Biology:Poribacteria
| Poribacteria | |
|---|---|
| |
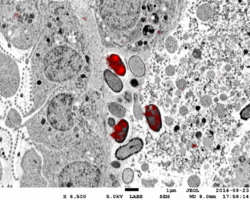
| Poribacteria localisation in the sponge Aplysina aerophoba | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Clade: | Hydrobacteria |
| Phylum: | Poribacteria |
Poribacteria are a candidate phylum of bacteria originally discovered[1] in the microbiome of marine sponges (Porifera). Poribacteria are Gram-negative primarily aerobic mixotrophs with the ability for oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis, and autotrophic carbon fixation via the Wood – Ljungdahl pathway.[2][3] Poribacterial heterotrophy is characterised by an enriched set of glycoside hydrolases, uronic acid degradation, as well as several specific sulfatases. This heterotrophic repertoire of poribacteria was suggested to be involved in the degradation of the extracellular sponge host matrix.[3]
Genome
Single-cell genomics and metagenomic shotgun sequencing approaches reveal a poribacterial genome size range between about 4.2 and 6.5 megabases[2][3][4][5] encoding 4,254 protein-coding genes, of which an unusually high 24% have no homology to known genes. Among the genes of identifiable homology, reconstructed pathways suggest that the poribacterial central metabolism is capable of glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, pentose phosphate pathways, oxidative phosphorylation, the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, and autotrophic carbon fixation via Wood–Ljungdahl pathway. Further, Poribacteria seem to engage in assimilatory denitrification and ammonia scavenging with potential relevance in nitrogen re-cycling within the sponge holobiont. The poribacterial genome is also reported to contain an unusually high number of phage defence systems including CRISPR-CAS and restriction modification systems.[6]
Cell compartmentalization
Cell compartmentalization into distinct membrane-bound organelles is a universal and defining property of eukaryotes, but had not been observed in prokaryotes other than the Planctomycetota. Poribacteria were previously thought to be distinguished from other microorganisms associated with marine sponges by such a distinctive morphology featuring a large membrane-bound cellular compartment that was suggested to contain DNA.[1] The distinctive poribacterial compartments were originally identified using fluorescence in situ hybridization and electron microscopy.[1] Genomic evidence suggests the presence of protein-bound organelles, but not for membrane-bound organelles.[6] More recently, correlative light-electron microscopy, confirmed two elements of poribacterial subcellular compartmentation:[7] Firstly, Bacterial microcompartments, atypically localized at the cell membrane. Secondly, spherical bipolar compartments which are discussed to be most likely carbon rich storage polymers such as Polyhydroxybutyrate.
Eukaryote-like proteins
Genomic analyses of poribacteria reveal several families of cell-surface repeat proteins that resemble those found in eukaryotes, and are infrequently found in prokaryotes. Examples include ankyrin and leucine-rich repeat domains,[2] as well as tetratricopeptides.[6] Unusual low-density lipoprotein receptor repeat proteins are also found, of unknown function. Most of these protein families are thought to be involved in surface interactions with the sponge host.[6] In addition, genetic infrastructure for sterol biosynthesis is observed in poribacterial genomes, otherwise found almost exclusively in eukaryotes and the planctomycete Gemmata obscuriglobus.[2]
Ecological niche
Poribacteria are symbionts of marine sponges, among the most abundant microorganisms in the highly diverse microbiome of the sponge mesohyl.[2] They have been found in a large variety of sponge species from diverse geographic origins.[8] The composition of microorganisms in the sponge microbiome can be vertically inherited, with adult sponges transmitting their distinctive microbial communities to offspring.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Fieseler, L; Horn, M; Wagner, M; Hentschel, U (June 2004). "Discovery of the novel candidate phylum "Poribacteria" in marine sponges". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 70 (6): 3724–32. doi:10.1128/aem.70.6.3724-3732.2004. PMID 15184179. Bibcode: 2004ApEnM..70.3724F.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Siegl, A; Kamke, J; Hochmuth, T; Piel, J; Richter, M; Liang, C; Dandekar, T; Hentschel, U (January 2011). "Single-cell genomics reveals the lifestyle of Poribacteria, a candidate phylum symbiotically associated with marine sponges". The ISME Journal 5 (1): 61–70. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.95. PMID 20613790.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Kamke, Janine; Sczyrba, Alexander; Ivanova, Natalia; Schwientek, Patrick; Rinke, Christian; Mavromatis, Kostas; Woyke, Tanja; Hentschel, Ute (December 2013). "Single-cell genomics reveals complex carbohydrate degradation patterns in poribacterial symbionts of marine sponges" (in en). The ISME Journal 7 (12): 2287–2300. doi:10.1038/ismej.2013.111. ISSN 1751-7362. PMID 23842652.
- ↑ Podell, Sheila; Blanton, Jessica M.; Neu, Alexander; Agarwal, Vinayak; Biggs, Jason S.; Moore, Bradley S.; Allen, Eric E. (February 2019). "Pangenomic comparison of globally distributed Poribacteria associated with sponge hosts and marine particles" (in en). The ISME Journal 13 (2): 468–481. doi:10.1038/s41396-018-0292-9. ISSN 1751-7370. PMID 30291328.
- ↑ Slaby, Beate M.; Hackl, Thomas; Horn, Hannes; Bayer, Kristina; Hentschel, Ute (November 2017). "Metagenomic binning of a marine sponge microbiome reveals unity in defense but metabolic specialization" (in en). The ISME Journal 11 (11): 2465–2478. doi:10.1038/ismej.2017.101. ISSN 1751-7370. PMID 28696422.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Kamke, J; Rinke, C; Schwientek, P; Mavromatis, K; Ivanova, N; Sczyrba, A; Woyke, T; Hentschel, U (2014). "The candidate phylum Poribacteria by single-cell genomics: new insights into phylogeny, cell-compartmentation, eukaryote-like repeat proteins, and other genomic features". PLOS ONE 9 (1): e87353. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0087353. PMID 24498082. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...987353K.
- ↑ Jahn, Martin T.; Markert, Sebastian M.; Ryu, Taewoo; Ravasi, Timothy; Stigloher, Christian; Hentschel, Ute; Moitinho-Silva, Lucas (December 2016). "Shedding light on cell compartmentation in the candidate phylum Poribacteria by high resolution visualisation and transcriptional profiling" (in en). Scientific Reports 6 (1): 35860. doi:10.1038/srep35860. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 27796326. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...635860J.
- ↑ Lafi, FF; Fuerst, JA; Fieseler, L; Engels, C; Goh, WW; Hentschel, U (September 2009). "Widespread distribution of poribacteria in demospongiae". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 75 (17): 5695–9. doi:10.1128/aem.00035-09. PMID 19561181. Bibcode: 2009ApEnM..75.5695L.
- ↑ Schmitt, S; Angermeier, H; Schiller, R; Lindquist, N; Hentschel, U (December 2008). "Molecular microbial diversity survey of sponge reproductive stages and mechanistic insights into vertical transmission of microbial symbionts". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 74 (24): 7694–708. doi:10.1128/aem.00878-08. PMID 18820053. Bibcode: 2008ApEnM..74.7694S.
Wikidata ☰ Q24975421 entry
 |
