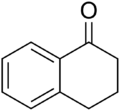
Chemistry:1-Tetralone
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4-Dihydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one | |
| Other names
α-Tetralone; 1-Tetralone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O | |
| Molar mass | 146.189 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | * 1.099 g·cm−3 (25 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 2–7 °C[1] |
| Boiling point | * 255–257 °C[2]
|
| insoluble[3] | |
| Solubility | soluble in organic solvents |
| Vapor pressure | 2.7 Pa (20 °C)[3] |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5672 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Tetralone is a bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and a ketone. In terms of its structure, it can also be regarded as benzo-fused cyclohexanone. It is a colorless oil with a faint odor.[4] It is used as starting material for agricultural and pharmaceutical agents. The carbon skeleton of 1-tetralone is found in natural products such as Aristelegone A (4,7-dimethyl-6-methoxy-1-tetralone) from the family of Aristolochiaceae used in traditional Chinese medicine.[5]
Preparation
By oxidation of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene
As already described in 1933 by Heinrich Hock, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene tends to autoxidize and gradually forms the 1-hydroperoxide with atmospheric oxygen.[6] The heavy metal ion catalyzed air oxidation of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene with Cr3+[7] or Cu2+ in the liquid phase leads via the hydroperoxide to a mixture of the intermediate 1-tetralol and the final product 1-tetralone.[8]
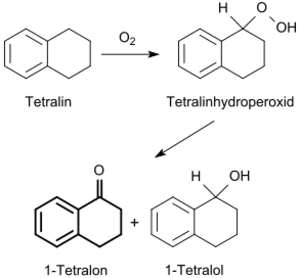
The boiling points of the main component 1-tetralone (255-257 °C) and the minor component 1-tetralol (255 °C)[2] are virtually identical, the latter is therefore removed by a chemical reaction.[9]
By Friedel-Crafts reactions
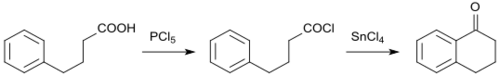
The starting compound 4-phenylbutanoic acid (whose sodium salt sodium phenylbutyrate is used to treat hyperammonaemia) is accessible from 3-benzoylpropanoic acid via catalytic hydrogenation, using a palladium contact catalyst.[4] 3-Benzoylpropanoic acid[10] itself can be obtained by a Haworth reaction (a variant of the Friedel-Crafts reaction) from benzene and succinic anhydride .
The intramolecular cyclization of 4-phenylbutanoic acid to 1-tetralone is catalyzed by polyphosphoric acid[4] and methanesulfonic acid.[11]
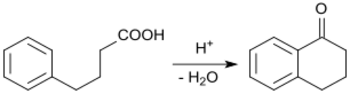
It has been described as a teaching experiment for chemistry lessons.[12] 4-Phenylbutanoic acid can also be quantitatively converted into 1-tetralone by heating in the presence of a strong Lewis acid catalyst such as bismuth(III)bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide[13] [Bi(NTf2)3], which is relatively easily accessible.[14]
The use of the acid chloride and tin(IV) chloride (SnCl4) allows significantly shorter reaction times than the Friedel-Crafts acylation with 4-phenylbutanoic acid.[9]
4-Phenylbutanoic acid chlorides with electron-donating groups can be cyclized to 1-tetralones under mild reaction conditions in yields greater than 90% using the strong hydrogen-bonding solvent hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP).[15]
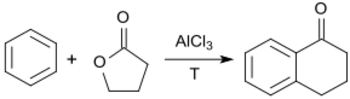
The AlCl3-catalyzed acylation of benzene with γ-butyrolactone produces 1-tetralone.[9]
Reactions
1-Tetralone can be reduced via a Birch reduction with lithium in liquid ammonia to 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene.[16] The keto group can also be reduced to a secondary alcohol giving 1-tetralol, when a modified process is applied, using the addition of aqueous ammonium chloride solution after evaporation of the ammonia.[17]
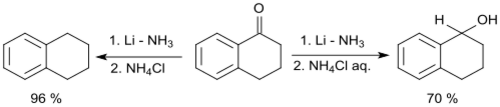
With calcium in liquid ammonia, 1-tetralone is reduced to 1-tetralol at -33 °C in 81% yield.[18]
The methylene group in α-position to the keto group is particularly reactive and can be converted with formaldehyde (in the form of the trimeric trioxane) to 2-methylene-1-tetralone in the presence of the trifluoroacetic acid salt of N-methylaniline with yields up to 91% .
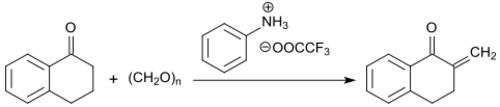
The 2-methylene ketone is stable at temperatures below -5 °C, but fully polymerizes at room temperature within 12 hours.[19]
In the Pfitzinger reaction of 1-tetralone with isatin, a compound called tetrofan (3,4-dihydro-1,2-benzacridine-5-carboxylic acid) is formed.
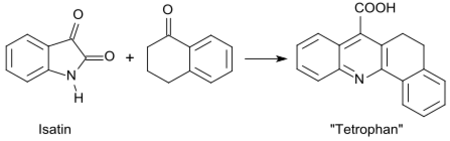
The reactivity of the α-methylene group is also exploited in the reaction of 1-tetralone with methanol at 270-290 °C, which produces via dehydrogenation and formation of the aromatic naphthalene ring system 2-methyl-1-naphthol in 66% yield.[20]
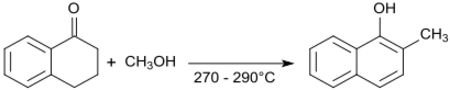
The oxime of 1-tetralone reacts with acetic anhydride leading to aromatization of the cycloalkanone ring. The resulting N-(1-naphthyl)acetamide[21] has biological properties akin to those of 2-(1-Naphthyl)acetic acid as a synthetic auxin.
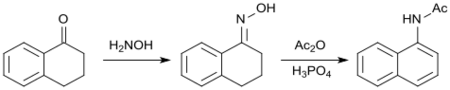
The tertiary alcohol formed in the Grignard reaction of 1-tetralone with phenylmagnesium bromide reacts with acetic anhydride upon elimination of water to 1-phenyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalene, which is dehydrated with elemental sulfur in an overall yield of about 45% to 1-phenylnaphthalene.[22]
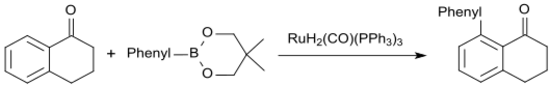
The ruthenium(II)-catalyzed arylation of 1-tetralone using phenyl boronic acid neopentyl glycol ester gives 8-phenyl-1-tetralone in up to 86% yield.[23]
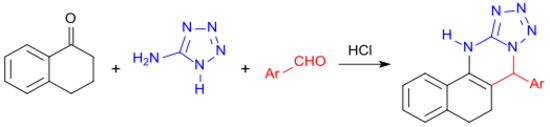
With 5-aminotetrazole and an aromatic aldehyde, 1-tetralone reacts in a multi-component reaction under microwave irradiation to form a four-membered heterocyclic ring system.[24]
Applications
By far the most important application of 1-tetralone is in the synthesis of 1-naphthol by aromatization, e.g. upon contact with platinum catalysts at 200 to 450 °C.[25]
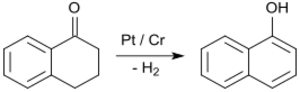
1-Naphthol is the starting material for the insecticides carbaryl and the beta-blockers propranolol.
Safety
Toxicological studies were dermally performed with rabbits, with an LD50 of 2192 mg·kg−1 body weight being observed.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Sigma-Aldrich Co., α-Tetralon. Retrieved on 25. November 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 William M. Haynes (2016), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th Edition, Boca Raton, FL, U.S.A.: CRC Press, pp. 3–504, ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "alpha-Tetralone 529-34-0 | TCI Deutschland GmbH" (in de). http://www.tcichemicals.com/eshop/de/de/commodity/T0134.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 H.R. Snyder, F.X. Werber (1940). "α-Tetralone". Org. Synth. 20: 94. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.020.0094.
- ↑ P.-C. Kuo; Y.-C. Li; T.-S. Wu (2012), "Chemical constituents and pharmacology of the Aristolochia species", EJTCM 2 (4): 249–266, doi:10.1016/S2225-4110(16)30111-0, PMID 24716140
- ↑ H. Hock; W. Susemihl (1933), "Autoxydation von Kohlenwasserstoffen: Über ein durch Autoxydation erhaltenes Tetrahydro-naphthalin-peroxyd (I. Mitteil.)" (in German), Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 66 (1): 61–68, doi:10.1002/cber.19330660113
- ↑ S. Bhattacharjee; Y.-R. Lee; W.-S. Ahn (2017), "Oxidation of tetraline to 1-tetralone over CrAPO-5" (in German), Korean J. Chem. Eng. 34 (3): 701–705, doi:10.1007/s11814-016-0310-4
- ↑ "Liquid-phase process for oxidation of tetralin" US patent 4473711, published 1984-09-25
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 C.E. Olson, A.R. Bader (1955). "α-Tetralone". Org. Synth. 35: 95. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.035.0095.
- ↑ L. F. Somerville, C. F. H. Allen (1933). "β-Benzoylpropionic acid". Org. Synth. 13: 12. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.013.0012.
- ↑ V. Premasagar; V.A. Palaniswamy; E.J. Eisenbraun (1981), "Methanesulfonic acid catalyzed cyclization of 3-arylpropanoic and 4-arylbutanoic acids to 1-indanones and 1-tetralones", J. Org. Chem. 46 (14): 2974–2976, doi:10.1021/jo00325a028
- ↑ M.S. Holden; R.D. Crouch; K.A. Barker (2005), "Formation of α-tetralone by intramolecular Friedel-Crafts acylation", J. Chem. Educ. 82 (6): 934–935, doi:10.1021/ed082p934
- ↑ S. Antoniotti; E. Dunach (2008), "Facile preparation of metallic triflates and triflimidates by oxidative dissolution of metal powders", Chem. Commun. 8 (8): 993–995, doi:10.1039/B717689A
- ↑ D.-M. Cui; M. Kawamura; S. Shimada; T. Hayashi; M. Tanaka (2003), "Synthesis of 1-tetralones by intramolecular Friedel-Crafts reaction of 4-arylbutyric acids using Lewis acid catalysts", Tetrahedron Lett. 44 (21): 4007–4010, doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(03)00855-4
- ↑ H. Motiwala; R.H. Vekariya; J. Aubé (2015), "Intramolecular Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction promoted by 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol" (in German), Org. Lett. 17 (21): 5484–5487, doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02851, PMID 26496158
- ↑ S.S. Hall; S.D. Lipsky; F.J. McEnroe; A.P. Bartels (1971), "Lithium-ammonia Reduction of Aromatic Ketones to Aromatic Hydrocarbons", J. Org. Chem. 38 (18): 2588–2591, doi:10.1021/jo00817a004
- ↑ Z. Marcinow; P.W. Rabideau (1988), "Metal-Ammonia Reduction of α-Tetralone. Competition Between Ring Reduction, Carbonyl Reduction, and Dimer Formation", J. Org. Chem. 53 (9): 2117–2119, doi:10.1021/jo00244a054
- ↑ J.R. Hwu; Y.S. Wein; Y.-J. Leu (1996), "Calcium metal in liquid ammonia for selective reduction of organic compounds" (in German), J. Org. Chem. 61 (4): 1493–1499, doi:10.1021/jo951219c
- ↑ "Methylene ketones and aldehydes by simple, direct methylene transfer: 2-Methylene-1-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.060.0088.
- ↑ I. Yuranov; L. Kiwi-Minsker; A. Renken (2002), "One-step vapour-phase synthesis of 2-methyl-1-naphthol from 1-tetralone" (in German), Appl. Catal. A 226 (1–2): 193–198, doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(01)00902-4, http://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/84417
- ↑ M.S. Newman; W.M. Hung (1973), "An improved aromatization of α-tetralone oximes to N-(1-naphthyl)acetamides" (in German), J. Org. Chem. 38 (23): 4073–4074, doi:10.1021/jo00987a029
- ↑ "1-Phenylnaphthalene". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.024.0084.
- ↑ "Ruthenium-catalyzed arylation of ortho C-H bond in an aromatic with an arylboronate: 8-Phenyl-1-tetralone". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.087.0209.
- ↑ G.P. Kantin; M. Krasavin (2016), "Reaction of α-tetralone, 1H-tetrazol-5-amine, and aromatic aldehydes upon microwave irradiation – a convenient method for the synthesis of 5,6,7,12-tetrahydrobenzo[h]tetrazolo[5,1-b]quinazolines" (in German), Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 52 (11): 918–922, doi:10.1007/s10593-017-1985-0
- ↑ "Verfahren zur Herstellung von α-Naphthol durch katalytische Dehydrierung von α-Tetralon" DE patent 2421745, published 1975-11-20

