Biology:Oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase
| oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
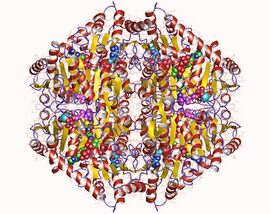 Oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase homotetramer, Oxalobacter formigenes | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.1.1.8 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9024-96-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
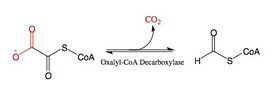
The enzyme oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase (OXC) (EC 4.1.1.8), primarily produced by the gastrointestinal bacterium Oxalobacter formigenes, catalyzes the chemical reaction
- oxalyl-CoA [math]\displaystyle{ \rightleftharpoons }[/math] formyl-CoA + CO2
OXC belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the carboxy-lyases (decarboxylases), which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is oxalyl-CoA carboxy-lyase (formyl-CoA-forming). Other names in common use include oxalyl coenzyme A decarboxylase, and oxalyl-CoA carboxy-lyase. This enzyme participates in glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. It employs one cofactor, thiamin diphosphate (TPP), and plays a key role in catabolism of oxalate, a highly toxic compound that is a product of the oxidation of carbohydrates in many bacteria and plants.[1] Oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase is extremely important for the elimination of ingested oxalates found in human foodstuffs like coffee, tea, and chocolate,[2] and the ingestion of such foods in the absence of Oxalobacter formigenes in the gut can result in kidney disease or even death as a result of oxalate poisoning.[3]
Evolution
Oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase is hypothesized to be evolutionarily related to acetolactate synthase, a TPP-dependent enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of branched chain amino acids in certain organisms.[4] Sequence alignments between the two enzymes support this claim, as do the presence of vestigial FAD-binding pockets that play no role in either enzyme's catalytic activity.[5] The binding of FAD at this site in acetolactate synthase and the binding of ADP at a cognate site in OXC are thought to play roles in the stabilization of the tertiary structures of the proteins.[6] No FAD binding is observed in oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase,[7] but an excess of coenzyme A in the crystal structure has led to the hypothesis that the binding site was co-opted during OXC evolution to bind the CoA moiety of its substrate.[8]> Despite their similarities, only oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase is necessary for the formation of ATP in Oxalobacter formigenes, and exogenous ADP has been demonstrated to increase the decarboxylase activity of OXC, but not acetolactate synthase.[9][10]
Reaction mechanism
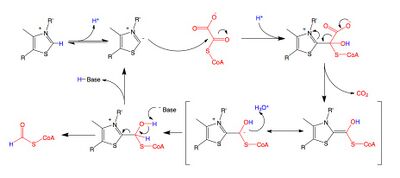
A key feature of the cofactor TPP is the relatively acidic proton bound to the carbon atom between the nitrogen and sulfur in the thiazole ring, which has a pKa near 10.[11] This carbon center ionizes to form a carbanion, which adds to the carbonyl group of oxalyl-CoA. This addition is followed by the decarboxylation of oxalyl-CoA, and then the oxidation and removal of formyl-CoA to regenerate the carbanion form of TPP. While the reaction mechanism is shared with other TPP-dependent enzymes, the residues found in the active site of OXC are unique, which has raised questions about whether TDP must be deprotonated by a basic amino acid at a second site away from the carbanion-forming site to activate the cofactor.[12]
Structure
Oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase is tetrameric, and each monomer consists of three α/β-type domains.[13] The thiamine diphosphate-binding site rests on the subunit-subunit interface between two of the domains, which is commonly seen in its class of enzymes. Oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase is structurally homologous to acetolactate synthase found in plants and other microorganisms, but OXC binds ADP in a region that is similar to the FAD-binding site in acetolactate synthase.[14][15]
See also
References
- ↑ "Purification and characterization of formyl-coenzyme A transferase from Oxalobacter formigenes". Journal of Bacteriology 172 (7): 3537–40. July 1990. doi:10.1128/jb.172.7.3537-3540.1990. PMID 2361939.
- ↑ "Tea and coffee as the main sources of oxalate in diets of patients with kidney oxalate stones". Roczniki Panstwowego Zakladu Higieny 58 (1): 61–7. 2007. PMID 17711092.
- ↑ "Oxalate-degrading activity in Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis: impact of acidic conditions on the transcriptional levels of the oxalyl coenzyme A (CoA) decarboxylase and formyl-CoA transferase genes". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 76 (16): 5609–20. August 2010. doi:10.1128/AEM.00844-10. PMID 20601517.
- ↑ "Acetohydroxy acid synthase I, a required enzyme for isoleucine and valine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12 during growth on acetate as the sole carbon source". Journal of Bacteriology 165 (2): 453–60. February 1986. doi:10.1128/jb.165.2.453-460.1986. PMID 3511034.
- ↑ "Biosynthesis of 2-aceto-2-hydroxy acids: acetolactate synthases and acetohydroxyacid synthases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 1385 (2): 401–19. June 1998. doi:10.1016/S0167-4838(98)00083-1. PMID 9655946.
- ↑ "Flavin adenine dinucleotide causes oligomerization of acetohydroxyacid synthase from Black Mexican Sweet corn cells.". FEBS Letters 258 (1): 113–5. November 1989. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(89)81628-X.
- ↑ "The enzymes of oxalate metabolism: unexpected structures and mechanisms". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 433 (1): 176–92. January 2005. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.032. PMID 15581576.
- ↑ "Crystallographic snapshots of oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase give insights into catalysis by nonoxidative ThDP-dependent decarboxylases". Structure 15 (7): 853–61. July 2007. doi:10.1016/j.str.2007.06.001. PMID 17637344.
- ↑ "Regulation by external pH and stationary growth phase of the acetolactate synthase from Synechocystis PCC6803". Molecular Microbiology 37 (4): 828–38. August 2000. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02048.x. PMID 10972805.
- ↑ "Regulation of acetohydroxy acid synthase in streptomycin-dependent Escherichia coli". Journal of Bacteriology 121 (1): 9–12. January 1975. doi:10.1128/JB.121.1.9-12.1975. PMID 46865.
- ↑ Biochemistry (6th ed.). NY: W.H. Freeman and Company. p. 479.
- ↑ "Structural basis for activation of the thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzyme oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase by adenosine diphosphate". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280 (50): 41645–54. December 2005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509921200. PMID 16216870.
- ↑ "New insights into structure-function relationships of oxalyl CoA decarboxylase from Escherichia coli". The FEBS Journal 277 (12): 2628–40. June 2010. doi:10.1111/j.1742-464X.2010.07673.x. PMID 20553497.
- ↑ "Acetohydroxyacid Synthase". Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 33 (1). 2000.
- ↑ "Transcriptional and functional analysis of oxalyl-coenzyme A (CoA) decarboxylase and formyl-CoA transferase genes from Lactobacillus acidophilus". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 72 (3): 1891–9. March 2006. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.3.1891-1899.2006. PMID 16517636.
 |