Chemistry:Diisopropanolamine
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-(2-Hydroxypropylamino)propan-2-ol
| |
| Other names
DIPA; Bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H15NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 133.191 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid[1] |
| Density | 0.99 g/cm3 (42 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 42 °C (108 °F; 315 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 249 °C (480 °F; 522 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
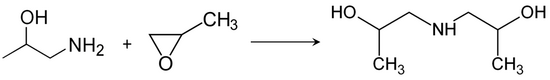
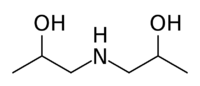
Diisopropanolamine is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H15NO2,used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and chemical intermediate.[2]
Diisopropanolamine can be prepared by the reaction of isopropanolamine or ammonia with propylene oxide.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ "Technical Data Sheet: Dow Isopropanolamine". Dow Chemical. http://msdssearch.dow.com/PublishedLiteratureDOWCOM/dh_005c/0901b8038005c440.pdf?filepath=amines/pdfs/noreg/111-01413.pdf.
- ↑ "Canadian Soil and Water Quality Guidelines for Diisopropanolamine (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment 2006)". http://www.ccme.ca/files/Resources/supporting_scientific_documents/dipa_ssd_soil_water1.0_e.pdf.
 |