Biology:Multiomics
Multiomics, multi-omics, integrative omics, "panomics" or "pan-omics" is a biological analysis approach in which the data consists of multiple "omes", such as the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, exposome, and microbiome (i.e., a meta-genome and/or meta-transcriptome, depending upon how it is sequenced);[1][2][3] in other words, the use of multiple omics technologies to study life in a concerted way. By combining these "omes", scientists can analyze complex biological big data to find novel associations between biological entities, pinpoint relevant biomarkers and build elaborate markers of disease and physiology. In doing so, multiomics integrates diverse omics data to find a coherently matching geno-pheno-envirotype relationship or association.[4] The OmicTools service lists more than 99 pieces of software related to multiomic data analysis, as well as more than 99 databases on the topic.
Systems biology approaches are often based upon the use of multiomic analysis data.[5][6] The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) defines panomics as referring to "the interaction of all biological functions within a cell and with other body functions, combining data collected by targeted tests ... and global assays (such as genome sequencing) with other patient-specific information."[7]
Combined multiomic data collection
Combined multiomic data collection approaches have evolved to address the limitations of traditional multiomics research, which typically requires separate sample processing for different molecular classes then subsequent computational integration, introducing variability and increasing costs. Early advances in this field include sequential extraction,[8] TRIzol-based sequential isolation methods, which demonstrated that a reagent traditionally used for RNA isolation could simultaneously extract DNA, RNA, proteins, metabolites, and lipids from a single sample. Similar approaches like the Metabolite, Protein, and Lipid extraction (MPLEx)[9] and the "Three-in-One"[10] method adapted biphasic fractionation to extract proteins, metabolites, and lipids for LC-MS/MS analysis. More recent technological developments include the Multi-Omic Single-Shot Technology (MOST),[11] which integrates proteome and lipidome analysis in a single LC-MS run using one reverse-phase column and a binary mobile phase system, and the Bead-enabled Accelerated Monophasic Multi-omics (BAMM)[12] method that combines n-butanol-based monophasic extraction with magnetic beads and accelerated protein digestion for the separate analysis of metabolites, lipids, and proteins. One of the most comprehensive technologies in this space is Dalton Bioanalytics Inc.'s Omni-MS®, a multiomic assay that uses its proprietary method to simultaneously profile proteins, lipids, electrolytes, metabolites, and other small molecules in a single preparation and single LC-MS analysis. This platform has been applied to biomarker discovery, identifying potential biomarkers across multiple molecular classes and across various conditions and diseases[13][14] including COVID severity during pregnancy,[15] 22q11.2 deletion syndrome,[16] and hereditary angioedema.[17] These integrated approaches significantly reduce sample requirements, processing time, and technical variation while improving correlation analysis across different molecular classes, making them increasingly valuable for precision medicine and systems biology research.
Single-cell multiomics
A branch of the field of multiomics is the analysis of multilevel single-cell data, called single-cell multiomics.[18][19] This approach gives us an unprecedented resolution to look at multilevel transitions in health and disease at the single cell level. An advantage in relation to bulk analysis is to mitigate confounding factors derived from cell to cell variation, allowing the uncovering of heterogeneous tissue architectures.[18]
Methods for parallel single-cell genomic and transcriptomic analysis can be based on simultaneous amplification[20] or physical separation of RNA and genomic DNA.[21] They allow insights that cannot be gathered solely from transcriptomic analysis, as RNA data do not contain non-coding genomic regions and information regarding copy-number variation, for example. An extension of this methodology is the integration of single-cell transcriptomes to single-cell methylomes, combining single-cell bisulfite sequencing[22][23] to single cell RNA-Seq.[24] Other techniques to query the epigenome, as single-cell ATAC-Seq[25] and single-cell Hi-C[26] also exist.
A different, but related, challenge is the integration of proteomic and transcriptomic data.[27][28] One approach to perform such measurement is to physically separate single-cell lysates in two, processing half for RNA, and half for proteins.[27] The protein content of lysates can be measured by proximity extension assays (PEA), for example, which use DNA-barcoded antibodies.[29] A different approach uses a combination of heavy-metal RNA probes and protein antibodies to adapt mass cytometry for multiomic analysis.[28]
Related to Single-cell multiomics is the field of Spatial Omics which assays tissues through omics readouts that preserve the relative spatial orientation of the cells in the tissue. The number of Spatial Omics methods published still lags behind the number of methods published for Single-Cell multiomics, but the numbers are catching up (Single-cell and Spatial methods).
Multiomics and machine learning
In parallel to the advances in high-throughput biology, machine learning applications to biomedical data analysis are flourishing. The integration of multi-omics data analysis and machine learning has led to the discovery of new biomarkers.[30][31][32] For example, one of the methods of the mixOmics project implements a method based on sparse Partial Least Squares regression for selection of features (putative biomarkers).[33] A unified and flexible statistical framewok for heterogeneous data integration called "Regularized Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis" (RGCCA [34][35][36][37]) enables identifying such putative biomarkers. This framework is implemented and made freely available within the RGCCA R package .
Multiomics in health and disease
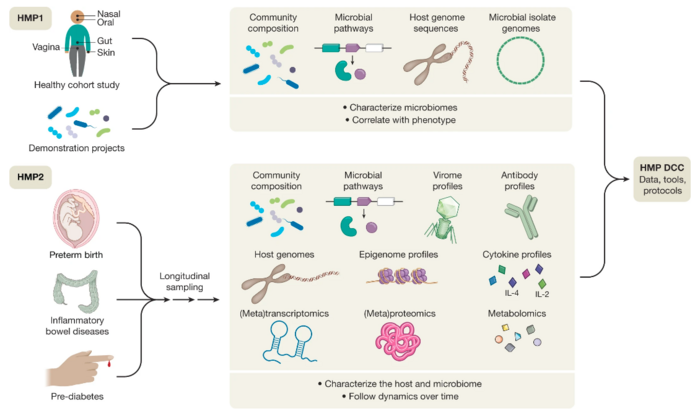
Multiomics currently holds a promise to fill gaps in the understanding of human health and disease, and many researchers are working on ways to generate and analyze disease-related data.[38] The applications range from understanding host-pathogen interactions and infectious diseases,[39][40] cancer,[41] to understanding better chronic and complex non-communicable diseases[42] and improving personalized medicine.[43]
Integrated Human Microbiome Project
The second phase of the $170 million Human Microbiome Project was focused on integrating patient data to different omic datasets, considering host genetics, clinical information and microbiome composition.[44][45] The phase one focused on characterization of communities in different body sites. Phase 2 focused in the integration of multiomic data from host & microbiome to human diseases. Specifically, the project used multiomics to improve the understanding of the interplay of gut and nasal microbiomes with type 2 diabetes,[46] gut microbiomes and inflammatory bowel disease[47] and vaginal microbiomes and pre-term birth.[48]
Systems Immunology
The complexity of interactions in the human immune system has prompted the generation of a wealth of immunology-related multi-scale omic data.[49] Multi-omic data analysis has been employed to gather novel insights about the immune response to infectious diseases, such as pediatric chikungunya,[50] as well as noncommunicable autoimmune diseases.[51] Integrative omics has also been employed strongly to understand effectiveness and side effects of vaccines, a field called systems vaccinology.[52] For example, multiomics was essential to uncover the association of changes in plasma metabolites and immune system transcriptome on response to vaccination against herpes zoster.[53]
List of software used for multi-omic analysis
The Bioconductor project curates a variety of R packages aimed at integrating omic data:
- omicade4, for multiple co-inertia analysis of multi omic datasets[54]
- MultiAssayExperiment, offering a bioconductor interface for overlapping samples[55]
- IMAS, a package focused on using multi omic data for evaluating alternative splicing[56]
- bioCancer, a package for visualization of multiomic cancer data[57]
- mixOmics, a suite of multivariate methods for data integration[33]
- MultiDataSet, a package for encapsulating multiple data sets[58]
The RGCCA package implements a versatile framework for data integration. This package is freely available on the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN).
The OmicTools[59] database further highlights R packages and othertools for multi omic data analysis:
- PaintOmics, a web resource for visualization of multi-omics datasets[60][61]
- SIGMA, a Java program focused on integrated analysis of cancer datasets[62]
- iOmicsPASS, a tool in C++ for multiomic-based phenotype prediction[63]
- Grimon, an R graphical interface for visualization of multiomic data[64]
- Omics Pipe, a framework in Python for reproducibly automating multiomic data analysis[65]
Multiomic Databases
A major limitation of classical omic studies is the isolation of only one level of biological complexity. For example, transcriptomic studies may provide information at the transcript level, but many different entities contribute to the biological state of the sample (genomic variants, post-translational modifications, metabolic products, interacting organisms, among others). With the advent of high-throughput biology, it is becoming increasingly affordable to make multiple measurements, allowing transdomain (e.g. RNA and protein levels) correlations and inferences. These correlations aid the construction or more complete biological networks, filling gaps in our knowledge.
Integration of data, however, is not an easy task. To facilitate the process, groups have curated database and pipelines to systematically explore multiomic data:
- Multi-Omics Profiling Expression Database (MOPED),[66] integrating diverse animal models,
- The Pancreatic Expression Database, integrating data related to pancreatic tissue,
- LinkedOmics,[67][68] connecting data from TCGA cancer datasets,
- OASIS,[69] a web-based resource for general cancer studies,
- BCIP,[70] a platform for breast cancer studies,
- C/VDdb,[71] connecting data from several cardiovascular disease studies,
- ZikaVR,[72] a multiomic resource for Zika virus data
- Ecomics,[73] a normalized multi-omic database for Escherichia coli data,
- GourdBase,[74] integrating data from studies with gourd,
- MODEM,[75] a database for multilevel maize data,
- SoyKB,[76] a database for multilevel soybean data,
- ProteomicsDB,[77] a multi-omics and multi-organism resource for life science research
See also
- DisGeNET
- Pangenomics
- Hologenomics
- Omics
- Systems Biology
- Network Medicine
References
- ↑ Bersanelli, Matteo; Mosca, Ettore; Remondini, Daniel; Giampieri, Enrico; Sala, Claudia; Castellani, Gastone; Milanesi, Luciano (1 January 2016). "Methods for the integration of multi-omics data: mathematical aspects". BMC Bioinformatics 17 (2): S15. doi:10.1186/s12859-015-0857-9. ISSN 1471-2105. PMID 26821531.
- ↑ Bock, Christoph; Farlik, Matthias; Sheffield, Nathan C. (August 2016). "Multi-Omics of Single Cells: Strategies and Applications". Trends in Biotechnology 34 (8): 605–608. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.04.004. PMID 27212022.
- ↑ Vilanova, Cristina; Porcar, Manuel (26 July 2016). "Are multi-omics enough?". Nature Microbiology 1 (8): 16101. doi:10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.101. PMID 27573112. https://zenodo.org/record/890860.
- ↑ Tarazona, S., Balzano-Nogueira, L., & Conesa, A. (2018). Multiomics Data Integration in Time Series Experiments. doi:10.1016/bs.coac.2018.06.005
- ↑ PSB'14 Cancer Panomics Session
- ↑ The Molecular Landscape of Cancer: Using Panomics to Drive Change
- ↑ "Glossary". Accelerating Progress Against Cancer: ASCO's blueprint for transforming clinical and translational cancer research. American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2011. p. 28. http://www.asco.org/sites/default/files/blueprint.pdf. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ↑ Shibko, S.; Koivistoinen, P.; Tratnyek, C. A.; Newhall, A. R.; Friedman, L. (June 1967). "A method for sequential quantitative separation and determination of protein, RNA, DNA, lipid, and glycogen from a single rat liver homogenate or from a subcellular fraction". Analytical Biochemistry 19 (3): 514–528. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(67)90242-4. ISSN 0003-2697. PMID 4292701.
- ↑ Nakayasu, Ernesto S.; Nicora, Carrie D.; Sims, Amy C.; Burnum-Johnson, Kristin E.; Kim, Young-Mo; Kyle, Jennifer E.; Matzke, Melissa M.; Shukla, Anil K. et al. (2016). "MPLEx: a Robust and Universal Protocol for Single-Sample Integrative Proteomic, Metabolomic, and Lipidomic Analyses". mSystems 1 (3): e00043–16. doi:10.1128/mSystems.00043-16. ISSN 2379-5077. PMID 27822525.
- ↑ Kang, Jianing; David, Lisa; Li, Yangyang; Cang, Jing; Chen, Sixue (2021). "Three-in-One Simultaneous Extraction of Proteins, Metabolites and Lipids for Multi-Omics". Frontiers in Genetics 12. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.635971. ISSN 1664-8021. PMID 33936167.
- ↑ He, Yuchen; Rashan, Edrees H.; Linke, Vanessa; Shishkova, Evgenia; Hebert, Alexander S.; Jochem, Adam; Westphall, Michael S.; Pagliarini, David J. et al. (2021-03-09). "Multi-Omic Single-Shot Technology for Integrated Proteome and Lipidome Analysis". Analytical Chemistry 93 (9): 4217–4222. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04764. ISSN 1520-6882. PMID 33617230.
- ↑ Muehlbauer, Laura K.; Jen, Annie; Zhu, Yunyun; He, Yuchen; Shishkova, Evgenia; Overmyer, Katherine A.; Coon, Joshua J. (2023-01-17). "Rapid Multi-Omics Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry 95 (2): 659–667. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02042. ISSN 1520-6882. PMID 36594155.
- ↑ Wagle, Basanta R.; Quach, Austin; Yeo, Seungjun; Assumpcao, Anna L. F. V.; Arsi, Komala; Donoghue, Annie M.; Jesudhasan, Palmy R. R. (2023-02-05). "A Multiomic Analysis of Chicken Serum Revealed the Modulation of Host Factors Due to Campylobacter jejuni Colonization and In-Water Supplementation of Eugenol Nanoemulsion". Animals 13 (4): 559. doi:10.3390/ani13040559. ISSN 2076-2615. PMID 36830346.
- ↑ Choi, Janghan; Shakeri, Majid; Bowker, Brian; Zhuang, Hong; Kong, Byungwhi (2025-04-14). "Differentially abundant proteins, metabolites, and lipid molecules in spaghetti meat compared to normal chicken breast meat: Multiomics analysis1". Poultry Science 104 (7). doi:10.1016/j.psj.2025.105165. ISSN 0032-5791. PMID 40286572.
- ↑ Altendahl, Marie; Mok, Thalia; Jang, Christine; Yeo, Seungjun; Quach, Austin; Afshar, Yalda (2022). "Severe COVID-19 in pregnancy has a distinct serum profile, including greater complement activation and dysregulation of serum lipids". PLOS ONE 17 (11). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0276766. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 36383608. Bibcode: 2022PLoSO..1776766A.
- ↑ Zafarullah, Marwa; Angkustsiri, Kathleen; Quach, Austin; Yeo, Seungjun; Durbin-Johnson, Blythe P.; Bowling, Heather; Tassone, Flora (2024-02-28). "Untargeted metabolomic, and proteomic analysis identifies metabolic biomarkers and pathway alterations in individuals with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome". Metabolomics 20 (2): 31. doi:10.1007/s11306-024-02088-0. ISSN 1573-3890. PMID 38418685.
- ↑ Mahajan, Supriya D.; Aalinkeel, Ravikumar; Reynolds, Jessica L.; Machhar, Janvhi S.; Ghebrehiwet, Berhane; Schwartz, Stanley A. (February 2025). "Omics analysis reveals galectin-3 to be a potential key regulator of allergic inflammation in hereditary angioedema". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Global 4 (1). doi:10.1016/j.jacig.2024.100353. ISSN 2772-8293. PMID 39583036.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 MacAulay, Iain C.; Ponting, Chris P.; Voet, Thierry (2017). "Single-Cell Multiomics: Multiple Measurements from Single Cells". Trends in Genetics 33 (2): 155–168. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2016.12.003. PMID 28089370.
- ↑ Hu, Youjin; An, Qin; Sheu, Katherine; Trejo, Brandon; Fan, Shuxin; Guo, Ying (2018-04-20). "Single Cell Multi-Omics Technology: Methodology and Application". Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 6: 28. doi:10.3389/fcell.2018.00028. ISSN 2296-634X. PMID 29732369.
- ↑ Kester, Lennart Spanjaard, Bastiaan Bienko, Magda van Oudenaarden, Alexander Dey, Siddharth S (2015). "Integrated genome and transcriptome sequencing of the same cell". Nature Biotechnology 33 (3): 285–289. doi:10.1038/nbt.3129. OCLC 931063996. PMID 25599178.
- ↑ Macaulay, Iain C; Teng, Mabel J; Haerty, Wilfried; Kumar, Parveen; Ponting, Chris P; Voet, Thierry (2016-09-29). "Separation and parallel sequencing of the genomes and transcriptomes of single cells using G&T-seq". Nature Protocols 11 (11): 2081–2103. doi:10.1038/nprot.2016.138. ISSN 1754-2189. PMID 27685099. https://www.research.ed.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/separation-and-parallel-sequencing-of-the-genomes-and-transcriptomes-of-single-cells-using-gtseq(015ce29d-7e2d-42c8-82fa-cb1290b761c0).html.
- ↑ Tang, Fuchou; Wen, Lu; Li, Xianlong; Wu, Xinglong; Zhu, Ping; Guo, Hongshan (2013-12-01). "Single-cell methylome landscapes of mouse embryonic stem cells and early embryos analyzed using reduced representation bisulfite sequencing". Genome Research 23 (12): 2126–2135. doi:10.1101/gr.161679.113. ISSN 1088-9051. PMID 24179143.
- ↑ Kelsey, Gavin; Reik, Wolf; Stegle, Oliver; Andrews, Simon R.; Julian Peat; Saadeh, Heba; Krueger, Felix; Angermueller, Christof et al. (August 2014). "Single-cell genome-wide bisulfite sequencing for assessing epigenetic heterogeneity". Nature Methods 11 (8): 817–820. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3035. ISSN 1548-7105. PMID 25042786.
- ↑ Angermueller, Christof; Clark, Stephen J; Lee, Heather J; Macaulay, Iain C; Teng, Mabel J; Hu, Tim Xiaoming; Krueger, Felix; Smallwood, Sébastien A et al. (2016-01-11). "Parallel single-cell sequencing links transcriptional and epigenetic heterogeneity". Nature Methods 13 (3): 229–232. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3728. ISSN 1548-7091. PMID 26752769.
- ↑ Greenleaf, William J.; Chang, Howard Y.; Snyder, Michael P.; Michael L. Gonzales; Ruff, Dave; Litzenburger, Ulrike M.; Wu, Beijing; Buenrostro, Jason D. (July 2015). "Single-cell chromatin accessibility reveals principles of regulatory variation". Nature 523 (7561): 486–490. doi:10.1038/nature14590. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 26083756. Bibcode: 2015Natur.523..486B.
- ↑ Fraser, Peter; Tanay, Amos; Laue, Ernest D.; Dean, Wendy; Yaffe, Eitan; Schoenfelder, Stefan; Stevens, Tim J.; Lubling, Yaniv et al. (October 2013). "Single-cell Hi-C reveals cell-to-cell variability in chromosome structure". Nature 502 (7469): 59–64. doi:10.1038/nature12593. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 24067610. Bibcode: 2013Natur.502...59N.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Darmanis, Spyros; Gallant, Caroline Julie; Marinescu, Voichita Dana; Niklasson, Mia; Segerman, Anna; Flamourakis, Georgios; Fredriksson, Simon; Assarsson, Erika et al. (2016-01-12). "Simultaneous Multiplexed Measurement of RNA and Proteins in Single Cells". Cell Reports 14 (2): 380–389. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.021. ISSN 2211-1247. PMID 26748716.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Gherardini, Pier Federico; Nolan, Garry P.; Chen, Shih-Yu; Hsieh, Elena W. Y.; Zunder, Eli R.; Bava, Felice-Alessio; Frei, Andreas P. (March 2016). "Highly multiplexed simultaneous detection of RNAs and proteins in single cells". Nature Methods 13 (3): 269–275. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3742. ISSN 1548-7105. PMID 26808670.
- ↑ Assarsson, Erika; Lundberg, Martin; Holmquist, Göran; Björkesten, Johan; Bucht Thorsen, Stine; Ekman, Daniel; Eriksson, Anna; Rennel Dickens, Emma et al. (2014-04-22). "Homogenous 96-Plex PEA Immunoassay Exhibiting High Sensitivity, Specificity, and Excellent Scalability". PLOS ONE 9 (4). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095192. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 24755770. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...995192A.
- ↑ Garmire, Lana X.; Chaudhary, Kumardeep; Huang, Sijia (2017). "More Is Better: Recent Progress in Multi-Omics Data Integration Methods" (in English). Frontiers in Genetics 8: 84. doi:10.3389/fgene.2017.00084. ISSN 1664-8021. PMID 28670325.
- ↑ Tagkopoulos, Ilias; Kim, Minseung (2018). "Data integration and predictive modeling methods for multi-omics datasets". Molecular Omics 14 (1): 8–25. doi:10.1039/C7MO00051K. PMID 29725673.
- ↑ Lin, Eugene; Lane, Hsien-Yuan (2017-01-20). "Machine learning and systems genomics approaches for multi-omics data". Biomarker Research 5 (1): 2. doi:10.1186/s40364-017-0082-y. ISSN 2050-7771. PMID 28127429.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Rohart, Florian; Gautier, Benoît; Singh, Amrit; Lê Cao, Kim-Anh (2017-02-14). "mixOmics: an R package for 'omics feature selection and multiple data integration". PLOS Computational Biology 13 (11). doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005752. PMID 29099853. Bibcode: 2017PLSCB..13E5752R.
- ↑ Tenenhaus, Arthur; Tenenhaus, Michel (2011-03-17). "Regularized Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis". Psychometrika 76 (2): 257–284. doi:10.1007/s11336-011-9206-8. ISSN 0033-3123.
- ↑ Tenenhaus, A.; Philippe, C.; Guillemot, V.; Le Cao, K.-A.; Grill, J.; Frouin, V. (2014-02-17). "Variable selection for generalized canonical correlation analysis". Biostatistics 15 (3): 569–583. doi:10.1093/biostatistics/kxu001. ISSN 1465-4644. PMID 24550197.
- ↑ Tenenhaus, Arthur; Philippe, Cathy; Frouin, Vincent (October 2015). "Kernel Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis". Computational Statistics & Data Analysis 90: 114–131. doi:10.1016/j.csda.2015.04.004. ISSN 0167-9473.
- ↑ Tenenhaus, Michel; Tenenhaus, Arthur; Groenen, Patrick J. F. (2017-05-23). "Regularized Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis: A Framework for Sequential Multiblock Component Methods". Psychometrika 82 (3): 737–777. doi:10.1007/s11336-017-9573-x. ISSN 0033-3123. PMID 28536930.
- ↑ Hasin, Yehudit; Seldin, Marcus; Lusis, Aldons (2017-05-05). "Multi-omics approaches to disease". Genome Biology 18 (1): 83. doi:10.1186/s13059-017-1215-1. ISSN 1474-760X. PMID 28476144.
- ↑ Khan, Mohd M.; Ernst, Orna; Manes, Nathan P.; Oyler, Benjamin L.; Fraser, Iain D. C.; Goodlett, David R.; Nita-Lazar, Aleksandra (2019-03-11). "Multi-Omics Strategies Uncover Host–Pathogen Interactions". ACS Infectious Diseases 5 (4): 493–505. doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00080. ISSN 2373-8227. PMID 30857388.
- ↑ Aderem, Alan; Adkins, Joshua N.; Ansong, Charles; Galagan, James; Kaiser, Shari; Korth, Marcus J.; Law, G. Lynn; McDermott, Jason G. et al. (2011-02-01). "A Systems Biology Approach to Infectious Disease Research: Innovating the Pathogen-Host Research Paradigm". mBio 2 (1): e00325-10. doi:10.1128/mbio.00325-10. ISSN 2150-7511. PMID 21285433.
- ↑ Mouchtouris, N; Smit, RD; Piper, K; Prashant, G; Evans, JJ; Karsy, M (4 March 2022). "A review of multiomics platforms in pituitary adenoma pathogenesis.". Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark Edition) 27 (3): 77. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2703077. PMID 35345309.
- ↑ Yan, Jingwen; Risacher, Shannon L; Shen, Li; Saykin, Andrew J. (2017-06-30). "Network approaches to systems biology analysis of complex disease: integrative methods for multi-omics data". Briefings in Bioinformatics 19 (6): 1370–1381. doi:10.1093/bib/bbx066. ISSN 1467-5463. PMID 28679163.
- ↑ He, Feng Q.; Ollert, Markus; Balling, Rudi; Bode, Sebastian F. N.; Delhalle, Sylvie (2018-02-06). "A roadmap towards personalized immunology". npj Systems Biology and Applications 4 (1): 9. doi:10.1038/s41540-017-0045-9. ISSN 2056-7189. PMID 29423275.
- ↑ Proctor, Lita M.; Creasy, Heather H.; Fettweis, Jennifer M.; Lloyd-Price, Jason; Mahurkar, Anup; Zhou, Wenyu; Buck, Gregory A.; Snyder, Michael P. et al. (May 2019). "The Integrative Human Microbiome Project". Nature 569 (7758): 641–648. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1238-8. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 31142853. Bibcode: 2019Natur.569..641I.
- ↑ "After the Integrative Human Microbiome Project, what's next for the microbiome community?". Nature 569 (7758): 599. 2019-05-29. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-01674-w. PMID 31142868. Bibcode: 2019Natur.569Q.599..
- ↑ Snyder, Michael; Weinstock, George M.; Sodergren, Erica; McLaughlin, Tracey; Tse, David; Rost, Hannes; Piening, Brian; Kukurba, Kim et al. (May 2019). "Longitudinal multi-omics of host–microbe dynamics in prediabetes". Nature 569 (7758): 663–671. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1236-x. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 31142858. Bibcode: 2019Natur.569..663Z.
- ↑ Huttenhower, Curtis; Xavier, Ramnik J.; Vlamakis, Hera; Franzosa, Eric A.; Clish, Clary B.; Winter, Harland S.; Stappenbeck, Thaddeus S.; Petrosino, Joseph F. et al. (May 2019). "Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem in inflammatory bowel diseases". Nature 569 (7758): 655–662. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1237-9. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 31142855. Bibcode: 2019Natur.569..655L.
- ↑ Buck, Gregory A.; Strauss, Jerome F.; Jefferson, Kimberly K.; Hendricks-Muñoz, Karen D.; Wijesooriya, N. Romesh; Rubens, Craig E.; Gravett, Michael G.; Sexton, Amber L. et al. (June 2019). "The vaginal microbiome and preterm birth". Nature Medicine 25 (6): 1012–1021. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0450-2. ISSN 1546-170X. PMID 31142849.
- ↑ Kidd, Brian A; Peters, Lauren A; Schadt, Eric E; Dudley, Joel T (2014-01-21). "Unifying immunology with informatics and multiscale biology". Nature Immunology 15 (2): 118–127. doi:10.1038/ni.2787. ISSN 1529-2908. PMID 24448569.
- ↑ Harris, Eva; Kasarskis, Andrew; Wolinsky, Steven M.; Suaréz-Fariñas, Mayte; Zhu, Jun; Wang, Li; Balmaseda, Angel; Thomas, Guajira P. et al. (2018-08-01). "Comprehensive innate immune profiling of chikungunya virus infection in pediatric cases". Molecular Systems Biology 14 (8). doi:10.15252/msb.20177862. ISSN 1744-4292. PMID 30150281.
- ↑ Firestein, Gary S.; Wang, Wei; Gay, Steffen; Ball, Scott T.; Bartok, Beatrix; Boyle, David L.; Whitaker, John W. (2015-04-22). "Integrative Omics Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Identifies Non-Obvious Therapeutic Targets". PLOS ONE 10 (4). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124254. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 25901943. Bibcode: 2015PLoSO..1024254W.
- ↑ Pulendran, Bali; Li, Shuzhao; Nakaya, Helder I. (2010-10-29). "Systems Vaccinology". Immunity 33 (4): 516–529. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.006. ISSN 1074-7613. PMID 21029962.
- ↑ Li, Shuzhao; Sullivan, Nicole L.; Rouphael, Nadine; Yu, Tianwei; Banton, Sophia; Maddur, Mohan S.; McCausland, Megan; Chiu, Christopher et al. (2017-05-18). "Metabolic Phenotypes of Response to Vaccination in Humans". Cell 169 (5): 862–877.e17. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.026. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 28502771.
- ↑ Meng, Chen; Kuster, Bernhard; Culhane, Aedín C; Gholami, Amin (2014). "A multivariate approach to the integration of multi-omics datasets". BMC Bioinformatics 15 (1): 162. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-15-162. ISSN 1471-2105. PMID 24884486.
- ↑ Ramos, Marcel; Schiffer, Lucas; Re, Angela; Azhar, Rimsha; Basunia, Azfar; Rodriguez, Carmen; Chan, Tiffany; Chapman, Phil et al. (1 November 2017). "Software for the Integration of Multiomics Experiments in Bioconductor". Cancer Research 77 (21): e39–e42. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0344. PMID 29092936.
- ↑ Seonggyun Han, Younghee Lee (2017), IMAS, Bioconductor, doi:10.18129/b9.bioc.imas, https://bioconductor.org/packages/IMAS, retrieved 2019-06-28
- ↑ Karim Mezhoud [Aut, Cre] (2017), bioCancer, Bioconductor, doi:10.18129/b9.bioc.biocancer, https://bioconductor.org/packages/bioCancer, retrieved 2019-06-28
- ↑ Hernandez-Ferrer, Carles; Ruiz-Arenas, Carlos; Beltran-Gomila, Alba; González, Juan R. (2017-01-17). "MultiDataSet: an R package for encapsulating multiple data sets with application to omic data integration". BMC Bioinformatics 18 (1): 36. doi:10.1186/s12859-016-1455-1. ISSN 1471-2105. PMID 28095799.
- ↑ "Reap the rewards of a biological insight engine". https://omictools.com/.
- ↑ Conesa, Ana; Dopazo, Joaquín; García-López, Federico; García-Alcalde, Fernando (2011-01-01). "Paintomics: a web based tool for the joint visualization of transcriptomics and metabolomics data". Bioinformatics 27 (1): 137–139. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq594. ISSN 1367-4803. PMID 21098431.
- ↑ Conesa, Ana; Pappas, Georgios J.; Furió-Tarí, Pedro; Balzano-Nogueira, Leandro; Martínez-Mira, Carlos; Tarazona, Sonia; Hernández-de-Diego, Rafael (2018-07-02). "PaintOmics 3: a web resource for the pathway analysis and visualization of multi-omics data". Nucleic Acids Research 46 (W1): W503–W509. doi:10.1093/nar/gky466. ISSN 0305-1048. PMID 29800320.
- ↑ Chari, Raj; Coe, Bradley P.; Wedseltoft, Craig; Benetti, Marie; Wilson, Ian M.; Vucic, Emily A.; MacAulay, Calum; Ng, Raymond T. et al. (2008-10-07). "SIGMA2: A system for the integrative genomic multi-dimensional analysis of cancer genomes, epigenomes, and transcriptomes". BMC Bioinformatics 9 (1): 422. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-422. ISSN 1471-2105. PMID 18840289.
- ↑ Choi, Hyungwon; Ewing, Rob; Choi, Kwok Pui; Fermin, Damian; Koh, Hiromi W. L. (2018-07-23). "iOmicsPASS: a novel method for integration of multi-omics data over biological networks and discovery of predictive subnetworks". bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/374520. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/374520v1.
- ↑ Kanai, Masahiro; Maeda, Yuichi; Okada, Yukinori (2018-06-19). "Grimon: graphical interface to visualize multi-omics networks". Bioinformatics 34 (22): 3934–3936. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bty488. ISSN 1367-4803. PMID 29931190.
- ↑ Su, Andrew I.; Loguercio, Salvatore; Carland, Tristan M.; Ducom, Jean-Christophe; Gioia, Louis; Meißner, Tobias; Fisch, Kathleen M. (2015-06-01). "Omics Pipe: a community-based framework for reproducible multi-omics data analysis". Bioinformatics 31 (11): 1724–1728. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv061. ISSN 1367-4803. PMID 25637560.
- ↑ Montague, Elizabeth; Stanberry, Larissa; Higdon, Roger; Janko, Imre; Lee, Elaine; Anderson, Nathaniel; Choiniere, John; Stewart, Elizabeth et al. (June 2014). "MOPED 2.5—An Integrated Multi-Omics Resource: Multi-Omics Profiling Expression Database Now Includes Transcriptomics Data". OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology 18 (6): 335–343. doi:10.1089/omi.2014.0061. ISSN 1536-2310. PMID 24910945.
- ↑ Zhang, Bing; Wang, Jing; Straub, Peter; Vasaikar, Suhas V. (2018-01-04). "LinkedOmics: analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types". Nucleic Acids Research 46 (D1): D956–D963. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx1090. ISSN 0305-1048. PMID 29136207.
- ↑ "LinkedOmics :: Login". http://www.linkedomics.org.
- ↑ Kan, Zhengyan; Rejto, Paul A.; Roberts, Peter; Ding, Ying; AChing, Keith; Wang, Kai; Deng, Shibing; Schefzick, Sabine et al. (January 2016). "OASIS: web-based platform for exploring cancer multi-omics data". Nature Methods 13 (1): 9–10. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3692. ISSN 1548-7105. PMID 26716558.
- ↑ Wu, Jiaqi; Hu, Shuofeng; Chen, Yaowen; Li, Zongcheng; Zhang, Jian; Yuan, Hanyu; Shi, Qiang; Shao, Ningsheng et al. (May 2017). "BCIP: a gene-centered platform for identifying potential regulatory genes in breast cancer". Scientific Reports 7 (1). doi:10.1038/srep45235. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 28327601. Bibcode: 2017NatSR...745235W.
- ↑ Husi, Holger; Patel, Alisha; Fernandes, Marco (2018-11-12). "C/VDdb: A multi-omics expression profiling database for a knowledge-driven approach in cardiovascular disease (CVD)". PLOS ONE 13 (11). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0207371. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 30419069. Bibcode: 2018PLoSO..1307371F.
- ↑ Gupta, Amit Kumar; Kaur, Karambir; Rajput, Akanksha; Dhanda, Sandeep Kumar; Sehgal, Manika; Khan, Md. Shoaib; Monga, Isha; Dar, Showkat Ahmad et al. (2016-09-16). "ZikaVR: An Integrated Zika Virus Resource for Genomics, Proteomics, Phylogenetic and Therapeutic Analysis". Scientific Reports 6 (1). doi:10.1038/srep32713. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 27633273. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...632713G.
- ↑ Tagkopoulos, Ilias; Violeta Zorraquino; Rai, Navneet; Kim, Minseung (2016-10-07). "Multi-omics integration accurately predicts cellular state in unexplored conditions for Escherichia coli". Nature Communications 7. doi:10.1038/ncomms13090. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 27713404. Bibcode: 2016NatCo...713090K.
- ↑ Li, Guojing; Lu, Zhongfu; Lin, Jiandong; Hu, Yaowen; Yunping Huang; Wang, Baogen; Wu, Xinyi; Wu, Xiaohua et al. (2018-02-26). "GourdBase: a genome-centered multi-omics database for the bottle gourd ( Lagenaria siceraria ), an economically important cucurbit crop". Scientific Reports 8 (1): 3604. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-22007-3. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 29483591. Bibcode: 2018NatSR...8.3604W.
- ↑ Liu, Haijun; Wang, Fan; Xiao, Yingjie; Tian, Zonglin; Wen, Weiwei; Zhang, Xuehai; Chen, Xi; Liu, Nannan et al. (2016). "MODEM: multi-omics data envelopment and mining in maize". Database 2016. doi:10.1093/database/baw117. ISSN 1758-0463. PMID 27504011.
- ↑ Xu, Dong; Nguyen, Henry T.; Stacey, Gary; Gaudiello, Eric C.; Endacott, Ryan Z.; Zhang, Hongxin; Liu, Yang; Chen, Shiyuan et al. (2014-01-01). "Soybean knowledge base (SoyKB): a web resource for integration of soybean translational genomics and molecular breeding". Nucleic Acids Research 42 (D1): D1245–D1252. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt905. ISSN 0305-1048. PMID 24136998.
- ↑ Samaras, Patroklos; Schmidt, Tobias; Frejno, Martin; Gessulat, Siegfried; Reinecke, Maria; Jarzab, Anna; Zecha, Jana; Mergner, Julia et al. (2020-01-08). "ProteomicsDB: a multi-omics and multi-organism resource for life science research" (in en). Nucleic Acids Research 48 (D1): D1153–D1163. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz974. ISSN 0305-1048. PMID 31665479.
 |
