Chemistry:Coumaroyl-CoA
From HandWiki
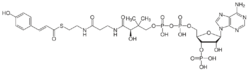
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-4-({3-[(2-{[(2E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)amino]-3-oxopropyl}amino)-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl (3R)-3-hydroxy-4-({3-[(2-{[(2E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)amino]-3-oxopropyl}amino)-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H42N7O18P3S | |
| Molar mass | 913.67 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids.[1]
Biosynthesis and significance
It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by PAL to trans-cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase:
- ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA [math]\displaystyle{ \rightleftharpoons }[/math] AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA.
Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A
- Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase
- Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase
- Chalcone synthase
- 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase
- 6'-Deoxychalcone synthase
- Agmatine N4-coumaroyltransferase
- Flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase
- Naringenin-chalcone synthase
- Shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase
- Trihydroxystilbene synthase
References
- ↑ Vogt, T. (2010). "Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis". Molecular Plant 3: 2–20. doi:10.1093/mp/ssp106. PMID 20035037.
 |

