membranes - predicted N-linked glycosylation and myristoylation sites are likely null. Phosphorylation is the only likely modification that can occur for this protein, but only a small handful of the predicted sites are conserved across MROH9 orthologs. Other phosphorylation sites, along with all the predicted N-linked glycosylation and myristoylation sites, are quite poorly conserved across orthologs.[11] Predicted eukaryotic linear motifs (ELMs) show several matched sequences for cleavage sites, implying that the MROH9 protein sequence might be cleaved as part of its function.[5]
Evolution
| Scientific name | Common name | Taxon | median date of divergence (MYA) | Accession # | Length (amino acids) | % identity to humans | % similarity to humans |
| Homo sapiens | Human | Primates | 0 | NP_001157101.1 | 861 | 100% | 100% |
| Chlorocebus sabaeus | Green monkey | Primates | 29 | XP_037842145.1 | 891 | 87% | 92% |
| Ochotona curzoniae | Black-lipped pika | Glires | 87 | XP_040842726.1 | 921 | 63% | 77% |
| Mus musculus | House mouse | Glires | 87 | NP_084347.1 | 891 | 59% | 76% |
| Balenoptera musculus | Blue whale | Artiodactyla | 94 | XP_036729523.1 | 912 | 70% | 82% |
| Sus scrofa | Wild pig | Artiodactyla | 94 | XP_020919615.1 | 912 | 70% | 81% |
| Hyaena hyaena | Striped hyena | Carnivora | 94 | XP_039077615.1 | 858 | 68% | 81% |
| Condylura cristata | Star-nosed mole | Eulipotyphla | 94 | XP_004688175.1 | 1007 | 64% | 80% |
| Rhinolophus ferrumequinum | Greater horseshoe bat | Chiroptera | 94 | XP_032948567.1 | 884 | 65% | 79% |
| Equus asinus | Ass | Perissodactyla | 94 | XP_044614605.1 | 901 | 63% | 75% |
| Loxodonta africana | African savanna elephant | Afrotheria | 99 | XP_010593357.1 | 907 | 65% | 79% |
| Choloepus didactylus | Southern two-toed sloth | Xenarthra | 99 | XP_037662834.1 | 855 | 64% | 78% |
| Vombatus ursinus | Common wombat | Marsupialia | 160 | XP_027724161.1 | 857 | 50% | 67% |
| Antechinus flavipes | Yellow-footed antechinus | Marsupialia | 160 | XP_051854920.1 | 798 | 51% | 70% |
Table 2: MROH9 orthologs and related properties
Orthologs of the human MROH9 gene (NP_001157101.1) in various animals across mammalian taxon groups.[3][12] MYA refers to how many million years ago the mammalian taxon diverged from the human species.
Interestingly, MROH9 orthologs were observed to only be found in mammalian species, as seen in the table above. Absolutely no homologs or orthologs were found in any birds, reptiles, amphibians, invertebrates, fungi, plants, or bacteria. Orthologs could be found in every extant mammalian species with the exception of Monotremes, which only showed homologs for different isoforms and various paralogs. It also appears that there is no direct correlation between estimated date of divergence and sequence similarity with humans; orthologs found in animals in the Glires taxon (which diverged most recently in mammals) showed less similarity to the human MROH9 sequence compared to mammal groups that diverged longer ago.[3]
Paralog
| Scientific name | Common name | Taxon | median date of divergence (MYA) | Accession # | Length (amino acids) | % identity to humans | % similarity to humans |
| Homo sapiens | Human | Primates | 0 | KAI2517273.1 | 898 | 100% | 100% |
| Ochotona curzoniae | Black-lipped pika | Glires | 87 | XP_040834542.1 | 1311 | 87% | 92% |
| Hyaena hyaena | Striped hyena | Carnivora | 94 | XP_039095139.1 | 1319 | 87% | 92% |
| Equus asinus | Ass | Perissodactyla | 94 | XP_014699852.1 | 1325 | 87% | 93% |
Table 3: Orthologs of MROH7 and related properties
Orthologs of the human MROH7 gene (KAI2517273.1), a paralog to MROH9, in various animals across mammalian taxon groups that had the ortholog.[3][12] MYA refers to how many million years ago the mammalian taxon diverged from the human species.
MROH7 is a notable paralog of the MROH9 gene and is found in humans as well as some other select mammal species. The second table above shows some of these paralogs and their sequence identity and similarity to the human MROH7 gene. Human MROH7 was found to have a 22% shared sequence identity to the human MROH9 gene.[3]
The graph to the right shows the corrected sequence divergence versus median date of divergence of MROH9. Plotted with the rate of evolution of MROH9 are rates for fibrinogen alpha (a rapidly evolving gene), cytochrome C (a slowly evolving gene), and the MROH7 paralog.[13][14] The graph shows that the slope for MROH7 evolution is much lower than MROH9, with its rate of divergence being almost similar to that of cytochrome C. All of the orthologs of the MROH7 gene show the same sequence identity despite having diverged at different times in history. This could imply that the orthologs for the MROH7 gene are closer related together, and might have diverged from MROH9 roughly 94 million years ago and did not evolve much since then. It is also possible that the MROH7 paralog is evolving slower than the MROH9 gene.[15]
Interacting proteins
Both GLO1 and RNF123 appear in several databases and articles, heightening the possibility of these being genuine interacting proteins for MROH9.[16][17] RNF123 and PARK2, another interacting protein, are both E3 Ubiquitin ligases, which are responsible for targeting proteins for degradation.[18] GLO1, or lactoylglutathione ligase, is an enzyme catalyzing isomerization of hemithioacetal adducts.[19] These results explain that MROH9 function may depend on the activity of these ligases and might be degraded.
Clinical significance
MROH9 appears in several publications indicating its potential role as an oncogene in various types of cancers. One paper found that there was excessive chromatin looping near MROH9 and several FMO genes (gene neighbors to MROH9 on chromosome 1), along with other key oncogenes in nasopharyngeal cancer, potentially linking MROH9 with oncogene properties.[20][21] MROH9 has also been found to play roles as an oncogene in other forms of cancer; studies have found it to be a potential necroptosis-related gene that is overexpressed in high-risk groups for pancreatic adenocarcinoma.[22][23] MROH9 has been further confirmed by some studies as an oncogene for breast cancers, with alterations in chromosome 1 being described in over half of breast cancer tumors. A large number of copy number variations (CNVs) are particularly found on the 1q arm of chromosome 1 where MROH9 is found.[24] Other research found MROH9 to be a predicted target of miR-3646, a type of microRNA that promotes cell proliferation in human breast cancer cells.[25] In addition to this, MROH9 is also found at a chromosome 1 locus that is associated with central corneal thickness, a measure of glaucoma. It is found at the associated locus together with PRRX1, another gene that, along with MROH9, was also found to be an associated variant in systemic lupus erythematosus[26][27]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Maestro heat-like repeat-containing protein family member 9 isoform 1 [Homo sapiens". NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/254692913.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "The elusive MAESTRO gene: Its human reproductive tissue-specific expression pattern". PLOS ONE 12 (4): e0174873. 2017-04-13. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174873. PMID 28406912. Bibcode: 2017PLoSO..1274873K.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 "Homo sapiens MROH9 gene". NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/80133.
- ↑ "MROH9 gene". GeneCards. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=MROH9.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "ELM - Search the ELM resource" (in en). http://elm.eu.org/.
- ↑ "Human BLAT Search". https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgBlat.
- ↑ "Clustal Omega < Multiple Sequence Alignment < EMBL-EBI". https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/.
- ↑ "I-TASSER results". https://seq2fun.dcmb.med.umich.edu//I-TASSER/output/S711851/.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Gene Detail :: Allen Brain Atlas: Mouse Brain". https://mouse.brain-map.org/gene/show/54098.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "PSORT II Prediction". https://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html.
- ↑ "Motif Scan" (in en). https://myhits.sib.swiss/cgi-bin/motif_scan.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "TimeTree :: The Timescale of Life" (in en). http://www.timetree.org.
- ↑ "Evolution and organization of the fibrinogen locus on chromosome 4: gene duplication accompanied by transposition and inversion". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 82 (8): 2344–2348. April 1985. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.8.2344. PMID 2986113. Bibcode: 1985PNAS...82.2344K.
- ↑ "The structures of cytochrome c and the rates of molecular evolution". Journal of Molecular Evolution 1 (1): 26–45. 1971-03-01. doi:10.1007/BF01659392. PMID 4377446. Bibcode: 1971JMolE...1...26D.
- ↑ "MROH7 maestro heat like repeat family member 7 [Homo sapiens (human) - Gene - NCBI"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=DetailsSearch&Term=374977.
- ↑ "Dual proteome-scale networks reveal cell-specific remodeling of the human interactome". Cell 184 (11): 3022–3040.e28. May 2021. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.011. PMID 33961781.
- ↑ "E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF123 targets lamin B1 and lamin-binding proteins". The FEBS Journal 285 (12): 2243–2262. June 2018. doi:10.1111/febs.14477. PMID 29676528.
- ↑ "Histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit cervical cancer growth through Parkin acetylation-mediated mitophagy". Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 12 (2): 838–852. February 2022. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.003. PMID 35256949.
- ↑ "GLO1 Gene - GeneCards | LGUL Protein | LGUL Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=GLO1.
- ↑ "Profiling of 3D Genome Organization in Nasopharyngeal Cancer Needle Biopsy Patient Samples by a Modified Hi-C Approach". Frontiers in Genetics 12: 673530. 2021. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.673530. PMID 34539729.
- ↑ "Molecular and functional characterization of flavin-containing monooxygenases in cynomolgus macaque". Biochemical Pharmacology 85 (12): 1837–1847. June 2013. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.04.012. PMID 23623750.
- ↑ "Novel necroptosis-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma". Aging 14 (2): 869–891. January 2022. doi:10.18632/aging.203846. PMID 35077391.
- ↑ "Identification and analysis of necroptosis-associated signatures for prognostic and immune microenvironment evaluation in hepatocellular carcinoma". Frontiers in Immunology 13: 973649. 2022. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.973649. PMID 36081504.
- ↑ "Copy number alterations associated with clinical features in an underrepresented population with breast cancer". Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine 7 (7): e00750. July 2019. doi:10.1002/mgg3.750. PMID 31099189.
- ↑ "miR-3646 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via regulating G2/M transition in human breast cancer cells". American Journal of Translational Research 8 (4): 1659–1677. 2016-04-15. PMID 27186291.
- ↑ "A multiethnic genome-wide analysis of 44,039 individuals identifies 41 new loci associated with central corneal thickness". Communications Biology 3 (1): 301. June 2020. doi:10.1038/s42003-020-1037-7. PMID 32528159.
- ↑ "Identification of 38 novel loci for systemic lupus erythematosus and genetic heterogeneity between ancestral groups". Nature Communications 12 (1): 772. February 2021. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21049-y. PMID 33536424. Bibcode: 2021NatCo..12..772W.
 |