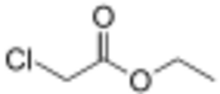
Chemistry:Ethyl chloroacetate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl chloroacetate | |
| Other names
Ethyl 2-chloroacetate
Ethyl monochloroacetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1181 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7ClO2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.55 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.145 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | −26 °C (−15 °F; 247 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 143 °C (289 °F; 416 K)[1] |
| -72.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H331, H400 | |
| P261, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P302+352, P304+340, P316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P330, P361+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl chloroacetate is a chemical compound used primarily in the chemical industry. It is used as a solvent for organic synthesis and as an intermediate in the production of pesticides (such as sodium fluoroacetate).[3]
An example for the use of this agent was in the synthesis of Cinepazet.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Ethyl chloroacetate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ "Ethyl chloroacetate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7751#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "Ethyl chloroacetate". April 2009. http://www.epa.gov/chemrtk/hpvis/rbp/105395_Ethyl%20Monochloroacetate_Web_April%202009.pdf.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
 |

