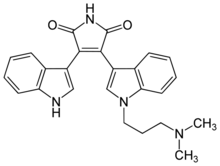
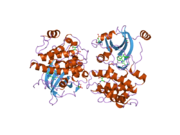Chemistry:BIM-1
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-{1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-1H-indol-3-yl}-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione
| |
| Other names
RBT205 INHIBITOR, BI1
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | bisindolylmaleimide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H24N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 412.493 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange solid |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 208 to 210 °C (406 to 410 °F; 481 to 483 K) |
| Solubility in DMSO | Soluble[vague] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
BIM-1 (GF 109203X) and the related compounds BIM-2, BIM-3, and BIM-8 are bisindolylmaleimide-based protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors. These inhibitors also inhibit PDK1 explaining the higher inhibitory potential of LY33331 compared to the other BIM compounds a bisindolylmaleimide inhibitor toward PDK1.[1]
Function
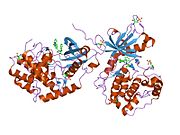
The protein kinase C[2] inhibitor bis(indolyl)maleimide inhibitor BIM1[1] is clearly seen in the structure of PKCiota[3] (residue 574-turn[4] motif), need to be phosphorylated towards a PKCbeta-specific inhibitor site-directed mutagenesis of the compound for its full activation[5] and co-crystallized as an asymmetric pair which is mediated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1)[6] are downstream characteristics of PKCs and PKB/AKT.[7]
Scope
The bound BIM1 inhibitor blocks bilobal[8] interactions, the ATP-binding site, features an ATP-competitive inhibitor, 2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl-BIM-1,[8] the crystal structure[8] and catalytic subunit with a 20-amino acid substrate analog inhibitor structure is bilobal MgATP a transport protein that provide a more precise description of which is influenced by lobe-lobe interactions binding in cells expressing both forms a pair of kinase-inhibitor complexes[7] with ferritin in a soluble and non-toxic form (Poisson-Boltzmann[9]) and a portion of the inhibitor peptide[10] a lysine residue, has been shown to be involved in ATP binding.
Interactions
The PKCiota-BIM1 complex[4] interacts with the zinc finger of lambda/iota PKC characterization of lambda-interacting protein (LIP)[5] (lambda-interacting protein; a selective activator of lambda/iota PKC). Phosphorylation of a PKC induces a conformation leading to import of a PKC into the nucleus.[11] The entire 587-amino acid coding region of a new PKC isoform, PKC iota.[11] Where Thr-412[5][12] (activation loop of the kinase domain) at PKCiota/lambda phosphorylates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)[13] that sort cargo to the anterograde pathway[14] the phosphorylation pathway(s) involved in this phenomenon[2] mimic glutamate and can adopt two limiting diastereomeric (syn and anti) conformation[15] biosynthetically related indolocarbazole analogs[16] and in Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase Pim-1-Peptide as a phosphorylation target including itself. The bound BIM1 inhibitor blocks the ATP-binding site and puts the kinase domain into an intermediate open[7] conformation.[4] The value of such calculations lies in understanding[9] a variant was designed which showed improved binding characteristics[17] of configurationally stable atropisomeric bisindolylmaleimides[15] where the two kinase domains, and two different inhibitor conformers bind in different orientations,[7] the hinge region of staurosporine[18]-Pim-1 resembles[19] co-crystallized[8] as an asymmetric pair of biosynthetically 'related' indolocarbazole analogs. It is a modulator of the 5-HT2A receptor.[20]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Interactions of LY333531 and other bisindolyl maleimide inhibitors with PDK1". Structure 12 (2): 215–26. February 2004. doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.01.005. PMID 14962382.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Synergistic induction of apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and flavopiridol proceeds via activation of both the intrinsic and tumor necrosis factor-mediated extrinsic cell death pathways". Mol. Pharmacol. 61 (6): 1313–21. June 2002. doi:10.1124/mol.61.6.1313. PMID 12021392.
- ↑ "Regulation of glioblastoma cell invasion by PKC iota and RhoB". Oncogene 27 (25): 3587–95. June 2008. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1211027. PMID 18212741.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human atypical protein kinase C-iota reveals interaction mode of phosphorylation site in turn motif". J Mol Biol 352 (4): 918–31. September 2005. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.060. PMID 16125198.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Lambda-interacting protein, a novel protein that specifically interacts with the zinc finger domain of the atypical protein kinase C isotype lambda/iota and stimulates its kinase activity in vitro and in vivo". Mol Cell Biol 16 (1): 105–14. January 1996. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.1.105. PMID 8524286.
- ↑ "Small-molecule inhibitors of PDK1". ChemMedChem 3 (12): 1810–38. December 2008. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200800195. PMID 18972468.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 "The protein kinase C inhibitor bisindolyl maleimide 2 binds with reversed orientations to different conformations of protein kinase A". J Biol Chem 279 (22): 23679–90. May 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314082200. PMID 14996846.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 "Structure of the catalytic domain of human protein kinase C beta II complexed with a bisindolylmaleimide inhibitor". Biochemistry 45 (47): 13970–81. November 2006. doi:10.1021/bi061128h. PMID 17115692.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Can MM-PBSA calculations predict the specificities of protein kinase inhibitors?". J. Comput. Chem. 27 (16): 1990–2007. December 2006. doi:10.1002/jcc.20534. PMID 17036304.
- ↑ "Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase". Science 253 (5018): 407–14. July 1991. doi:10.1126/science.1862342. PMID 1862342. Bibcode: 1991Sci...253..407K.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Phosphorylation of tyrosine 256 facilitates nuclear import of atypical protein kinase C". J Cell Biochem 85 (1): 42–53. January 2002. doi:10.1002/jcb.10101. PMID 11891849.
- ↑ "Combining protein-based IMAC, peptide-based IMAC, and MudPIT for efficient phosphoproteomic analysis". J Proteome Res 7 (3): 1346–51. March 2008. doi:10.1021/pr0705441. PMID 18220336.
- ↑ Tisdale EJ. (December 2003). "Rab2 interacts directly with atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) iota/lambda and inhibits aPKCiota/lambda-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase phosphorylation". J Biol Chem 278 (52): 52424–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309343200. PMID 14570876.
- ↑ "Src-dependent aprotein kinase C iota/lambda (aPKCiota/lambda) tyrosine phosphorylation is required for aPKCiota/lambda association with Rab2 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase on pre-golgi intermediates". J Biol Chem 281 (13): 8436–42. March 2006. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513031200. PMID 16452474.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Configurational stability of bisindolylmaleimide cyclophanes: from conformers to the first configurationally stable, atropisomeric bisindolylmaleimides". Chemistry: A European Journal 11 (21): 6277–85. October 2005. doi:10.1002/chem.200500520. PMID 16075446.
- ↑ "Indolocarbazole natural products: occurrence, biosynthesis, and biological activity". Nat Prod Rep 23 (6): 1007–45. December 2006. doi:10.1039/B601930G. PMID 17119643.
- ↑ "Structure of wild-type Plk-1 kinase domain in complex with a selective DARPin". Acta Crystallogr D 64 (4): 339–53. April 2008. doi:10.1107/S0907444907068217. PMID 18391401.
- ↑ "Divergent effects of protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors staurosporine and bisindolylmaleimide I (GF109203X) on bone resorption". Biochem. Pharmacol. 60 (7): 923–6. October 2000. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(00)00418-4. PMID 10974200.
- ↑ M.D.Jacobs; J.Black; O.Futer; L.Swenson; B.Hare; M.Fleming; K.Saxena (May 2005). "Pim-1 ligand-bound structures reveal the mechanism of serine/threonine kinase inhibition by LY294002". J Biol Chem 280 (14): 13728–13734. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413155200. PMID 15657054.
- ↑ Minami K, Minami M, Harris RA. Inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2A receptor-induced currents by n-alcohols and anesthetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jun;281(3):1136-43. PMID 9190846
 |