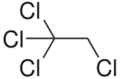
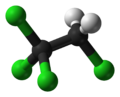
Chemistry:1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane | |||
| Other names
R-130a; acetylidene tetrachloride, asymmetrical tetrachloroethane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2Cl4 | |||
| Molar mass | 167.848 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Clear liquid | ||
| Density | 1.5532 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −70.2 °C (−94.4 °F; 203.0 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 130.5 °C (266.9 °F; 403.6 K) | ||
| 0.1% (20°C)[2] | |||
| Vapor pressure | 14 mmHg (25°C)[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[2] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
Handle with caution in the workplace.[2] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[2] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colorless liquid with a sweet chloroform-like odor. It is used as a solvent and in the production of wood stains and varnishes. It is an isomer of 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
Production
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane can be obtained by a two-step addition reaction of acetylene with chlorine (via dichloroethene), but this mainly produces 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane.
[math]\ce{ C2H2 + Cl2 -> C2H2Cl2 }[/math] [math]\ce{ C2H2Cl2 + Cl2 -> C2H2Cl4 }[/math]
It can be obtained directly by chlorination of 1,1,2-trichloroethane:[3]
[math]\ce{ CHCl2-CH2Cl + Cl2 -> CHCl2-CCl3 + HCl }[/math]
Safety
IARC has classified 1,1,1,2-tetrachloroethane as a possible carcinogen for humans in 2014.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "National Pollutant Inventory Substance Profile". http://www.npi.gov.au/database/substance-info/profiles/79.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0597". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0597.html.
- ↑ Lawrance Waddams: The Petroleum chemicals Industry, S. 175.
- ↑ IARC Monograph 106 – 1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane, 2014
 |