Biology:Von Willebrand factor type A domain
| von Willebrand factor type A domain | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
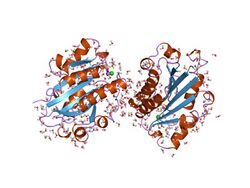 Structure of the I-domain from the CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1, alpha L beta 2) integrin.[1] | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | VWA | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00092 | ||||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0128 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002035 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1lfa / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| CDD | cd00198 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The von Willebrand factor type A (vWA) domain is a protein domain named after its occurrence in von Willebrand factor (vWF), a large multimeric glycoprotein found in blood plasma. Mutant forms of vWF are involved in the aetiology of bleeding disorders.[2] This type A domain is the prototype for a protein superfamily (InterPro: IPR036465; see also Pfam clan).
The vWA domain is found in various plasma proteins: complement factors B, C2, CR3 and CR4; the integrins (I-domains); collagen types VI, VII, XII and XIV; and other extracellular proteins.[3][4][5] Although the majority of vWA-containing proteins are extracellular, the most ancient ones present in all eukaryotes are all intracellular proteins involved in functions such as transcription, DNA repair, ribosomal and membrane transport and the proteasome. A common feature appears to be involvement in multiprotein complexes. Proteins that incorporate vWA domains participate in numerous biological events (e.g. cell adhesion, migration, homing, pattern formation, and signal transduction), involving interaction with a large array of ligands.[3] A number of human diseases arise from mutations in vWA domains.
Secondary structure prediction from 75 aligned vWA sequences has revealed a largely alternating sequence of alpha-helices and beta-strands.[4] Fold recognition algorithms were used to score sequence compatibility with a library of known structures: the vWA domain fold was predicted to be a doubly wound, open, twisted beta-sheet flanked by alpha-helices.[6] 3D structures have been determined for the I-domains of integrins CD11b (with bound magnesium)[7] and CD11a (with bound manganese).[8] The domain adopts a classic alpha/beta Rossmann fold and contains an unusual metal ion coordination site at its surface. It has been suggested that this site represents a general metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) for binding protein ligands.[7] The residues constituting the MIDAS motif in the CD11b and CD11a I-domains are completely conserved, but the manner in which the metal ion is coordinated differs slightly.[8]
Human proteins containing this domain
ANTXR1; ANTXR2; BF; C2; CACHD1; CACNA2D1; CACNA2D2; CACNA2D3; CACNA2D4; CFB; CLCA1; CLCA2; CLCA4; COCH; COL12A1; COL14A1; COL20A1; COL21A1; COL22A1; COL28; COL6A1; COL6A2; COL6A3; COL7A1; COLA1L; CaCC1; ITGA1; ITGA10; ITGA11; ITGA2; ITGAD; ITGAE; ITGAL; ITGAM; ITGAX; ITIH1; ITIH2; ITIH3; ITIH4; ITIH5; ITIH5L; LOC285929; LOC340267; LOC389462; LOH11CR2A; MATN1; MATN2; MATN3; MATN4; PARP4; SVEP1(SEL-OB); VIT; VWA1; VWA2; VWF; hCLCA1; hCLCA2; CMG2;
References
- ↑ "Crystal structure of the I-domain from the CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1, alpha L beta 2) integrin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (22): 10277–81. October 1995. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10277. PMID 7479767.
- ↑ "von Willebrand factor". FASEB J. 7 (2): 308–316. 1993. doi:10.1096/fasebj.7.2.8440408. PMID 8440408.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Type A modules: interacting domains found in several non-fibrillar collagens and in other extracellular matrix proteins". Matrix 13 (4): 297–306. 1993. doi:10.1016/S0934-8832(11)80025-9. PMID 8412987.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "The secondary structure of the von Willebrand factor type A domain in factor B of human complement by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Its occurrence in collagen types VI, VII, XII and XIV, the integrins and other proteins by averaged structure predictions". J. Mol. Biol. 238 (1): 104–119. 1994. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1271. PMID 8145250.
- ↑ Bork P (1991). "Shuffled domains in extracellular proteins". FEBS Lett. 286 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)80937-X. PMID 1864378.
- ↑ "The protein fold of the von Willebrand factor type A domain is predicted to be similar to the open twisted beta-sheet flanked by alpha-helices found in human ras-p21". FEBS Lett. 358 (3): 283–286. 1995. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)01447-9. PMID 7843416.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Crystal structure of the A domain from the alpha subunit of integrin CR3 (CD11b/CD18)". Cell 80 (4): 631–638. 1995. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90517-0. PMID 7867070.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Crystal structure of the I-domain from the CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1, alpha L beta 2) integrin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (22): 10277–10281. 1995. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10277. PMID 7479767.
- Bork, P; Rohde, K (1991). "More von Willebrand factor type a domains? Sequence similarities with malaria thrombospondin-related anonymous protein, dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel and inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor". The Biochemical Journal 279 (3): 908–10. doi:10.1042/bj2790908. PMID 1659389.
External links
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_IBS_1
 |

