Biology:Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (/ˌmaɪtəˈkɒndriən/;[1] pl.: mitochondria) is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy.[2] They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857[3] in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term mitochondrion was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.[4]
Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures.[5] The eukaryote Monocercomonoides is known to have completely lost its mitochondria,[6] and the multicellular organism Henneguya salminicola is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles in association with a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome.[6][7][8]
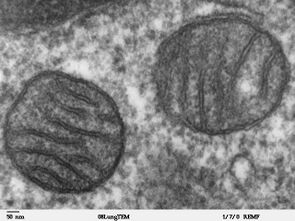
Mitochondria are commonly between 0.75 and 3 μm2 in cross section,[9] but vary considerably in size and structure. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth.[10] Mitochondrial biogenesis is in turn temporally coordinated with these cellular processes.[11][12] Mitochondria have been implicated in several human disorders and conditions, such as mitochondrial diseases,[13] cardiac dysfunction,[14] heart failure[15] and autism.[16]
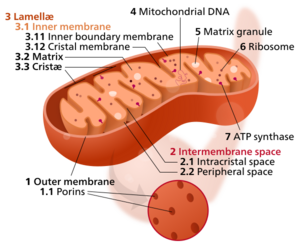
The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. A mature red blood cell has no mitochondria,[17] whereas a liver cell can have more than 2000.[18][19] The mitochondrion is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix.
Although most of a eukaryotic cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own genome ("mitogenome") that is substantially similar to bacterial genomes.[20] This finding has led to general acceptance of the endosymbiotic hypothesis - that free-living prokaryotic ancestors of modern mitochondria permanently fused with eukaryotic cells in the distant past, evolving such that modern animals, plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes are able to respire to generate cellular energy.[21]
Structure
| Cell biology | |
|---|---|
| The mitochondrion | |
 Components of a typical mitochondrion
3 Lamella
4 Mitochondrial DNA |
Mitochondria may have a number of different shapes.[22] A mitochondrion contains outer and inner membranes composed of phospholipid bilayers and proteins.[18] The two membranes have different properties. Because of this double-membraned organization, there are five distinct parts to a mitochondrion:
- The outer mitochondrial membrane,
- The intermembrane space (the space between the outer and inner membranes),
- The inner mitochondrial membrane,
- The cristae space (formed by infoldings of the inner membrane), and
- The matrix (space within the inner membrane), which is a fluid.
Mitochondria have folding to increase surface area, which in turn increases ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production. Mitochondria stripped of their outer membrane are called mitoplasts.
Outer membrane
The outer mitochondrial membrane, which encloses the entire organelle, is 60 to 75 angstroms (Å) thick. It has a protein-to-phospholipid ratio similar to that of the cell membrane (about 1:1 by weight). It contains large numbers of integral membrane proteins called porins. A major trafficking protein is the pore-forming voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). The VDAC is the primary transporter of nucleotides, ions and metabolites between the cytosol and the intermembrane space.[23][24] It is formed as a beta barrel that spans the outer membrane, similar to that in the gram-negative bacterial membrane.[25] Larger proteins can enter the mitochondrion if a signaling sequence at their N-terminus binds to a large multisubunit protein called translocase in the outer membrane, which then actively moves them across the membrane.[26] Mitochondrial pro-proteins are imported through specialised translocation complexes.
The outer membrane also contains enzymes involved in such diverse activities as the elongation of fatty acids, oxidation of epinephrine, and the degradation of tryptophan. These enzymes include monoamine oxidase, rotenone-insensitive NADH-cytochrome c-reductase, kynurenine hydroxylase and fatty acid Co-A ligase. Disruption of the outer membrane permits proteins in the intermembrane space to leak into the cytosol, leading to cell death.[27] The outer mitochondrial membrane can associate with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, in a structure called MAM (mitochondria-associated ER-membrane). This is important in the ER-mitochondria calcium signaling and is involved in the transfer of lipids between the ER and mitochondria.[28] Outside the outer membrane are small (diameter: 60 Å) particles named sub-units of Parson.
Intermembrane space
The mitochondrial intermembrane space is the space between the outer membrane and the inner membrane. It is also known as perimitochondrial space. Because the outer membrane is freely permeable to small molecules, the concentrations of small molecules, such as ions and sugars, in the intermembrane space is the same as in the cytosol.[18] However, large proteins must have a specific signaling sequence to be transported across the outer membrane, so the protein composition of this space is different from the protein composition of the cytosol. One protein that is localized to the intermembrane space in this way is cytochrome c.[27]
Inner membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane contains proteins with three types of functions:[18]
- Those that perform the electron transport chain redox reactions
- ATP synthase, which generates ATP in the matrix
- Specific transport proteins that regulate metabolite passage into and out of the mitochondrial matrix
It contains more than 151 different polypeptides, and has a very high protein-to-phospholipid ratio (more than 3:1 by weight, which is about 1 protein for 15 phospholipids). The inner membrane is home to around 1/5 of the total protein in a mitochondrion.[29] Additionally, the inner membrane is rich in an unusual phospholipid, cardiolipin. This phospholipid was originally discovered in cow hearts in 1942, and is usually characteristic of mitochondrial and bacterial plasma membranes.[30] Cardiolipin contains four fatty acids rather than two, and may help to make the inner membrane impermeable,[18] and its disruption can lead to multiple clinical disorders including neurological disorders and cancer.[31] Unlike the outer membrane, the inner membrane does not contain porins, and is highly impermeable to all molecules. Almost all ions and molecules require special membrane transporters to enter or exit the matrix. Proteins are ferried into the matrix via the translocase of the inner membrane (TIM) complex or via OXA1L.[26] In addition, there is a membrane potential across the inner membrane, formed by the action of the enzymes of the electron transport chain. Inner membrane fusion is mediated by the inner membrane protein OPA1.[32]
Cristae
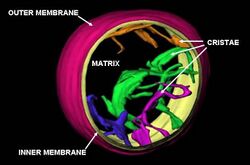
The inner mitochondrial membrane is compartmentalized into numerous folds called cristae, which expand the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, enhancing its ability to produce ATP. For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about five times as large as that of the outer membrane. This ratio is variable and mitochondria from cells that have a greater demand for ATP, such as muscle cells, contain even more cristae. Mitochondria within the same cell can have substantially different crista-density, with the ones that are required to produce more energy having much more crista-membrane surface.[33] These folds are studded with small round bodies known as F1 particles or oxysomes.[34]
Matrix
The matrix is the space enclosed by the inner membrane. It contains about 2/3 of the total proteins in a mitochondrion.[18] The matrix is important in the production of ATP with the aid of the ATP synthase contained in the inner membrane. The matrix contains a highly concentrated mixture of hundreds of enzymes, special mitochondrial ribosomes, tRNA, and several copies of the mitochondrial DNA genome. Of the enzymes, the major functions include oxidation of pyruvate and fatty acids, and the citric acid cycle.[18] The DNA molecules are packaged into nucleoids by proteins, one of which is TFAM.[35]
Function
The most prominent roles of mitochondria are to produce the energy currency of the cell, ATP (i.e., phosphorylation of ADP), through respiration and to regulate cellular metabolism.[19] The central set of reactions involved in ATP production are collectively known as the citric acid cycle, or the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. However, the mitochondrion has many other functions in addition to the production of ATP.
Energy conversion
A dominant role for the mitochondria is the production of ATP, as reflected by the large number of proteins in the inner membrane for this task. This is done by oxidizing the major products of glucose: pyruvate, and NADH, which are produced in the cytosol.[19] This type of cellular respiration, known as aerobic respiration, is dependent on the presence of oxygen. When oxygen is limited, the glycolytic products will be metabolized by anaerobic fermentation, a process that is independent of the mitochondria.[19] The production of ATP from glucose and oxygen has an approximately 13-times higher yield during aerobic respiration compared to fermentation.[36] Plant mitochondria can also produce a limited amount of ATP either by breaking the sugar produced during photosynthesis or without oxygen by using the alternate substrate nitrite.[37] ATP crosses out through the inner membrane with the help of a specific protein, and across the outer membrane via porins.[38] After conversion of ATP to ADP by dephosphorylation that releases energy, ADP returns via the same route.
Pyruvate and the citric acid cycle
Pyruvate molecules produced by glycolysis are actively transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and into the matrix where they can either be oxidized and combined with coenzyme A to form CO2, acetyl-CoA, and NADH,[19] or they can be carboxylated (by pyruvate carboxylase) to form oxaloacetate. This latter reaction "fills up" the amount of oxaloacetate in the citric acid cycle and is therefore an anaplerotic reaction, increasing the cycle's capacity to metabolize acetyl-CoA when the tissue's energy needs (e.g., in muscle) are suddenly increased by activity.[39]
In the citric acid cycle, all the intermediates (e.g. citrate, iso-citrate, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinate, fumarate, malate and oxaloacetate) are regenerated during each turn of the cycle. Adding more of any of these intermediates to the mitochondrion therefore means that the additional amount is retained within the cycle, increasing all the other intermediates as one is converted into the other. Hence, the addition of any one of them to the cycle has an anaplerotic effect, and its removal has a cataplerotic effect. These anaplerotic and cataplerotic reactions will, during the course of the cycle, increase or decrease the amount of oxaloacetate available to combine with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. This in turn increases or decreases the rate of ATP production by the mitochondrion, and thus the availability of ATP to the cell.[39]
Acetyl-CoA, on the other hand, derived from pyruvate oxidation, or from the beta-oxidation of fatty acids, is the only fuel to enter the citric acid cycle. With each turn of the cycle one molecule of acetyl-CoA is consumed for every molecule of oxaloacetate present in the mitochondrial matrix, and is never regenerated. It is the oxidation of the acetate portion of acetyl-CoA that produces CO2 and water, with the energy thus released captured in the form of ATP.[39]
In the liver, the carboxylation of cytosolic pyruvate into intra-mitochondrial oxaloacetate is an early step in the gluconeogenic pathway, which converts lactate and de-aminated alanine into glucose,[19][39] under the influence of high levels of glucagon and/or epinephrine in the blood.[39] Here, the addition of oxaloacetate to the mitochondrion does not have a net anaplerotic effect, as another citric acid cycle intermediate (malate) is immediately removed from the mitochondrion to be converted to cytosolic oxaloacetate, and ultimately to glucose, in a process that is almost the reverse of glycolysis.[39]
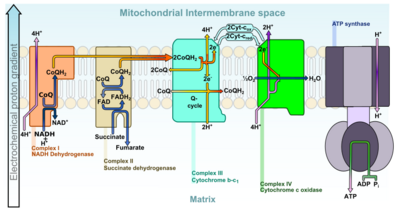
The enzymes of the citric acid cycle are located in the mitochondrial matrix, with the exception of succinate dehydrogenase, which is bound to the inner mitochondrial membrane as part of Complex II.[40] The citric acid cycle oxidizes the acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide, and, in the process, produces reduced cofactors (three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH2) that are a source of electrons for the electron transport chain, and a molecule of GTP (which is readily converted to an ATP).[19]
O2 and NADH: energy-releasing reactions
The electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred to oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (protons) in several steps via an electron transport chain. NADH and FADH2 molecules are produced within the matrix via the citric acid cycle and in the cytoplasm by glycolysis. Reducing equivalents from the cytoplasm can be imported via the malate-aspartate shuttle system of antiporter proteins or fed into the electron transport chain using a glycerol phosphate shuttle.[19]
The major energy-releasing reactions [41][42] that make the mitochondrion the "powerhouse of the cell" occur at protein complexes I, III and IV in the inner mitochondrial membrane (NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), cytochrome c reductase, and cytochrome c oxidase). At complex IV, O2 reacts with the reduced form of iron in cytochrome c:
[math]\ce{ O2{} + 4H+(aq){} + 4 Fe^{2+}(cyt\,c) -> 2H2O{} + 4 Fe^{3+}(cyt\,c) }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta_r G^{o'}=-218 \text{ kJ/mol} }[/math]
releasing a lot of free energy[42][41] from the reactants without breaking bonds of an organic fuel. The free energy put in to remove an electron from Fe2+ is released at complex III when Fe3+ of cytochrome c reacts to oxidize ubiquinol (QH2):
[math]\ce{ 2 Fe^{3+}(cyt\,c){} + QH2 -> 2 Fe^{2+}(cyt\,c){} + Q{} + 2H+(aq) }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta_r G^{o'}=-30 \text{ kJ/mol} }[/math]
The ubiquinone (Q) generated reacts, in complex I, with NADH:
[math]\ce{ Q + H+(aq){} + NADH -> QH2 + NAD+ { } }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta_r G^{o'}=-81 \text{ kJ/mol} }[/math]
While the reactions are controlled by an electron transport chain, free electrons are not amongst the reactants or products in the three reactions shown and therefore do not affect the free energy released, which is used to pump protons (H+) into the intermembrane space. This process is efficient, but a small percentage of electrons may prematurely reduce oxygen, forming reactive oxygen species such as superoxide.[19] This can cause oxidative stress in the mitochondria and may contribute to the decline in mitochondrial function associated with aging.[43]
As the proton concentration increases in the intermembrane space, a strong electrochemical gradient is established across the inner membrane. The protons can return to the matrix through the ATP synthase complex, and their potential energy is used to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).[19] This process is called chemiosmosis, and was first described by Peter Mitchell,[44][45] who was awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work. Later, part of the 1997 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Paul D. Boyer and John E. Walker for their clarification of the working mechanism of ATP synthase.[46]
Heat production
Under certain conditions, protons can re-enter the mitochondrial matrix without contributing to ATP synthesis. This process is known as proton leak or mitochondrial uncoupling and is due to the facilitated diffusion of protons into the matrix. The process results in the unharnessed potential energy of the proton electrochemical gradient being released as heat.[19] The process is mediated by a proton channel called thermogenin, or UCP1.[47] Thermogenin is primarily found in brown adipose tissue, or brown fat, and is responsible for non-shivering thermogenesis. Brown adipose tissue is found in mammals, and is at its highest levels in early life and in hibernating animals. In humans, brown adipose tissue is present at birth and decreases with age.[47]
Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis
Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFASII) is essential for cellular respiration and mitochondrial biogenesis.[48] It is also thought to play a role as a mediator in intracellular signaling due to its influence on the levels of bioactive lipids, such as lysophospholipids and sphingolipids.[49]
Octanoyl-ACP (C8) is considered to be the most important end product of mtFASII, which also forms the starting substrate of lipoic acid biosynthesis.[50] Since lipoic acid is the cofactor of important mitochondrial enzyme complexes, such as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (OGDC), branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC), and in the glycine cleavage system (GCS), mtFASII has an influence on energy metabolism.[51]
Other products of mtFASII play a role in the regulation of mitochondrial translation, FeS cluster biogenesis and assembly of oxidative phosphorylation complexes.[50]
Furthermore, with the help of mtFASII and acylated ACP, acetyl-CoA regulates its consumption in mitochondria.[50]
Uptake, storage and release of calcium ions
The concentrations of free calcium in the cell can regulate an array of reactions and is important for signal transduction in the cell. Mitochondria can transiently store calcium, a contributing process for the cell's homeostasis of calcium.[52] [53] Their ability to rapidly take in calcium for later release makes them good "cytosolic buffers" for calcium.[54][55][56] The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the most significant storage site of calcium,[57] and there is a significant interplay between the mitochondrion and ER with regard to calcium.[58] The calcium is taken up into the matrix by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter on the inner mitochondrial membrane.[59] It is primarily driven by the mitochondrial membrane potential.[53] Release of this calcium back into the cell's interior can occur via a sodium-calcium exchange protein or via "calcium-induced-calcium-release" pathways.[59] This can initiate calcium spikes or calcium waves with large changes in the membrane potential. These can activate a series of second messenger system proteins that can coordinate processes such as neurotransmitter release in nerve cells and release of hormones in endocrine cells.[60]
Ca2+ influx to the mitochondrial matrix has recently been implicated as a mechanism to regulate respiratory bioenergetics by allowing the electrochemical potential across the membrane to transiently "pulse" from ΔΨ-dominated to pH-dominated, facilitating a reduction of oxidative stress.[61] In neurons, concomitant increases in cytosolic and mitochondrial calcium act to synchronize neuronal activity with mitochondrial energy metabolism. Mitochondrial matrix calcium levels can reach the tens of micromolar levels, which is necessary for the activation of isocitrate dehydrogenase, one of the key regulatory enzymes of the Krebs cycle.[62]
Cellular proliferation regulation
The relationship between cellular proliferation and mitochondria has been investigated. Tumor cells require ample ATP to synthesize bioactive compounds such as lipids, proteins, and nucleotides for rapid proliferation.[63] The majority of ATP in tumor cells is generated via the oxidative phosphorylation pathway (OxPhos).[64] Interference with OxPhos cause cell cycle arrest suggesting that mitochondria play a role in cell proliferation.[64] Mitochondrial ATP production is also vital for cell division and differentiation in infection [65] in addition to basic functions in the cell including the regulation of cell volume, solute concentration, and cellular architecture.[66][67][68] ATP levels differ at various stages of the cell cycle suggesting that there is a relationship between the abundance of ATP and the cell's ability to enter a new cell cycle.[69] ATP's role in the basic functions of the cell make the cell cycle sensitive to changes in the availability of mitochondrial derived ATP.[69] The variation in ATP levels at different stages of the cell cycle support the hypothesis that mitochondria play an important role in cell cycle regulation.[69] Although the specific mechanisms between mitochondria and the cell cycle regulation is not well understood, studies have shown that low energy cell cycle checkpoints monitor the energy capability before committing to another round of cell division.[10]
Additional functions
Mitochondria play a central role in many other metabolic tasks, such as:
- Signaling through mitochondrial reactive oxygen species[70]
- Regulation of the membrane potential[19]
- Apoptosis-programmed cell death[71]
- Calcium signaling (including calcium-evoked apoptosis)[72]
- Regulation of cellular metabolism[10]
- Certain heme synthesis reactions[73] (see also: Porphyrin)
- Steroid synthesis[54]
- Hormonal signaling[74] – mitochondria are sensitive and responsive to hormones, in part by the action of mitochondrial estrogen receptors (mtERs). These receptors have been found in various tissues and cell types, including brain[75] and heart[76]
- Immune signaling[77]
- Neuronal mitochondria also contribute to cellular quality control by reporting neuronal status towards microglia through specialised somatic-junctions.[78]
- Mitochondria of developing neurons contribute to intercellular signaling towards microglia, which communication is indispensable for proper regulation of brain development.[79]
Some mitochondrial functions are performed only in specific types of cells. For example, mitochondria in liver cells contain enzymes that allow them to detoxify ammonia, a waste product of protein metabolism. A mutation in the genes regulating any of these functions can result in mitochondrial diseases.
Mitochondrial proteins (proteins transcribed from mitochondrial DNA) vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of proteins have been identified from cardiac mitochondria,[80] whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported.[81] The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated.[82]
Organization and distribution
File:HeLa mtGFP.tif Mitochondria (or related structures) are found in all eukaryotes (except the Oxymonad Monocercomonoides).[6] Although commonly depicted as bean-like structures they form a highly dynamic network in the majority of cells where they constantly undergo fission and fusion. The population of all the mitochondria of a given cell constitutes the chondriome.[83] Mitochondria vary in number and location according to cell type. A single mitochondrion is often found in unicellular organisms, while human liver cells have about 1000–2000 mitochondria per cell, making up 1/5 of the cell volume.[18] The mitochondrial content of otherwise similar cells can vary substantially in size and membrane potential,[84] with differences arising from sources including uneven partitioning at cell division, leading to extrinsic differences in ATP levels and downstream cellular processes.[85] The mitochondria can be found nestled between myofibrils of muscle or wrapped around the sperm flagellum.[18] Often, they form a complex 3D branching network inside the cell with the cytoskeleton. The association with the cytoskeleton determines mitochondrial shape, which can affect the function as well:[86] different structures of the mitochondrial network may afford the population a variety of physical, chemical, and signalling advantages or disadvantages.[87] Mitochondria in cells are always distributed along microtubules and the distribution of these organelles is also correlated with the endoplasmic reticulum.[88] Recent evidence suggests that vimentin, one of the components of the cytoskeleton, is also critical to the association with the cytoskeleton.[89]
Mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM)
The mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM) is another structural element that is increasingly recognized for its critical role in cellular physiology and homeostasis. Once considered a technical snag in cell fractionation techniques, the alleged ER vesicle contaminants that invariably appeared in the mitochondrial fraction have been re-identified as membranous structures derived from the MAM—the interface between mitochondria and the ER.[90] Physical coupling between these two organelles had previously been observed in electron micrographs and has more recently been probed with fluorescence microscopy.[90] Such studies estimate that at the MAM, which may comprise up to 20% of the mitochondrial outer membrane, the ER and mitochondria are separated by a mere 10–25 nm and held together by protein tethering complexes.[90][28][91]
Purified MAM from subcellular fractionation is enriched in enzymes involved in phospholipid exchange, in addition to channels associated with Ca2+ signaling.[90][91] These hints of a prominent role for the MAM in the regulation of cellular lipid stores and signal transduction have been borne out, with significant implications for mitochondrial-associated cellular phenomena, as discussed below. Not only has the MAM provided insight into the mechanistic basis underlying such physiological processes as intrinsic apoptosis and the propagation of calcium signaling, but it also favors a more refined view of the mitochondria. Though often seen as static, isolated 'powerhouses' hijacked for cellular metabolism through an ancient endosymbiotic event, the evolution of the MAM underscores the extent to which mitochondria have been integrated into overall cellular physiology, with intimate physical and functional coupling to the endomembrane system.
Phospholipid transfer
The MAM is enriched in enzymes involved in lipid biosynthesis, such as phosphatidylserine synthase on the ER face and phosphatidylserine decarboxylase on the mitochondrial face.[92][93] Because mitochondria are dynamic organelles constantly undergoing fission and fusion events, they require a constant and well-regulated supply of phospholipids for membrane integrity.[94][95] But mitochondria are not only a destination for the phospholipids they finish synthesis of; rather, this organelle also plays a role in inter-organelle trafficking of the intermediates and products of phospholipid biosynthetic pathways, ceramide and cholesterol metabolism, and glycosphingolipid anabolism.[93][95]
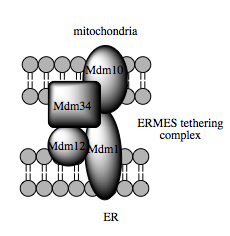
Such trafficking capacity depends on the MAM, which has been shown to facilitate transfer of lipid intermediates between organelles.[92] In contrast to the standard vesicular mechanism of lipid transfer, evidence indicates that the physical proximity of the ER and mitochondrial membranes at the MAM allows for lipid flipping between opposed bilayers.[95] Despite this unusual and seemingly energetically unfavorable mechanism, such transport does not require ATP.[95] Instead, in yeast, it has been shown to be dependent on a multiprotein tethering structure termed the ER-mitochondria encounter structure, or ERMES, although it remains unclear whether this structure directly mediates lipid transfer or is required to keep the membranes in sufficiently close proximity to lower the energy barrier for lipid flipping.[95][96]
The MAM may also be part of the secretory pathway, in addition to its role in intracellular lipid trafficking. In particular, the MAM appears to be an intermediate destination between the rough ER and the Golgi in the pathway that leads to very-low-density lipoprotein, or VLDL, assembly and secretion.[93][97] The MAM thus serves as a critical metabolic and trafficking hub in lipid metabolism.
Calcium signaling
A critical role for the ER in calcium signaling was acknowledged before such a role for the mitochondria was widely accepted, in part because the low affinity of Ca2+ channels localized to the outer mitochondrial membrane seemed to contradict this organelle's purported responsiveness to changes in intracellular Ca2+ flux.[90][57] But the presence of the MAM resolves this apparent contradiction: the close physical association between the two organelles results in Ca2+ microdomains at contact points that facilitate efficient Ca2+ transmission from the ER to the mitochondria.[90] Transmission occurs in response to so-called "Ca2+ puffs" generated by spontaneous clustering and activation of IP3R, a canonical ER membrane Ca2+ channel.[90][28]
The fate of these puffs—in particular, whether they remain restricted to isolated locales or integrated into Ca2+ waves for propagation throughout the cell—is determined in large part by MAM dynamics. Although reuptake of Ca2+ by the ER (concomitant with its release) modulates the intensity of the puffs, thus insulating mitochondria to a certain degree from high Ca2+ exposure, the MAM often serves as a firewall that essentially buffers Ca2+ puffs by acting as a sink into which free ions released into the cytosol can be funneled.[90][98][99] This Ca2+ tunneling occurs through the low-affinity Ca2+ receptor VDAC1, which recently has been shown to be physically tethered to the IP3R clusters on the ER membrane and enriched at the MAM.[90][28][100] The ability of mitochondria to serve as a Ca2+ sink is a result of the electrochemical gradient generated during oxidative phosphorylation, which makes tunneling of the cation an exergonic process.[100] Normal, mild calcium influx from cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix causes transient depolarization that is corrected by pumping out protons.
But transmission of Ca2+ is not unidirectional; rather, it is a two-way street.[57] The properties of the Ca2+ pump SERCA and the channel IP3R present on the ER membrane facilitate feedback regulation coordinated by MAM function. In particular, the clearance of Ca2+ by the MAM allows for spatio-temporal patterning of Ca2+ signaling because Ca2+ alters IP3R activity in a biphasic manner.[90] SERCA is likewise affected by mitochondrial feedback: uptake of Ca2+ by the MAM stimulates ATP production, thus providing energy that enables SERCA to reload the ER with Ca2+ for continued Ca2+ efflux at the MAM.[98][100] Thus, the MAM is not a passive buffer for Ca2+ puffs; rather it helps modulate further Ca2+ signaling through feedback loops that affect ER dynamics.
Regulating ER release of Ca2+ at the MAM is especially critical because only a certain window of Ca2+ uptake sustains the mitochondria, and consequently the cell, at homeostasis. Sufficient intraorganelle Ca2+ signaling is required to stimulate metabolism by activating dehydrogenase enzymes critical to flux through the citric acid cycle.[101][102] However, once Ca2+ signaling in the mitochondria passes a certain threshold, it stimulates the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in part by collapsing the mitochondrial membrane potential required for metabolism.[90] Studies examining the role of pro- and anti-apoptotic factors support this model; for example, the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 has been shown to interact with IP3Rs to reduce Ca2+ filling of the ER, leading to reduced efflux at the MAM and preventing collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential post-apoptotic stimuli.[90] Given the need for such fine regulation of Ca2+ signaling, it is perhaps unsurprising that dysregulated mitochondrial Ca2+ has been implicated in several neurodegenerative diseases, while the catalogue of tumor suppressors includes a few that are enriched at the MAM.[100]
Molecular basis for tethering
Recent advances in the identification of the tethers between the mitochondrial and ER membranes suggest that the scaffolding function of the molecular elements involved is secondary to other, non-structural functions. In yeast, ERMES, a multiprotein complex of interacting ER- and mitochondrial-resident membrane proteins, is required for lipid transfer at the MAM and exemplifies this principle. One of its components, for example, is also a constituent of the protein complex required for insertion of transmembrane beta-barrel proteins into the lipid bilayer.[95] However, a homologue of the ERMES complex has not yet been identified in mammalian cells. Other proteins implicated in scaffolding likewise have functions independent of structural tethering at the MAM; for example, ER-resident and mitochondrial-resident mitofusins form heterocomplexes that regulate the number of inter-organelle contact sites, although mitofusins were first identified for their role in fission and fusion events between individual mitochondria.[90] Glucose-related protein 75 (grp75) is another dual-function protein. In addition to the matrix pool of grp75, a portion serves as a chaperone that physically links the mitochondrial and ER Ca2+ channels VDAC and IP3R for efficient Ca2+ transmission at the MAM.[90][28] Another potential tether is Sigma-1R, a non-opioid receptor whose stabilization of ER-resident IP3R may preserve communication at the MAM during the metabolic stress response.[103][104]
Perspective
The MAM is a critical signaling, metabolic, and trafficking hub in the cell that allows for the integration of ER and mitochondrial physiology. Coupling between these organelles is not simply structural but functional as well and critical for overall cellular physiology and homeostasis. The MAM thus offers a perspective on mitochondria that diverges from the traditional view of this organelle as a static, isolated unit appropriated for its metabolic capacity by the cell.[105] Instead, this mitochondrial-ER interface emphasizes the integration of the mitochondria, the product of an endosymbiotic event, into diverse cellular processes. Recently it has also been shown, that mitochondria and MAM-s in neurons are anchored to specialised intercellular communication sites (so called somatic-junctions). Microglial processes monitor and protect neuronal functions at these sites, and MAM-s are supposed to have an important role in this type of cellular quality-control.[78]
Origin and evolution
There are two hypotheses about the origin of mitochondria: endosymbiotic and autogenous. The endosymbiotic hypothesis suggests that mitochondria were originally prokaryotic cells, capable of implementing oxidative mechanisms that were not possible for eukaryotic cells; they became endosymbionts living inside the eukaryote.[21][106][107][108] In the autogenous hypothesis, mitochondria were born by splitting off a portion of DNA from the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell at the time of divergence with the prokaryotes; this DNA portion would have been enclosed by membranes, which could not be crossed by proteins. Since mitochondria have many features in common with bacteria, the endosymbiotic hypothesis is the more widely accepted of the two accounts.[108][109]
A mitochondrion contains DNA, which is organized as several copies of a single, usually circular chromosome. This mitochondrial chromosome contains genes for redox proteins, such as those of the respiratory chain. The CoRR hypothesis proposes that this co-location is required for redox regulation. The mitochondrial genome codes for some RNAs of ribosomes, and the 22 tRNAs necessary for the translation of mRNAs into protein. The circular structure is also found in prokaryotes. The proto-mitochondrion was probably closely related to Rickettsia.[110][111] However, the exact relationship of the ancestor of mitochondria to the alphaproteobacteria and whether the mitochondrion was formed at the same time or after the nucleus, remains controversial.[112] For example, it has been suggested that the SAR11 clade of bacteria shares a relatively recent common ancestor with the mitochondria,[113] while phylogenomic analyses indicate that mitochondria evolved from a Pseudomonadota lineage that is closely related to or a member of alphaproteobacteria.[114][115] Some papers describe mitochondria as sister to the alphaproteobactera, together forming the sister the marineproteo1 group, together forming the sister to Magnetococcidae.[116][117][118][119]
| Proteobacteria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The ribosomes coded for by the mitochondrial DNA are similar to those from bacteria in size and structure.[120] They closely resemble the bacterial 70S ribosome and not the 80S cytoplasmic ribosomes, which are coded for by nuclear DNA.
The endosymbiotic relationship of mitochondria with their host cells was popularized by Lynn Margulis.[121] The endosymbiotic hypothesis suggests that mitochondria descended from aerobic bacteria that somehow survived endocytosis by another cell, and became incorporated into the cytoplasm. The ability of these bacteria to conduct respiration in host cells that had relied on glycolysis and fermentation would have provided a considerable evolutionary advantage. This symbiotic relationship probably developed 1.7 to 2 billion years ago.[122][123]
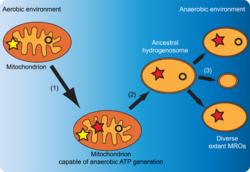
A few groups of unicellular eukaryotes have only vestigial mitochondria or derived structures: The microsporidians, metamonads, and archamoebae.[124] These groups appear as the most primitive eukaryotes on phylogenetic trees constructed using rRNA information, which once suggested that they appeared before the origin of mitochondria. However, this is now known to be an artifact of long-branch attraction: They are derived groups and retain genes or organelles derived from mitochondria (e. g., mitosomes and hydrogenosomes).[5] Hydrogenosomes, mitosomes, and related organelles as found in some loricifera (e. g. Spinoloricus)[125][126] and myxozoa (e. g. Henneguya zschokkei) are together classified as MROs, mitochondrion-related organelles.[8][127]
Monocercomonoides appear to have lost their mitochondria completely and at least some of the mitochondrial functions seem to be carried out by cytoplasmic proteins now.[6]
Mitochondrial genetics
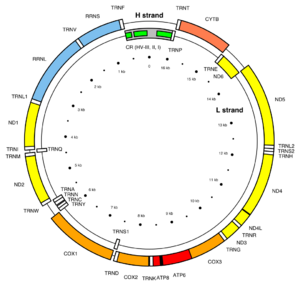
Mitochondria contain their own genome. The human mitochondrial genome is a circular double-stranded DNA molecule of about 16 kilobases.[128] It encodes 37 genes: 13 for subunits of respiratory complexes I, III, IV and V, 22 for mitochondrial tRNA (for the 20 standard amino acids, plus an extra gene for leucine and serine), and 2 for rRNA (12S and 16S rRNA).[128] One mitochondrion can contain two to ten copies of its DNA.[129] One of the two mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) strands has a disproportionately higher ratio of the heavier nucleotides adenine and guanine, and this is termed the heavy strand (or H strand), whereas the other strand is termed the light strand (or L strand). The weight difference allows the two strands to be separated by centrifugation. mtDNA has one long non-coding stretch known as the non-coding region (NCR), which contains the heavy strand promoter (HSP) and light strand promoter (LSP) for RNA transcription, the origin of replication for the H strand (OriH) localized on the L strand, three conserved sequence boxes (CSBs 1–3), and a termination-associated sequence (TAS). The origin of replication for the L strand (OriL) is localized on the H strand 11,000 bp downstream of OriH, located within a cluster of genes coding for tRNA.[130]
As in prokaryotes, there is a very high proportion of coding DNA and an absence of repeats. Mitochondrial genes are transcribed as multigenic transcripts, which are cleaved and polyadenylated to yield mature mRNAs. Most proteins necessary for mitochondrial function are encoded by genes in the cell nucleus and the corresponding proteins are imported into the mitochondrion.[131] The exact number of genes encoded by the nucleus and the mitochondrial genome differs between species. Most mitochondrial genomes are circular.[132] In general, mitochondrial DNA lacks introns, as is the case in the human mitochondrial genome;[131] however, introns have been observed in some eukaryotic mitochondrial DNA,[133] such as that of yeast[134] and protists,[135] including Dictyostelium discoideum.[136] Between protein-coding regions, tRNAs are present. Mitochondrial tRNA genes have different sequences from the nuclear tRNAs, but lookalikes of mitochondrial tRNAs have been found in the nuclear chromosomes with high sequence similarity.[137]
In animals, the mitochondrial genome is typically a single circular chromosome that is approximately 16 kb long and has 37 genes. The genes, while highly conserved, may vary in location. Curiously, this pattern is not found in the human body louse (Pediculus humanus). Instead, this mitochondrial genome is arranged in 18 minicircular chromosomes, each of which is 3–4 kb long and has one to three genes.[138] This pattern is also found in other sucking lice, but not in chewing lice. Recombination has been shown to occur between the minichromosomes.
Human population genetic studies
The near-absence of genetic recombination in mitochondrial DNA makes it a useful source of information for studying population genetics and evolutionary biology.[139] Because all the mitochondrial DNA is inherited as a single unit, or haplotype, the relationships between mitochondrial DNA from different individuals can be represented as a gene tree. Patterns in these gene trees can be used to infer the evolutionary history of populations. The classic example of this is in human evolutionary genetics, where the molecular clock can be used to provide a recent date for mitochondrial Eve.[140][141] This is often interpreted as strong support for a recent modern human expansion out of Africa.[142] Another human example is the sequencing of mitochondrial DNA from Neanderthal bones. The relatively large evolutionary distance between the mitochondrial DNA sequences of Neanderthals and living humans has been interpreted as evidence for the lack of interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans.[143]
However, mitochondrial DNA reflects only the history of the females in a population. This can be partially overcome by the use of paternal genetic sequences, such as the non-recombining region of the Y-chromosome.[142]
Recent measurements of the molecular clock for mitochondrial DNA[144] reported a value of 1 mutation every 7884 years dating back to the most recent common ancestor of humans and apes, which is consistent with estimates of mutation rates of autosomal DNA (10−8 per base per generation).[145]
Alternative genetic code
| Organism | Codon | Standard | Mitochondria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mammals | AGA, AGG | Arginine | Stop codon |
| Invertebrates | AGA, AGG | Arginine | Serine |
| Fungi | CUA | Leucine | Threonine |
| All of the above | AUA | Isoleucine | Methionine |
| UGA | Stop codon | Tryptophan |
While slight variations on the standard genetic code had been predicted earlier,[146] none was discovered until 1979, when researchers studying human mitochondrial genes determined that they used an alternative code.[147] Nonetheless, the mitochondria of many other eukaryotes, including most plants, use the standard code.[148] Many slight variants have been discovered since,[148] including various alternative mitochondrial codes.[149] Further, the AUA, AUC, and AUU codons are all allowable start codons.
Some of these differences should be regarded as pseudo-changes in the genetic code due to the phenomenon of RNA editing, which is common in mitochondria. In higher plants, it was thought that CGG encoded for tryptophan and not arginine; however, the codon in the processed RNA was discovered to be the UGG codon, consistent with the standard genetic code for tryptophan.[150] Of note, the arthropod mitochondrial genetic code has undergone parallel evolution within a phylum, with some organisms uniquely translating AGG to lysine.[151]
Replication and inheritance
Mitochondria divide by mitochondrial fission, a form of binary fission that is also done by bacteria[152] although the process is tightly regulated by the host eukaryotic cell and involves communication between and contact with several other organelles. The regulation of this division differs between eukaryotes. In many single-celled eukaryotes, their growth and division are linked to the cell cycle. For example, a single mitochondrion may divide synchronously with the nucleus. This division and segregation process must be tightly controlled so that each daughter cell receives at least one mitochondrion. In other eukaryotes (in mammals for example), mitochondria may replicate their DNA and divide mainly in response to the energy needs of the cell, rather than in phase with the cell cycle. When the energy needs of a cell are high, mitochondria grow and divide. When energy use is low, mitochondria are destroyed or become inactive. In such examples mitochondria are apparently randomly distributed to the daughter cells during the division of the cytoplasm. Mitochondrial dynamics, the balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission, is an important factor in pathologies associated with several disease conditions.[153]
The hypothesis of mitochondrial binary fission has relied on the visualization by fluorescence microscopy and conventional transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The resolution of fluorescence microscopy (~200 nm) is insufficient to distinguish structural details, such as double mitochondrial membrane in mitochondrial division or even to distinguish individual mitochondria when several are close together. Conventional TEM has also some technical limitations[which?] in verifying mitochondrial division. Cryo-electron tomography was recently used to visualize mitochondrial division in frozen hydrated intact cells. It revealed that mitochondria divide by budding.[154]
An individual's mitochondrial genes are inherited only from the mother, with rare exceptions.[155] In humans, when an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm, the mitochondria, and therefore the mitochondrial DNA, usually come from the egg only. The sperm's mitochondria enter the egg, but do not contribute genetic information to the embryo.[156] Instead, paternal mitochondria are marked with ubiquitin to select them for later destruction inside the embryo.[157] The egg cell contains relatively few mitochondria, but these mitochondria divide to populate the cells of the adult organism. This mode is seen in most organisms, including the majority of animals. However, mitochondria in some species can sometimes be inherited paternally. This is the norm among certain coniferous plants, although not in pine trees and yews.[158] For Mytilids, paternal inheritance only occurs within males of the species.[159][160][161] It has been suggested that it occurs at a very low level in humans.[162]
Uniparental inheritance leads to little opportunity for genetic recombination between different lineages of mitochondria, although a single mitochondrion can contain 2–10 copies of its DNA.[129] What recombination does take place maintains genetic integrity rather than maintaining diversity. However, there are studies showing evidence of recombination in mitochondrial DNA. It is clear that the enzymes necessary for recombination are present in mammalian cells.[163] Further, evidence suggests that animal mitochondria can undergo recombination.[164] The data are more controversial in humans, although indirect evidence of recombination exists.[165][166]
Entities undergoing uniparental inheritance and with little to no recombination may be expected to be subject to Muller's ratchet, the accumulation of deleterious mutations until functionality is lost. Animal populations of mitochondria avoid this buildup through a developmental process known as the mtDNA bottleneck. The bottleneck exploits stochastic processes in the cell to increase the cell-to-cell variability in mutant load as an organism develops: a single egg cell with some proportion of mutant mtDNA thus produces an embryo where different cells have different mutant loads. Cell-level selection may then act to remove those cells with more mutant mtDNA, leading to a stabilization or reduction in mutant load between generations. The mechanism underlying the bottleneck is debated,[167][168][169] with a recent mathematical and experimental metastudy providing evidence for a combination of random partitioning of mtDNAs at cell divisions and random turnover of mtDNA molecules within the cell.[170]
DNA repair
Mitochondria can repair oxidative DNA damage by mechanisms analogous to those occurring in the cell nucleus. The proteins employed in mtDNA repair are encoded by nuclear genes, and are translocated to the mitochondria. The DNA repair pathways in mammalian mitochondria include base excision repair, double-strand break repair, direct reversal and mismatch repair.[171][172] Alternatively, DNA damage may be bypassed, rather than repaired, by translesion synthesis.
Of the several DNA repair process in mitochondria, the base excision repair pathway has been most comprehensively studied.[172] Base excision repair is carried out by a sequence of enzyme-catalyzed steps that include recognition and excision of a damaged DNA base, removal of the resulting abasic site, end processing, gap filling and ligation. A common damage in mtDNA that is repaired by base excision repair is 8-oxoguanine produced by oxidation of guanine.[173]
Double-strand breaks can be repaired by homologous recombinational repair in both mammalian mtDNA[174] and plant mtDNA.[175] Double-strand breaks in mtDNA can also be repaired by microhomology-mediated end joining.[176] Although there is evidence for the repair processes of direct reversal and mismatch repair in mtDNA, these processes are not well characterized.[172]
Lack of mitochondrial DNA
Some organisms have lost mitochondrial DNA altogether. In these cases, genes encoded by the mitochondrial DNA have been lost or transferred to the nucleus.[128] Cryptosporidium have mitochondria that lack any DNA, presumably because all their genes have been lost or transferred.[177] In Cryptosporidium, the mitochondria have an altered ATP generation system that renders the parasite resistant to many classical mitochondrial inhibitors such as cyanide, azide, and atovaquone.[177] Mitochondria that lack their own DNA have been found in a marine parasitic dinoflagellate from the genus Amoebophyra. This microorganism, A. cerati, has functional mitochondria that lack a genome.[178] In related species, the mitochondrial genome still has three genes, but in A. cerati only a single mitochondrial gene — the cytochrome c oxidase I gene (cox1) — is found, and it has migrated to the genome of the nucleus.[179]
Dysfunction and disease
Mitochondrial diseases
Damage and subsequent dysfunction in mitochondria is an important factor in a range of human diseases due to their influence in cell metabolism. Mitochondrial disorders often present as neurological disorders, including autism.[16] They can also manifest as myopathy, diabetes, multiple endocrinopathy, and a variety of other systemic disorders.[180] Diseases caused by mutation in the mtDNA include Kearns–Sayre syndrome, MELAS syndrome and Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.[181] In the vast majority of cases, these diseases are transmitted by a female to her children, as the zygote derives its mitochondria and hence its mtDNA from the ovum. Diseases such as Kearns-Sayre syndrome, Pearson syndrome, and progressive external ophthalmoplegia are thought to be due to large-scale mtDNA rearrangements, whereas other diseases such as MELAS syndrome, Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy, MERRF syndrome, and others are due to point mutations in mtDNA.[180]
It has also been reported that drug tolerant cancer cells have an increased number and size of mitochondria which suggested an increase in mitochondrial biogenesis.[182] A 2022 study in Nature Nanotechnology has reported that cancer cells can hijack the mitochondria from immune cells via physical tunneling nanotubes.[183]
In other diseases, defects in nuclear genes lead to dysfunction of mitochondrial proteins. This is the case in Friedreich's ataxia, hereditary spastic paraplegia, and Wilson's disease.[184] These diseases are inherited in a dominance relationship, as applies to most other genetic diseases. A variety of disorders can be caused by nuclear mutations of oxidative phosphorylation enzymes, such as coenzyme Q10 deficiency and Barth syndrome.[180] Environmental influences may interact with hereditary predispositions and cause mitochondrial disease. For example, there may be a link between pesticide exposure and the later onset of Parkinson's disease.[185][186] Other pathologies with etiology involving mitochondrial dysfunction include schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, dementia, Alzheimer's disease,[187][188] Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, stroke, cardiovascular disease, chronic fatigue syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa, and diabetes mellitus.[189][190]
Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress plays a role in cardiomyopathy in type 2 diabetics. Increased fatty acid delivery to the heart increases fatty acid uptake by cardiomyocytes, resulting in increased fatty acid oxidation in these cells. This process increases the reducing equivalents available to the electron transport chain of the mitochondria, ultimately increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. ROS increases uncoupling proteins (UCPs) and potentiate proton leakage through the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT), the combination of which uncouples the mitochondria. Uncoupling then increases oxygen consumption by the mitochondria, compounding the increase in fatty acid oxidation. This creates a vicious cycle of uncoupling; furthermore, even though oxygen consumption increases, ATP synthesis does not increase proportionally because the mitochondria are uncoupled. Less ATP availability ultimately results in an energy deficit presenting as reduced cardiac efficiency and contractile dysfunction. To compound the problem, impaired sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release and reduced mitochondrial reuptake limits peak cytosolic levels of the important signaling ion during muscle contraction. Decreased intra-mitochondrial calcium concentration increases dehydrogenase activation and ATP synthesis. So in addition to lower ATP synthesis due to fatty acid oxidation, ATP synthesis is impaired by poor calcium signaling as well, causing cardiac problems for diabetics.[191]
Mitochondria also modulate processes such as testicular somatic cell development, spermatogonial stem cell differentiation, luminal acidification, testosterone production in testes, and more. Thus, dysfunction of mitochondria in spermatozoa can be a cause for infertility.[192]
In efforts to combat mitochondrial disease, mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT) has been developed. This form of in vitro fertilization uses donor mitochondria, which avoids the transmission of diseases caused by mutations of mitochondrial DNA.[193] However, this therapy is still being researched and can introduce genetic modification, as well as safety concerns. These diseases are rare but can be extremely debilitating and progressive diseases, thus posing complex ethical questions for public policy.[194]
Relationships to aging
There may be some leakage of the electrons transferred in the respiratory chain to form reactive oxygen species. This was thought to result in significant oxidative stress in the mitochondria with high mutation rates of mitochondrial DNA.[195] Hypothesized links between aging and oxidative stress are not new and were proposed in 1956,[196] which was later refined into the mitochondrial free radical theory of aging.[197] A vicious cycle was thought to occur, as oxidative stress leads to mitochondrial DNA mutations, which can lead to enzymatic abnormalities and further oxidative stress.
A number of changes can occur to mitochondria during the aging process.[198] Tissues from elderly humans show a decrease in enzymatic activity of the proteins of the respiratory chain.[199] However, mutated mtDNA can only be found in about 0.2% of very old cells.[200] Large deletions in the mitochondrial genome have been hypothesized to lead to high levels of oxidative stress and neuronal death in Parkinson's disease.[201] Mitochondrial dysfunction has also been shown to occur in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.[202][203]
Since mitochondria cover a pivotal role in the ovarian function, by providing ATP necessary for the development from germinal vesicle to mature oocyte, a decreased mitochondria function can lead to inflammation, resulting in premature ovarian failure and accelerated ovarian aging. The resulting dysfunction is then reflected in quantitative (such as mtDNA copy number and mtDNA deletions), qualitative (such as mutations and strand breaks) and oxidative damage (such as dysfunctional mitochondria due to ROS), which are not only relevant in ovarian aging, but perturb oocyte-cumulus crosstalk in the ovary, are linked to genetic disorders (such as Fragile X) and can interfere with embryo selection.[204]
History
The first observations of intracellular structures that probably represented mitochondria were published in 1857, by the physiologist Albert von Kolliker.[205][206] Richard Altmann, in 1890, established them as cell organelles and called them "bioblasts."[206][207] In 1898, Carl Benda coined the term "mitochondria" from the Greek μίτος, mitos, "thread", and χονδρίον, chondrion, "granule."[208][206][209] Leonor Michaelis discovered that Janus green can be used as a supravital stain for mitochondria in 1900.[210] In 1904, Friedrich Meves made the first recorded observation of mitochondria in plants in cells of the white waterlily, Nymphaea alba,[206][211] and in 1908, along with Claudius Regaud, suggested that they contain proteins and lipids. Benjamin F. Kingsbury, in 1912, first related them with cell respiration, but almost exclusively based on morphological observations.[212][206] In 1913, Otto Heinrich Warburg linked respiration to particles which he had obtained from extracts of guinea-pig liver and which he called "grana".[213] Warburg and Heinrich Otto Wieland, who had also postulated a similar particle mechanism, disagreed on the chemical nature of the respiration. It was not until 1925, when David Keilin discovered cytochromes, that the respiratory chain was described.[206]
In 1939, experiments using minced muscle cells demonstrated that cellular respiration using one oxygen molecule can form four adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules, and in 1941, the concept of the phosphate bonds of ATP being a form of energy in cellular metabolism was developed by Fritz Albert Lipmann. In the following years, the mechanism behind cellular respiration was further elaborated, although its link to the mitochondria was not known.[206] The introduction of tissue fractionation by Albert Claude allowed mitochondria to be isolated from other cell fractions and biochemical analysis to be conducted on them alone. In 1946, he concluded that cytochrome oxidase and other enzymes responsible for the respiratory chain were isolated to the mitochondria. Eugene Kennedy and Albert Lehninger discovered in 1948 that mitochondria are the site of oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotes. Over time, the fractionation method was further developed, improving the quality of the mitochondria isolated, and other elements of cell respiration were determined to occur in the mitochondria.[206]
The first high-resolution electron micrographs appeared in 1952, replacing the Janus Green stains as the preferred way to visualize mitochondria.[206] This led to a more detailed analysis of the structure of the mitochondria, including confirmation that they were surrounded by a membrane. It also showed a second membrane inside the mitochondria that folded up in ridges dividing up the inner chamber and that the size and shape of the mitochondria varied from cell to cell.
The popular term "powerhouse of the cell" was coined by Philip Siekevitz in 1957.[4][214]
In 1967, it was discovered that mitochondria contained ribosomes.[215] In 1968, methods were developed for mapping the mitochondrial genes, with the genetic and physical map of yeast mitochondrial DNA completed in 1976.[206]
See also
- Anti-mitochondrial antibodies
- Mitochondrial metabolic rates
- Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
- Mitophagy
- Nebenkern
- Oncocyte
- Oncocytoma
- Paternal mtDNA transmission
- Plastid
- Submitochondrial particle
References
- ↑ "mitochondrion". mitochondrion. Oxford University Press. http://www.lexico.com/definition/mitochondrion.
- ↑ Biology: Exploring Life. Boston, Massachusetts: Pearson/Prentice Hall. 2006. ISBN 978-0132508827. http://www.phschool.com/el_marketing.html.
- ↑ "Mighty Mitochondria and Neurodegenerative Diseases". 2012-02-01. https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2012/issue111/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Powerhouse of the cell". Scientific American 197 (1): 131–140. 1957. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0757-131. Bibcode: 1957SciAm.197a.131S.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Evolutionary biology: essence of mitochondria". Nature 426 (6963): 127–128. November 2003. doi:10.1038/426127a. PMID 14614484. Bibcode: 2003Natur.426..127H.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "A Eukaryote without a Mitochondrial Organelle". Current Biology 26 (10): 1274–1284. May 2016. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.03.053. PMID 27185558.
- ↑ "Animal that doesn't need oxygen to survive discovered New Scientist". New Scientist. https://www.newscientist.com/article/2235009-animal-that-doesnt-need-oxygen-to-survive-discovered/amp/.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "A cnidarian parasite of salmon (Myxozoa: Henneguya) lacks a mitochondrial genome". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 117 (10): 5358–5363. March 2020. doi:10.1073/pnas.1909907117. PMID 32094163. Bibcode: 2020PNAS..117.5358Y.
- ↑ "Quantification of mitochondrial morphology in neurites of dopaminergic neurons using multiple parameters". Journal of Neuroscience Methods 262: 56–65. March 2016. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.01.008. PMID 26777473.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Mitochondria: more than just a powerhouse". Current Biology 16 (14): R551–R560. July 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.06.054. PMID 16860735.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches". Current Pharmaceutical Design 20 (35): 5507–5509. 2014. doi:10.2174/138161282035140911142118. PMID 24606795. "Mitochondrial biogenesis is therefore defined as the process via which cells increase their individual mitochondrial mass [3]. ... Mitochondrial biogenesis occurs by growth and division of pre-existing organelles and is temporally coordinated with cell cycle events [1].".
- ↑ "Mitochondrial biogenesis in health and disease. Molecular and therapeutic approaches". Current Pharmaceutical Design 20 (35): 5619–5633. 2014. doi:10.2174/1381612820666140306095106. PMID 24606801. "Mitochondrial biogenesis (MB) is the essential mechanism by which cells control the number of mitochondria".
- ↑ "Is a 'Mitochondrial Psychiatry' in the Future? A Review". Curr. Psychiatry Rev. 1 (3): 255–271. 2005. doi:10.2174/157340005774575064.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiac disease: ischemia – reperfusion, aging, and heart failure". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 33 (6): 1065–1089. June 2001. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2001.1378. PMID 11444914.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics in the developing and diseased heart". Genes & Development 29 (19): 1981–1991. October 2015. doi:10.1101/gad.269894.115. PMID 26443844.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Evidence of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Autism: Biochemical Links, Genetic-Based Associations, and Non-Energy-Related Mechanisms". Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2017: 4314025. 2017. doi:10.1155/2017/4314025. PMID 28630658.
- ↑ "Normal and disordered reticulocyte maturation". Current Opinion in Hematology 18 (3): 152–157. May 2011. doi:10.1097/MOH.0b013e328345213e. PMID 21423015.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 18.7 18.8 18.9 Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Publishing Inc.. 2005. ISBN 978-0815341055.
- ↑ 19.00 19.01 19.02 19.03 19.04 19.05 19.06 19.07 19.08 19.09 19.10 19.11 Fundamentals of Biochemistry (2nd ed.). John Wiley and Sons, Inc.. 2006. pp. 547, 556. ISBN 978-0471214953. https://archive.org/details/fundamentalsofbi00voet_0/page/547.
- ↑ "On the origin of mitochondria: a genomics perspective". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences 358 (1429): 165–77; discussion 177–9. January 2003. doi:10.1098/rstb.2002.1193. PMID 12594925.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Origin and Early Evolution of the Eukaryotic Cell". Annual Review of Microbiology 75 (1): 631–647. October 2021. doi:10.1146/annurev-micro-090817-062213. PMID 34343017.
- ↑ "Mitochondrion – much more than an energy converter". British Society for Cell Biology. http://www.bscb.org/?url=softcell/mito.
- ↑ "VDAC channels". IUBMB Life 52 (3–5): 113–118. September 2001. doi:10.1080/15216540152845902. PMID 11798022.
- ↑ "The supramolecular assemblies of voltage-dependent anion channels in the native membrane". Journal of Molecular Biology 370 (2): 246–255. July 2007. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.073. PMID 17524423.
- ↑ "Structure and evolution of mitochondrial outer membrane proteins of beta-barrel topology". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1797 (6–7): 1292–1299. June 2010. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.04.019. PMID 20450883.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Protein transport into mitochondria". Current Opinion in Microbiology 3 (2): 210–214. April 2000. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(00)00077-1. PMID 10744987. https://epub.ub.uni-muenchen.de/7488/1/7488.pdf.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis: the innocent bystander scenario". Cell Death and Differentiation 13 (8): 1396–1402. August 2006. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401963. PMID 16710362.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 28.3 28.4 "MAM: more than just a housekeeper". Trends in Cell Biology 19 (2): 81–88. February 2009. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2008.12.002. PMID 19144519.
- ↑ "Formation and regulation of mitochondrial membranes". International Journal of Cell Biology 2014: 709828. January 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/709828. PMID 24578708.
- ↑ "Cardiolipin and apoptosis". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1585 (2–3): 97–107. December 2002. doi:10.1016/S1388-1981(02)00329-3. PMID 12531542.
- ↑ "Advances in methods to analyse cardiolipin and their clinical applications". Trends in Analytical Chemistry 157: 116808. December 2022. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2022.116808. PMID 36751553.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress". Science 337 (6098): 1062–1065. August 2012. doi:10.1126/science.1219855. PMID 22936770. Bibcode: 2012Sci...337.1062Y.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial Ultrastructure Is Coupled to Synaptic Performance at Axonal Release Sites". eNeuro 5 (1): ENEURO.0390–17.2018. 2018. doi:10.1523/ENEURO.0390-17.2018. PMID 29383328.
- ↑ "Structure and dynamics of the mitochondrial inner membrane cristae". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1763 (5–6): 542–548. 2006. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.04.006. PMID 16730811.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial DNA nucleoid structure". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms 1819 (9–10): 914–920. September 2012. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.11.005. PMID 22142616.
- ↑ "The molecular machinery of Keilin's respiratory chain". Biochemical Society Transactions 31 (Pt 6): 1095–1105. December 2003. doi:10.1042/BST0311095. PMID 14641005.
- ↑ "Nitrite-driven anaerobic ATP synthesis in barley and rice root mitochondria". Planta 226 (2): 465–474. July 2007. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0496-0. PMID 17333252. Bibcode: 2007Plant.226..465S.
- ↑ "Protein import into mitochondria". Annual Review of Biochemistry 66: 863–917. 1997. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.863. PMID 9242927.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 39.3 39.4 39.5 "Citric acid cycle.". In: Biochemistry. (Fourth ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. 1995. pp. 509–527, 569–579, 614–616, 638–641, 732–735, 739–748, 770–773. ISBN 0716720094.
- ↑ "Succinate dehydrogenase and fumarate hydratase: linking mitochondrial dysfunction and cancer". Oncogene 25 (34): 4675–4682. August 2006. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209594. PMID 16892081.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Voet, D.; Voet, J. G. (2004). Biochemistry, 3rd edition, p. 804, Wiley. ISBN:047119350X
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. (2006) "Physical Chemistry", 8th ed.; pp. 225-229, Freeman: New York, 2006.
- ↑ "The role of oxidative damage in mitochondria during aging: a review". Frontiers in Bioscience 9 (1–3): 1100–1117. May 2004. doi:10.2741/1298. PMID 14977532. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/af47/55d91a23bdfa50f49773c6b87e1c695b6404.pdf.
- ↑ "Chemiosmotic hypothesis of oxidative phosphorylation". Nature 213 (5072): 137–139. January 1967. doi:10.1038/213137a0. PMID 4291593. Bibcode: 1967Natur.213..137M.
- ↑ "Proton current flow in mitochondrial systems". Nature 214 (5095): 1327–1328. June 1967. doi:10.1038/2141327a0. PMID 6056845. Bibcode: 1967Natur.214.1327M.
- ↑ Nobel Foundation. "Chemistry 1997". http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1997/.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 "Thermoregulation: what role for UCPs in mammals and birds?". Bioscience Reports 25 (3–4): 227–249. November 2005. doi:10.1007/s10540-005-2887-4. PMID 16283555.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis, fatty acids and mitochondrial physiology". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1862 (1): 39–48. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.08.011. PMID 27553474.
- ↑ "Altering the Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Synthesis (mtFASII) Pathway Modulates Cellular Metabolic States and Bioactive Lipid Profiles as Revealed by Metabolomic Profiling". PLOS ONE 11 (3): e0151171. March 2016. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0151171. PMID 26963735. Bibcode: 2016PLoSO..1151171C.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 "Impact of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Synthesis on Mitochondrial Biogenesis". Current Biology 28 (20): R1212–R1219. October 2018. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2018.08.022. PMID 30352195.
- ↑ "The emerging role of the mitochondrial fatty-acid synthase (mtFASII) in the regulation of energy metabolism". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1864 (11): 1629–1643. November 2019. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.07.012. PMID 31376476.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial calcium overload is a key determinant in heart failure". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 112 (36): 11389–11394. September 2015. doi:10.1073/pnas.1513047112. PMID 26217001. Bibcode: 2015PNAS..11211389S.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Basic Neurochemistry (6 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 1999. ISBN 978-0397518203.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 "T channels and steroid biosynthesis: in search of a link with mitochondria". Cell Calcium 40 (2): 155–164. August 2006. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2006.04.020. PMID 16759697.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial calcium and its role in calcification. Histochemical localization of calcium in electron micrographs of the epiphyseal growth plate with K-pyroantimonate". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 100 (5): 406–416. May 1974. doi:10.1097/00003086-197405000-00057. PMID 4134194.
- ↑ "The role of mitochondria in growth plate calcification as demonstrated in a rachitic model". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 60 (5): 630–639. July 1978. doi:10.2106/00004623-197860050-00007. PMID 681381.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 57.2 "Essential Roles of Intracellular Calcium Release Channels in Muscle, Brain, Metabolism, and Aging". Current Molecular Pharmacology 8 (2): 206–222. 2015. doi:10.2174/1874467208666150507105105. PMID 25966694.
- ↑ "Mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum choreography: structure and signaling dynamics". Trends in Cell Biology 17 (10): 511–517. October 2007. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2007.07.011. PMID 17851078.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 "Mitochondria – the Kraken wakes!". Trends in Neurosciences 21 (3): 95–97. March 1998. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(97)01206-X. PMID 9530913.
- ↑ "Calcium release channel RyR2 regulates insulin release and glucose homeostasis". The Journal of Clinical Investigation 125 (5): 1968–1978. May 2015. doi:10.1172/JCI79273. PMID 25844899.
- ↑ "Pulsing of membrane potential in individual mitochondria: a stress-induced mechanism to regulate respiratory bioenergetics in Arabidopsis". The Plant Cell 24 (3): 1188–1201. March 2012. doi:10.1105/tpc.112.096438. PMID 22395486.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial free Ca²⁺ levels and their effects on energy metabolism in Drosophila motor nerve terminals". Biophysical Journal 104 (11): 2353–2361. June 2013. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2013.03.064. PMID 23746507. Bibcode: 2013BpJ...104.2353I.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1177 (1): 66–73. October 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05039.x. PMID 19845608. Bibcode: 2009NYASA1177...66W.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 "Energy metabolism in tumor cells". The FEBS Journal 274 (6): 1393–1418. March 2007. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05686.x. PMID 17302740.
- ↑ "ROS-mediated PI3K activation drives mitochondrial transfer from stromal cells to hematopoietic stem cells in response to infection". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116 (49): 24610–24619. December 2019. doi:10.1073/pnas.1913278116. PMID 31727843. Bibcode: 2019PNAS..11624610M.
- ↑ "ATP synthase. The machine that makes ATP". Current Biology 4 (12): 1138–1141. December 1994. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00257-8. PMID 7704582.
- ↑ "The metabolism of human mesenchymal stem cells during proliferation and differentiation". Journal of Cellular Physiology 226 (10): 2562–2570. October 2011. doi:10.1002/jcp.22605. PMID 21792913.
- ↑ "A role for anions in ATP synthesis and its molecular mechanistic interpretation". Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes 43 (3): 299–310. June 2011. doi:10.1007/s10863-011-9358-3. PMID 21647635.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 69.2 "Changes in mitochondrial mass, membrane potential, and cellular adenosine triphosphate content during the cell cycle of human leukemic (HL-60) cells". Journal of Cellular Physiology 180 (1): 91–96. July 1999. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199907)180:1<91::AID-JCP10>3.0.CO;2-6. PMID 10362021.
- ↑ "Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers". Journal of Hematology & Oncology 6 (19): 19. February 2013. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-6-19. PMID 23442817.
- ↑ "Apoptotic pathways: the roads to ruin". Cell 94 (6): 695–698. September 1998. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81728-6. PMID 9753316.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial calcium signalling and cell death: approaches for assessing the role of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake in apoptosis". Cell Calcium 40 (5–6): 553–560. 2006. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2006.08.016. PMID 17074387.
- ↑ "Evolutionary consideration on 5-aminolevulinate synthase in nature". Origins of Life and Evolution of the Biosphere 27 (4): 405–412. August 1997. doi:10.1023/A:1006583601341. PMID 9249985. Bibcode: 1997OLEB...27..405O.
- ↑ "Estrogenic control of mitochondrial function and biogenesis". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 105 (6): 1342–1351. December 2008. doi:10.1002/jcb.21936. PMID 18846505.
- ↑ "Different expression of alpha and beta mitochondrial estrogen receptors in the aging rat brain: interaction with respiratory complex V". Experimental Gerontology 45 (7–8): 580–585. August 2010. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2010.01.015. PMID 20096765.
- ↑ "Sexual hormones: effects on cardiac and mitochondrial activity after ischemia-reperfusion in adult rats. Gender difference". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 132 (1–2): 135–146. October 2012. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.05.003. PMID 22609314.
- ↑ "Mitochondria as central hub of the immune system". Redox Biology 26: 101255. September 2019. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101255. PMID 31247505.
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 "Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions". Science 367 (6477): 528–537. January 2020. doi:10.1126/science.aax6752. PMID 31831638. Bibcode: 2020Sci...367..528C. https://epub.ub.uni-muenchen.de/76442/.
- ↑ "Microglial control of neuronal development via somatic purinergic junctions". Cell Reports 40 (12): 111369. September 2022. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111369. PMID 36130488.
- ↑ "Characterization of the human heart mitochondrial proteome". Nature Biotechnology 21 (3): 281–286. March 2003. doi:10.1038/nbt793. PMID 12592411.
- ↑ "Systematic characterization of the murine mitochondrial proteome using functionally validated cardiac mitochondria". Proteomics 8 (8): 1564–1575. April 2008. doi:10.1002/pmic.200700851. PMID 18348319.
- ↑ "Altered proteome biology of cardiac mitochondria under stress conditions". Journal of Proteome Research 7 (6): 2204–2214. June 2008. doi:10.1021/pr070371f. PMID 18484766.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial fusion, division and positioning in plants". Biochemical Society Transactions 38 (3): 789–795. June 2010. doi:10.1042/bst0380789. PMID 20491666.
- ↑ "Connecting variability in global transcription rate to mitochondrial variability". PLOS Biology 8 (12): e1000560. December 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000560. PMID 21179497.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial variability as a source of extrinsic cellular noise". PLOS Computational Biology 8 (3): e1002416. 2012. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002416. PMID 22412363. Bibcode: 2012PLSCB...8E2416J.
- ↑ "Cytoskeleton and mitochondrial morphology and function". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 184 (1–2): 101–105. July 1998. doi:10.1023/A:1006843113166. PMID 9746315.
- ↑ "What is the function of mitochondrial networks? A theoretical assessment of hypotheses and proposal for future research". BioEssays 37 (6): 687–700. June 2015. doi:10.1002/bies.201400188. PMID 25847815.
- ↑ "Interrelationships of endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, intermediate filaments, and microtubules – a quadruple fluorescence labeling study". Biochemistry and Cell Biology 70 (10–11): 1174–1186. 1992. doi:10.1139/o92-163. PMID 1363623.
- ↑ "Vimentin supports mitochondrial morphology and organization". The Biochemical Journal 410 (1): 141–146. February 2008. doi:10.1042/BJ20071072. PMID 17983357.
- ↑ 90.00 90.01 90.02 90.03 90.04 90.05 90.06 90.07 90.08 90.09 90.10 90.11 90.12 90.13 "Ca(2+) transfer from the ER to mitochondria: when, how and why". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1787 (11): 1342–1351. November 2009. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.03.015. PMID 19341702.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 "An intimate liaison: spatial organization of the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria relationship". The EMBO Journal 29 (16): 2715–2723. August 2010. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.177. PMID 20717141.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "Intracellular trafficking of phospholipids: import of phosphatidylserine into mitochondria". Anticancer Research 16 (3B): 1333–1339. 1996. PMID 8694499.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 93.2 "Interactions between the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, plasma membrane and other subcellular organelles". The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 41 (10): 1805–1816. October 2009. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.02.017. PMID 19703651.
- ↑ "Fission and selective fusion govern mitochondrial segregation and elimination by autophagy". The EMBO Journal 27 (2): 433–446. January 2008. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601963. PMID 18200046.
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 95.2 95.3 95.4 95.5 "Making heads or tails of phospholipids in mitochondria". The Journal of Cell Biology 192 (1): 7–16. January 2011. doi:10.1083/jcb.201006159. PMID 21220505.
- ↑ "An ER-mitochondria tethering complex revealed by a synthetic biology screen". Science 325 (5939): 477–481. July 2009. doi:10.1126/science.1175088. PMID 19556461. Bibcode: 2009Sci...325..477K.
- ↑ "A unique mitochondria-associated membrane fraction from rat liver has a high capacity for lipid synthesis and contains pre-Golgi secretory proteins including nascent lipoproteins". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 269 (44): 27494–27502. November 1994. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47012-3. PMID 7961664.
- ↑ 98.0 98.1 "Functional coupling between ryanodine receptors, mitochondria and Ca(2+) ATPases in rat submandibular acinar cells". Cell Calcium 43 (5): 469–481. May 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2007.08.001. PMID 17889347.
- ↑ "Sorting of calcium signals at the junctions of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria". Cell Calcium 29 (4): 249–262. April 2001. doi:10.1054/ceca.2000.0191. PMID 11243933.
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 100.2 100.3 "The IP(3) receptor-mitochondria connection in apoptosis and autophagy". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1813 (5): 1003–1013. May 2011. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.11.023. PMID 21146562.
- ↑ "Mag-Fluo4 in T cells: Imaging of intra-organelle free Ca2+ concentrations". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1864 (6): 977–986. June 2017. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.026. PMID 27913206.
- ↑ "Old players in a new role: mitochondria-associated membranes, VDAC, and ryanodine receptors as contributors to calcium signal propagation from endoplasmic reticulum to the mitochondria". Cell Calcium 32 (5–6): 363–377. 2011. doi:10.1016/S0143416002001872. PMID 12543096.
- ↑ "σ-1 receptor at the mitochondrial-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane is responsible for mitochondrial metabolic regulation". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 343 (3): 578–586. December 2012. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.198168. PMID 22923735.
- ↑ "Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca(2+) signaling and cell survival". Cell 131 (3): 596–610. November 2007. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036. PMID 17981125.
- ↑ Csordás et al., Trends Cell Biol. 2018 Jul;28(7):523-540. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 24.
- ↑ "The Genomics and Cell Biology of Host-Beneficial Intracellular Infections". Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 37 (1): 115–142. October 2021. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-120219-024122. PMID 34242059.
- ↑ "Mitochondria and the origin of eukaryotes". Knowable Magazine. 8 June 2022. doi:10.1146/knowable-060822-2. https://knowablemagazine.org/article/living-world/2022/mitochondria-origin-eukaryotes. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ↑ 108.0 108.1 Origins of Sex: Three billion years of genetic recombination. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. 1986. pp. 69–71, 87. ISBN 978-0300033403. https://archive.org/details/originsofsexthre00marg/page/69.
- ↑ Origin of mitochondria and hydrogenosomes. Heidelberg, DE: Springer Verlag. 2007.
- ↑ Emelyanov, V.V. (April 2003). "Mitochondrial connection to the origin of the eukaryotic cell". European Journal of Biochemistry 270 (8): 1599–1618. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03499.x. PMID 12694174.
- ↑ "The genome of Rickettsia prowazekii and some thoughts on the origin of mitochondria and hydrogenosomes". BioEssays 21 (5): 377–381. May 1999. doi:10.1002/(sici)1521-1878(199905)21:5<377::aid-bies4>3.0.co;2-w. PMID 10376009.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial evolution". Science 283 (5407): 1476–1481. March 1999. doi:10.1126/science.283.5407.1476. PMID 10066161. Bibcode: 1999Sci...283.1476G.
- ↑ "Phylogenomic evidence for a common ancestor of mitochondria and the SAR11 clade" (in en). Scientific Reports 1 (1): 13. 2011-06-14. doi:10.1038/srep00013. PMID 22355532. Bibcode: 2011NatSR...1E..13T.
- ↑ "Deep mitochondrial origin outside the sampled alphaproteobacteria". Nature 557 (7703): 101–105. May 2018. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0059-5. PMID 29695865. Bibcode: 2018Natur.557..101M.
- ↑ "Phylogenetic analyses with systematic taxon sampling show that mitochondria branch within Alphaproteobacteria". Nature Ecology & Evolution (Springer Science and Business Media LLC) 4 (9): 1213–1219. September 2020. doi:10.1038/s41559-020-1239-x. PMID 32661403. Bibcode: 2020NatEE...4.1213F.
- ↑ "Dating Alphaproteobacteria evolution with eukaryotic fossils". Nature Communications 12 (1): 3324. June 2021. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23645-4. PMID 34083540. Bibcode: 2021NatCo..12.3324W.
- ↑ "On the bacterial ancestry of mitochondria: New insights with triangulated approaches" (in en). bioRxiv: 2022.05.15.491939. 2022-05-16. doi:10.1101/2022.05.15.491939.
- ↑ "Site-and-branch-heterogeneous analyses of an expanded dataset favour mitochondria as sister to known Alphaproteobacteria". Nature Ecology & Evolution 6 (3): 253–262. March 2022. doi:10.1038/s41559-021-01638-2. PMID 35027725. Bibcode: 2022NatEE...6..253M. https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-557223/latest.pdf.
- ↑ "The evolutionary origin of host association in the Rickettsiales". Nature Microbiology 7 (8): 1189–1199. August 2022. doi:10.1038/s41564-022-01169-x. PMID 35798888.
- ↑ "Properties of human mitochondrial ribosomes". IUBMB Life 55 (9): 505–513. September 2003. doi:10.1080/15216540310001626610. PMID 14658756.
- ↑ "On the origin of mitosing cells". Journal of Theoretical Biology 14 (3): 255–274. March 1967. doi:10.1016/0022-5193(67)90079-3. PMID 11541392. Bibcode: 1967JThBi..14..225S.
- ↑ "Rickettsiaceae, rickettsia-like endosymbionts, and the origin of mitochondria". Bioscience Reports 21 (1): 1–17. February 2001. doi:10.1023/A:1010409415723. PMID 11508688.
- ↑ "Determining divergence times with a protein clock: update and reevaluation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94 (24): 13028–13033. November 1997. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.24.13028. PMID 9371794. Bibcode: 1997PNAS...9413028F.
- ↑ "Archamoebae: the ancestral eukaryotes?". Bio Systems 25 (1–2): 25–38. 1991. doi:10.1016/0303-2647(91)90010-I. PMID 1854912.
- ↑ "The first metazoa living in permanently anoxic conditions". BMC Biology 8: 30. April 2010. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-8-30. PMID 20370908.
- ↑ "The mud creature that lives without oxygen". New Scientist. 7 April 2010. https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn18744-zoologger-the-mud-creature-that-lives-without-oxygen/.
- ↑ "Mitochondrion-related organelles in eukaryotic protists". Annual Review of Microbiology 64: 409–429. 2010. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162826. PMID 20528687.
- ↑ 128.0 128.1 128.2 "Mitochondria: dynamic organelles in disease, aging, and development". Cell 125 (7): 1241–1252. June 2006. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.010. PMID 16814712.
- ↑ 129.0 129.1 "Counting target molecules by exponential polymerase chain reaction: copy number of mitochondrial DNA in rat tissues". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 183 (2): 553–559. March 1992. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)90517-O. PMID 1550563.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial DNA replication in mammalian cells: overview of the pathway". Essays in Biochemistry 62 (3): 287–296. July 2018. doi:10.1042/ebc20170100. PMID 29880722.
- ↑ 131.0 131.1 "Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome". Nature 290 (5806): 457–465. April 1981. doi:10.1038/290457a0. PMID 7219534. Bibcode: 1981Natur.290..457A.
- ↑ "Linear mitochondrial DNAs of yeasts: frequency of occurrence and general features". Molecular and Cellular Biology 13 (4): 2309–2314. April 1993. doi:10.1128/mcb.13.4.2309. PMID 8455612.
- ↑ "Intervening sequences in the mitochondrial genome". Nature 276 (5688): 558–559. December 1978. doi:10.1038/276558a0. PMID 214710. Bibcode: 1978Natur.276..558B.
- ↑ "A maturase-encoding group IIA intron of yeast mitochondria self-splices in vitro". Nucleic Acids Research 20 (7): 1747–1754. April 1992. doi:10.1093/nar/20.7.1747. PMID 1579468.
- ↑ "Genome structure and gene content in protist mitochondrial DNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 26 (4): 865–878. February 1998. doi:10.1093/nar/26.4.865. PMID 9461442.
- ↑ "Mitochondria of protists". Annual Review of Genetics 38: 477–524. 2004. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.37.110801.142526. PMID 15568984.
- ↑ "Nuclear and mitochondrial tRNA-lookalikes in the human genome". Frontiers in Genetics 5: 344. 2014. doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00344. PMID 25339973.
- ↑ "The single mitochondrial chromosome typical of animals has evolved into 18 minichromosomes in the human body louse, Pediculus humanus". Genome Research 19 (5): 904–912. May 2009. doi:10.1101/gr.083188.108. PMID 19336451.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial DNA: a tool for populational genetics studies". International Microbiology 1 (4): 327–332. December 1998. PMID 10943382.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution". Nature 325 (6099): 31–36. January 1987. doi:10.1038/325031a0. PMID 3025745. Bibcode: 1987Natur.325...31C.
- ↑ "Harvesting the fruit of the human mtDNA tree". Trends in Genetics 22 (6): 339–345. June 2006. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2006.04.001. PMID 16678300.
- ↑ 142.0 142.1 "Reconstructing human origins in the genomic era". Nature Reviews. Genetics 7 (9): 669–680. September 2006. doi:10.1038/nrg1941. PMID 16921345.
- ↑ "Neandertal DNA sequences and the origin of modern humans". Cell 90 (1): 19–30. July 1997. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80310-4. PMID 9230299.
- ↑ "Correcting for purifying selection: an improved human mitochondrial molecular clock". American Journal of Human Genetics 84 (6): 740–759. June 2009. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.05.001. PMID 19500773.
- ↑ "Estimate of the mutation rate per nucleotide in humans". Genetics 156 (1): 297–304. September 2000. doi:10.1093/genetics/156.1.297. PMID 10978293.
- ↑ "Directed panspermia". Icarus 19 (3): 341–346. 1973. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(73)90110-3. Bibcode: 1973Icar...19..341C. http://profiles.nlm.nih.gov/ps/access/SCBCCP.pdf. "p. 344: It is a little surprising that organisms with somewhat different codes do not coexist.". Further discussion.
- ↑ "A different genetic code in human mitochondria". Nature 282 (5735): 189–194. November 1979. doi:10.1038/282189a0. PMID 226894. Bibcode: 1979Natur.282..189B.
- ↑ 148.0 148.1 "The Genetic Codes". 2019-01-07. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Utils/wprintgc.cgi.
- ↑ "The genetic code in mitochondria and chloroplasts". Experientia 46 (11–12): 1117–1126. December 1990. doi:10.1007/BF01936921. PMID 2253709.
- ↑ "RNA editing in plant mitochondria". Science 246 (4937): 1632–1634. December 1989. doi:10.1126/science.2480644. PMID 2480644. Bibcode: 1989Sci...246.1632H.
- ↑ "Parallel evolution of the genetic code in arthropod mitochondrial genomes". PLOS Biology 4 (5): e127. May 2006. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040127. PMID 16620150.
- ↑ Parkinson's Disease. CRC Press. 2012. p. 583. ISBN 978-1439807149. https://books.google.com/books?id=uWI0Ia3mkf8C&pg=PA583.
- ↑ "New insights into the role of mitochondria in aging: mitochondrial dynamics and more". Journal of Cell Science 123 (Pt 15): 2533–2542. August 2010. doi:10.1242/jcs.070490. PMID 20940129.
- ↑ "Whole cell cryo-electron tomography suggests mitochondria divide by budding". Microscopy and Microanalysis 20 (4): 1180–1187. August 2014. doi:10.1017/S1431927614001317. PMID 24870811. Bibcode: 2014MiMic..20.1180H.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial DNA can be inherited from fathers, not just mothers". Nature 565 (7739): 296–297. January 2019. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-00093-1. PMID 30643304. Bibcode: 2019Natur.565..296M.
- ↑ Kimball, J.W. (2006) "Sexual Reproduction in Humans: Copulation and Fertilization", Kimball's Biology Pages (based on Biology, 6th ed., 1996)
- ↑ "Ubiquitin tag for sperm mitochondria". Nature 402 (6760): 371–372. November 1999. doi:10.1038/46466. PMID 10586873. Bibcode: 1999Natur.402..371S. Discussed in Science News .
- ↑ Mogensen HL (1996). "The Hows and Whys of Cytoplasmic Inheritance in Seed Plants". American Journal of Botany 83 (3): 383–404. doi:10.2307/2446172.
- ↑ "The exceptional mitochondrial DNA system of the mussel family Mytilidae". Genes & Genetic Systems 75 (6): 313–318. December 2000. doi:10.1266/ggs.75.313. PMID 11280005.
- ↑ "The fate of paternal mitochondrial DNA in developing female mussels, Mytilus edulis: implications for the mechanism of doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondrial DNA". Genetics 148 (1): 341–347. January 1998. doi:10.1093/genetics/148.1.341. PMID 9475744.
- ↑ Male and Female Mitochondrial DNA Lineages in the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Species Group by Donald T. Stewart, Carlos Saavedra, Rebecca R. Stanwood, Amy 0. Ball, and Eleftherios Zouros
- ↑ "Paternal transmission of mitochondrial DNA is (fortunately) rare". Annals of Neurology 54 (4): 422–424. October 2003. doi:10.1002/ana.10771. PMID 14520651.
- ↑ "Mammalian mitochondria possess homologous DNA recombination activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 271 (44): 27536–27543. November 1996. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.44.27536. PMID 8910339.
- ↑ "Animal mitochondrial DNA recombination". Nature 387 (6630): 247. May 1997. doi:10.1038/387247a0. PMID 9153388. Bibcode: 1997Natur.387..247L.
- ↑ "How clonal are human mitochondria?". Proceedings. Biological Sciences 266 (1418): 477–483. March 1999. doi:10.1098/rspb.1999.0662. PMID 10189711.
- ↑ "Linkage disequilibrium and recombination in hominid mitochondrial DNA". Science 286 (5449): 2524–2525. December 1999. doi:10.1126/science.286.5449.2524. PMID 10617471.
- ↑ "A reduction of mitochondrial DNA molecules during embryogenesis explains the rapid segregation of genotypes". Nature Genetics 40 (2): 249–254. February 2008. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.63. PMID 18223651.
- ↑ "The mitochondrial bottleneck occurs without reduction of mtDNA content in female mouse germ cells". Nature Genetics 39 (3): 386–390. March 2007. doi:10.1038/ng1970. PMID 17293866.
- ↑ "The mitochondrial DNA genetic bottleneck results from replication of a subpopulation of genomes". Nature Genetics 40 (12): 1484–1488. December 2008. doi:10.1038/ng.258. PMID 19029901.
- ↑ "Stochastic modelling, Bayesian inference, and new in vivo measurements elucidate the debated mtDNA bottleneck mechanism". eLife 4: e07464. June 2015. doi:10.7554/eLife.07464. PMID 26035426.
- ↑ "Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA repair in selected eukaryotic aging model systems". Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2012: 282438. 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/282438. PMID 23050036.
- ↑ 172.0 172.1 172.2 "DNA damage related crosstalk between the nucleus and mitochondria". Free Radical Biology & Medicine 107: 216–227. June 2017. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.050. PMID 27915046.
- ↑ "8-Oxoguanine accumulation in mitochondrial DNA causes mitochondrial dysfunction and impairs neuritogenesis in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons under oxidative conditions". Scientific Reports 6: 22086. February 2016. doi:10.1038/srep22086. PMID 26912170. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...622086L.
- ↑ "Homologous recombination-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks operates in mammalian mitochondria". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 75 (9): 1641–1655. May 2018. doi:10.1007/s00018-017-2702-y. PMID 29116362.
- ↑ "Involvement of mitochondrial-targeted RecA in the repair of mitochondrial DNA in the moss, Physcomitrella patens". Genes & Genetic Systems 82 (1): 43–51. February 2007. doi:10.1266/ggs.82.43. PMID 17396019.
- ↑ "Microhomology-mediated end joining is the principal mediator of double-strand break repair during mitochondrial DNA lesions". Molecular Biology of the Cell 27 (2): 223–235. January 2016. doi:10.1091/mbc.E15-05-0260. PMID 26609070.
- ↑ 177.0 177.1 "The unusual mitochondrial compartment of Cryptosporidium parvum". Trends in Parasitology 21 (2): 68–74. February 2005. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2004.11.010. PMID 15664529.
- ↑ "An aerobic eukaryotic parasite with functional mitochondria that likely lacks a mitochondrial genome". Science Advances 5 (4): eaav1110. April 2019. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aav1110. PMID 31032404. Bibcode: 2019SciA....5.1110J.
- ↑ "Veritable powerhouse – even without DNA: Parasitic algae from the dinoflagellate lineage have organized their genetic material in an unprecedented way". https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/04/190424153617.htm.
- ↑ 180.0 180.1 180.2 "Mitochondrial disorders". Brain 127 (Pt 10): 2153–2172. October 2004. doi:10.1093/brain/awh259. PMID 15358637.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human disease". Nature Reviews. Genetics 6 (5): 389–402. May 2005. doi:10.1038/nrg1606. PMID 15861210.
- ↑ "Targeting tumor phenotypic plasticity and metabolic remodeling in adaptive cross-drug tolerance". Science Signaling 12 (595). August 2019. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aas8779. PMID 31431543.
- ↑ "Intercellular nanotubes mediate mitochondrial trafficking between cancer and immune cells". Nature Nanotechnology 17 (1): 98–106. January 2022. doi:10.1038/s41565-021-01000-4. PMID 34795441. Bibcode: 2022NatNa..17...98S.
- ↑ "Mitochondria". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 74 (9): 1188–1199. September 2003. doi:10.1136/jnnp.74.9.1188. PMID 12933917.
- ↑ "Environment, mitochondria, and Parkinson's disease". The Neuroscientist 8 (3): 192–197. June 2002. doi:10.1177/1073858402008003004. PMID 12061498.
- ↑ "Pesticides and impairment of mitochondrial function in relation with the parkinsonian syndrome". Frontiers in Bioscience 12: 1079–1093. January 2007. doi:10.2741/2128. PMID 17127363.
- ↑ "Abeta and human amylin share a common toxicity pathway via mitochondrial dysfunction". Proteomics 10 (8): 1621–1633. April 2010. doi:10.1002/pmic.200900651. PMID 20186753.
- ↑ "Molecular basis of substrate recognition and degradation by human presequence protease". Structure 22 (7): 996–1007. July 2014. doi:10.1016/j.str.2014.05.003. PMID 24931469.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial disease". Lancet 368 (9529): 70–82. July 2006. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68970-8. PMID 16815381.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial dysfunction and molecular pathways of disease". Experimental and Molecular Pathology 83 (1): 84–92. August 2007. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2006.09.008. PMID 17239370.
- ↑ "Mitochondria in the diabetic heart". Cardiovascular Research 88 (2): 229–240. November 2010. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq239. PMID 20639213.
- ↑ Podolak, Amira; Woclawek-Potocka, Izabela; Lukaszuk, Krzysztof (2022-02-24). "The Role of Mitochondria in Human Fertility and Early Embryo Development: What Can We Learn for Clinical Application of Assessing and Improving Mitochondrial DNA?". Cells 11 (5): 797. doi:10.3390/cells11050797. ISSN 2073-4409. PMID 35269419.
- ↑ May-Panloup, Pascale; Boguenet, Magalie; El Hachem, Hady; Bouet, Pierre-Emmanuel; Reynier, Pascal (2021-01-20). "Embryo and Its Mitochondria". Antioxidants 10 (2): 139. doi:10.3390/antiox10020139. ISSN 2076-3921. PMID 33498182.
- ↑ Claiborne, Anne; English, Rebecca; Kahn, Jeffrey; Diseases, Committee on the Ethical and Social Policy Considerations of Novel Techniques for Prevention of Maternal Transmission of Mitochondrial DNA; Policy, Board on Health Sciences; Medicine, Institute of; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering (2016-03-17), "Introduction" (in en), Mitochondrial Replacement Techniques: Ethical, Social, and Policy Considerations (National Academies Press (US)), https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK355458/, retrieved 2023-12-05
- ↑ "Normal oxidative damage to mitochondrial and nuclear DNA is extensive". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 85 (17): 6465–6467. September 1988. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.17.6465. PMID 3413108. Bibcode: 1988PNAS...85.6465R.
- ↑ "Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry". Journal of Gerontology 11 (3): 298–300. July 1956. doi:10.1093/geronj/11.3.298. PMID 13332224.
- ↑ "The biologic clock: the mitochondria?". Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 20 (4): 145–147. April 1972. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1972.tb00787.x. PMID 5016631.
- ↑ "Mitochondria and Aging". circuitblue.co. http://www.circuitblue.com/biogerontology/mito.shtml.
- ↑ "Decline with age of the respiratory chain activity in human skeletal muscle". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 1226 (1): 73–82. April 1994. doi:10.1016/0925-4439(94)90061-2. PMID 8155742.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial mutations in mammalian aging: an over-hasty about-turn?". Rejuvenation Research 7 (3): 171–174. 2004. doi:10.1089/rej.2004.7.171. PMID 15588517.
- ↑ "High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and Parkinson disease". Nature Genetics 38 (5): 515–517. May 2006. doi:10.1038/ng1769. PMID 16604074.
- ↑ "Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Brain Communications 1 (1): fcz009. August 2019. doi:10.1093/braincomms/fcz009. PMID 32133457.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficits in C9orf72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor neurons cause dysfunctional axonal homeostasis". Acta Neuropathologica 141 (2): 257–279. February 2021. doi:10.1007/s00401-020-02252-5. PMID 33398403.
- ↑ "Mitochondria in Ovarian Aging and Reproductive Longevity". Ageing Research Reviews 63: 101168. November 2020. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101168. PMID 32896666.
- ↑ "Einige Bemerkungen über die Endigungen der Hautnerven und den Bau der Muskeln" (in German). Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie 8: 311–325. 1857. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/49190#page/319/mode/1up. On p. 316, Kölliker described mitochondria which he observed in fresh frog muscles: " … sehr blasse rundliche Körnchen, welche in langen linienförmigen Zügen […] wenn man einmal auf dieselben aufmerksam geworden ist." ( … [they are] very faint round granules, which are embedded in the [muscle's] contractile substance in long linear trains. These granules are located in the whole thickness of the muscle fiber, on the surface as in the interior, and [they] are so numerous that they appear as a not unimportant element of the muscle fibers, once one has become alert to them.) Kölliker said (p. 321) that he had found mitochondria in the muscles of other animals. In Figure 3 of Table XIV, Kölliker depicted mitochondria in frog muscles.
- ↑ 206.0 206.1 206.2 206.3 206.4 206.5 206.6 206.7 206.8 206.9 "Mitochondria: a historical review". The Journal of Cell Biology 91 (3 Pt 2): 227s–255s. December 1981. doi:10.1083/jcb.91.3.227s. PMID 7033239.
- ↑ (in German) Die Elementarorganismen und ihre Beziehungen zu den Zellen. Leipzig, Germany: Veit & Co.. 1890. p. 125. https://www.deutschestextarchiv.de/book/view/altmann_elementarorganismen_1890?p=141. From p. 125: "Da auch sonst mancherlei Umstände dafür sprechen, dass Mikroorganismen und Granula einander gleichwerthig sind und Elementarorganismen vorstellen, welche sich überall finden, wo lebendige Kräfte ausgelöst werden, so wollen wir sie mit dem gemeinschaftlichen Namen der Bioblasten bezeichnen." (Since otherwise some circumstances indicate that microorganisms and granula are equivalent to each other and suggest elementary organisms, which are to be found wherever living forces are unleashed, we will designate them with the collective name of "bioblasts".)
- ↑ "mitochondria". mitochondria. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=mitochondria&allowed_in_frame=0.
- ↑ "Ueber die Spermatogenese der Vertebraten und höherer Evertebraten. II. Theil: Die Histiogenese der Spermien." (in de). Archiv für Physiologie 1898: 393–398. 1898. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/109725#page/403/mode/1up. From p. 397: After Brenda states that " … ich bereits in vielen Zellarten aller möglichen Thierclassen gefunden habe, … " ( … I have already found [them (mitochondria)] in many types of cells of all possible classes of animals, … ), he suggests: "Ich möchte vorläufig vorschlagen, ihnen als Mitochondria eine besondere Stellung vorzubehalten, die ich in weiteren Arbeiten begründen werde." (I would like to suggest provisionally reserving for them, as "mitochondria", a special status which I will justify in further work.)
- "Weitere Mitteilungen über die Mitochondria" (in German). Archiv für Physiologie: Verhandlungen der Berliner Physiologischen Gesellschaft 1899: 376–383. 1899. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/109704#page/388/mode/1up.
- ↑ "Die vitale Farbung, eine Darstellungsmethode der Zellgranula" (in German). Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 55: 558–575. 1900. doi:10.1007/BF02977747. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47675#page/580/mode/1up.
- ↑ Ernster's citation "Die Chondriosomen als Träger erblicher Anlagen. Cytologische Studien am Hühnerembryo". Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie 72 (1): 816–867. May 1908. doi:10.1007/BF02982402. https://zenodo.org/record/2034475. is wrong, correct citation is "Über das Vorkommen von Mitochondrien bezw. Chondromiten in Pflanzenzellen". Ber. Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 22: 284–286. 1904. doi:10.1111/j.1438-8677.1904.tb05237.x., cited in Meves' 1908 paper and in "Pflanzliche Mitochondrien". Progressus Rei Botanicae 4: 164–183. 1913. https://archive.org/stream/progressusreibot04lots/progressusreibot04lots_djvu.txt. Retrieved 21 September 2012., with confirmation of Nymphaea alba
- ↑ "Cytoplasmic fixation". The Anatomical Record 6 (2): 39–52. 1912. doi:10.1002/ar.1090060202. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/87070#page/51/mode/1up. From p. 47: " … the mitochondria are the structural expression thereof [i.e., of the chemical reducing processes in the cytoplasm], … "
- ↑ "Über sauerstoffatmende Körnchen aus Leberzellen und über Sauerstoffatmung in Berkefeld-Filtraten wässriger Leberextrake" (in German). Pflügers Archiv für die gesamte Physiologie des Menschen und der Tiere (Pfluger's Archive for All Physiology of Humans and Animals) 154: 599–617. 1913. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/108058#page/613/mode/1up.
- ↑ "Mitochondrial biology, targets, and drug delivery". Journal of Controlled Release 207: 40–58. June 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.03.036. PMID 25841699.
- ↑ "Endosymbiotic theories for eukaryote origin". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences 370 (1678): 20140330. September 2015. doi:10.1098/rstb.2014.0330. PMID 26323761.
General
 This article incorporates public domain material from the NCBI document "Science Primer".
This article incorporates public domain material from the NCBI document "Science Primer".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mitochondrion. |
- The Vital Question: Energy, Evolution, and the Origins of Complex Life. WW Norton & Company. 2016. ISBN 978-0393352979.
- Powering the Cell Mitochondria – XVIVO Scientific Animation
- Mitodb.com – The mitochondrial disease database.
- Mitochondria Atlas at University of Mainz
- Mitochondria Research Portal at mitochondrial.net
- Mitochondria: Architecture dictates function at cytochemistry.net
- Mitochondria links at University of Alabama
- MIP Mitochondrial Physiology Society
- 3D structures of proteins from inner mitochondrial membrane at University of Michigan
- 3D structures of proteins associated with outer mitochondrial membrane at University of Michigan
- Mitochondrial Protein Partnership at University of Wisconsin
- MitoMiner – A mitochondrial proteomics database[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}] at MRC Mitochondrial Biology Unit
- Mitochondrion – Cell Centered Database
- Mitochondrion Reconstructed by Electron Tomography at San Diego State University
- Video Clip of Rat-liver Mitochondrion from Cryo-electron Tomography
 |