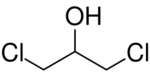
Chemistry:1,3-Dichloropropan-2-ol
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Dichloropropan-2-ol | |
| Other names
1,3-Dichloropropanol-2; 1,3-Dichloroisopropyl alcohol; 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol; 1,3-Dichloroisopropanol; Glycerol-α,γ-dichlorohydrin; α-Dichlorohydrin; 1,3-DCP; DC2P
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2750 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6Cl2O | |
| Molar mass | 128.98 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Phenol-like[1] |
| Density | 1.39 g/cm3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | −4 °C (25 °F; 269 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K)[1] |
| 110 g/L (20 °C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H312, H336, H350, H370, H373 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P307+311, P308+313, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 74 °C (165 °F; 347 K)[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
110 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] 1080 mg/kg (dermal, rabbit)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1,3-Dichloropropan-2-ol (1,3-DCP) is an organic compound with the formula HOCH2CHClCH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid. It is an intermediate in the production of epichlorohydrin.[2][3]
1,3-DCP is a believed to be a carcinogen and mutagen.[4] The International Agency for Research on Cancer classifies it as a Group 2B carcinogen ("possibly carcinogenic to humans").[5]
Along with 3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol (3-MCPD), 1,3-DCP is found in some Asian style sauces such as soy sauce and oyster sauce.[6][7][8]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ "1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol". Some Chemicals Present in Industrial and Consumer Products, Food and Drinking-Water. International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2013. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK373196/.
- ↑ Howard, Philip H.; Muir, Derek C. G. (2010). "Identifying New Persistent and Bioaccumulative Organics Among Chemicals in Commerce". Environmental Science & Technology 44 (7): 2277–2285. doi:10.1021/es903383a. PMID 20163179. Bibcode: 2010EnST...44.2277H.
- ↑ "Evidence on the Carcinogenicity of 1,3-Dichloro-2-Propanol (1,3-DCP; α,γ-Dichlorohydrin)". Reproductive and Cancer Hazard Assessment Branch Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, California Environmental Protection Agency. June 2010. https://oehha.ca.gov/media/downloads/proposition-65/13-dcphida.pdf.
- ↑ "List of Classifications". International Agency for Research on Cancer. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/latest_classif.php.
- ↑ Genualdi, Susan; Nyman, Patricia; Dejager, Lowri (2017). "Simultaneous Analysis of 3-MCPD and 1,3-DCP in Asian Style Sauces Using QuEChERS Extraction and Gas Chromatography–Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 65 (4): 981–985. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05051. PMID 28064506.
- ↑ Crews, C; Lebrun, G; Brereton, P. A (2002). "Determination of 1,3-dichloropropanol in soy sauces by automated headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry". Food Additives and Contaminants 19 (4): 343–349. doi:10.1080/02652030110098580. PMID 11962691.
- ↑ Lee, Bai Qin; Khor, Sook Mei (2015). "3-Chloropropane-1,2-diol (3-MCPD) in Soy Sauce: A Review on the Formation, Reduction, and Detection of This Potential Carcinogen". Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 14 (1): 48–66. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12120. PMID 33401813. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/2063397/1/files/3666990.pdf.
 |
