Chemistry:4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Amino-5-[(4-hydroxy-4-oxobutyl)amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid[citation needed] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Amino-5-((3-carboxypropyl)amino)-5-oxopentanoic acid[citation needed] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
|Section1=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Identifiers
|-
| CASNo = 5105-96-4
| CASNo_Ref = ![]() | CASNo_Comment = S
| PubChem = 355553
| PubChem1 = 23724570
| PubChem1_Comment = S
| ChemSpiderID = 315618
| ChemSpiderID_Ref =
| CASNo_Comment = S
| PubChem = 355553
| PubChem1 = 23724570
| PubChem1_Comment = S
| ChemSpiderID = 315618
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = ![]() | KEGG = C15767
| KEGG_Ref =
| KEGG = C15767
| KEGG_Ref = ![]() | ChEBI = 49260
| ChEBI_Ref =
| ChEBI = 49260
| ChEBI_Ref = ![]() | ChEMBL = 269574
| ChEMBL_Ref =
| ChEMBL = 269574
| ChEMBL_Ref = ![]() | Beilstein = 2418119
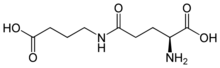
| SMILES = NC(CCC(=O)NCCCC(O)=O)C(O)=O
| StdInChI = 1S/C9H16N2O5/c10-6(9(15)16)3-4-7(12)11-5-1-2-8(13)14/h6H,1-5,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)
| StdInChI_Ref =
| Beilstein = 2418119
| SMILES = NC(CCC(=O)NCCCC(O)=O)C(O)=O
| StdInChI = 1S/C9H16N2O5/c10-6(9(15)16)3-4-7(12)11-5-1-2-8(13)14/h6H,1-5,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)
| StdInChI_Ref = ![]() | StdInChIKey = MKYPKZSGLSOGLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
| StdInChIKey_Ref =
| StdInChIKey = MKYPKZSGLSOGLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
| StdInChIKey_Ref = ![]() }}
|Section2=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Properties
}}
|Section2=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Properties
|-
|
| C9H16N2O5
|- | Molar mass
| 232.236 g·mol−1
|-
| log P
| −1.434
|-
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.223 |- | Basicity (pKb) | 11.777 |- |Section3=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Related compounds
|-
|
|
|- }}
4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid is molecule that consists of L-glutamate conjugated to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is the substrate of the enzyme γ-glutamyl-γ-aminobutyrate hydrolase, which is involved in the biosynthesis of polyamines.[1]
References
- ↑ "A novel putrescine utilization pathway involves gamma-glutamylated intermediates of Escherichia coli K-12". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (6): 4602–8. 2005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411114200. PMID 15590624.
 |

