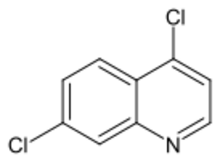
Chemistry:4,7-Dichloroquinoline
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4,7-Dichloroquinoline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H5Cl2N | |
| Molar mass | 198.05 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 87 °C (189 °F; 360 K) |
| Boiling point | 317 °C (603 °F; 590 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H317, H319, H335, H411 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P272, P273, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 164 °C (327 °F; 437 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
4,7-Dichloroquinoline is a two-ring heterocyclic compound used as a chemical intermediate to aminoquinoline antimalarial drugs including amodiaquine, chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine.
Synthesis
4,7-Dichloroquinoline was first reported in a patent filed by IG Farben in 1937.[2] However, its synthesis was not investigated in detail until chloroquine was developed as an antimalarial drug.[3]:130–132 A route to the intermediate starting from 3-chloroaniline was developed by chemists at Winthrop Chemical Co.[4]
The substituted aniline is condensed with the diethyl ester of oxaloacetic acid under mildly acidic conditions, forming an imine, which is cyclised to form the pyridine ring by heating in mineral oil. Hydrolysis and decarboxylation follows, before the hydroxy group in the 4-position is converted into the second chloro group using phosphoryl chloride.[4]
The availability of 4,7-dichloroquinoline allowed alternative structural analogs of the 4-aminoquinoline type to be investigated, leading to the discovery of hydroxychloroquine in 1949.[5][6] By that time, chloroquine manufacturing processes had been established to allow its widespread use.[7] 4,7-Dichloroquinoline has also been prepared by the Gould–Jacobs reaction using an alternative method of constructing the pyridine ring from 3-chloroaniline.[8]
Reactions
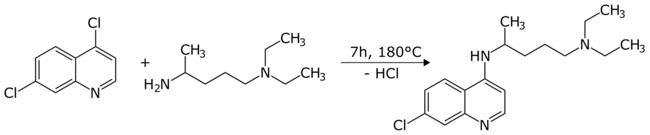
The chlorine atom in the 4-position in the pyridine ring is much more reactive in nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions[9] than the chlorine in the benzene ring. As a result, it can be replaced selectively to form derivatives at that position. A typical reaction with a specific primary amine gives chloroquine in high yield:[6][7]
Uses
Apart from its use in the manufacture of antimalarials already described, 4,7-dichloroquinoline is of continuing interest as an intermediate to new drug candidates.[10][11]
References
- ↑ PubChem Database. "4,7-Dichloroquinoline". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6866.
- ↑ ; Breitner, Stefan & Jung, Heinrich"Process for the preparation of quinoline compounds containing amino groups with basic substituents in the 4-position" DE patent 683692, issued 1939-11-13, assigned to IG Farbenindustrie AG
- ↑ Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on the Economics of Antimalarial Drugs; Arrow, K. J.; Panosian, C.; Gelband, H. (2004). Saving lives, buying time : economics of malaria drugs in an age of resistance. National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/11017. ISBN 9780309092180.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Surrey, Alexander R.; Hammer, Henry F. (1946). "Some 7-Substituted 4-Aminoquinoline Derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society 68: 113–116. doi:10.1021/ja01205a036. PMID 21008327.
- ↑ "7-chloro-4-[5-(N-ethyl-N-2-hydroxyethylamino)-2-pentyl] aminoquinoline, its acid addition salts, and method of preparation" US patent 2546658, issued 1951-03-27, assigned to Sterling Drug Inc.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Surrey, Alexander R.; Hammer, Henry F. (1950). "The Preparation of 7-Chloro-4-(4-(N-ethyl-N-β-hydroxyethylamino)-1- methylbutylamino)-quinoline and Related Compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society 72 (4): 1814–1815. doi:10.1021/ja01160a116.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Kenyon, R.L.; Wiesner, J.A.; Kwartler, C.E. (1949-04-01). "Chloroquine manufacture". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry 41 (4): 654–662. doi:10.1021/ie50472a002.
- ↑ Price, Charles C.; Roberts, Royston M. (1948). "4,7-Dichloroquinoline (Quinoline, 4,7-dichloro-)". Organic Syntheses 28: 38. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.028.0038. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV3P0272.; Collective Volume, 3, pp. 272
- ↑ Rohrbach, Simon; Smith, Andrew J.; Pang, Jia Hao; Poole, Darren L.; Tuttle, Tell; Chiba, Shunsuke; Murphy, John A. (2019). "Concerted Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 58 (46): 16368–16388. doi:10.1002/anie.201902216. PMID 30990931.
- ↑ Raj, Raghu; Land, Kirkwood M.; Kumar, Vipan (2015). "4-Aminoquinoline-hybridization en route towards the development of rationally designed antimalarial agents". RSC Advances 5 (101): 82676–82698. doi:10.1039/C5RA16361G. Bibcode: 2015RSCAd...582676R. https://scholarlycommons.pacific.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1797&context=cop-facarticles.
- ↑ Janeba, Zlatko (2015). "Development of Small-Molecule Antivirals for Ebola". Medicinal Research Reviews 35 (6): 1182. doi:10.1002/med.21355. PMID 26172225.
Further reading
- Slater, Leo (9 January 2009). War and Disease: Biomedical Research on Malaria in the Twentieth Century. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813546469.
 |